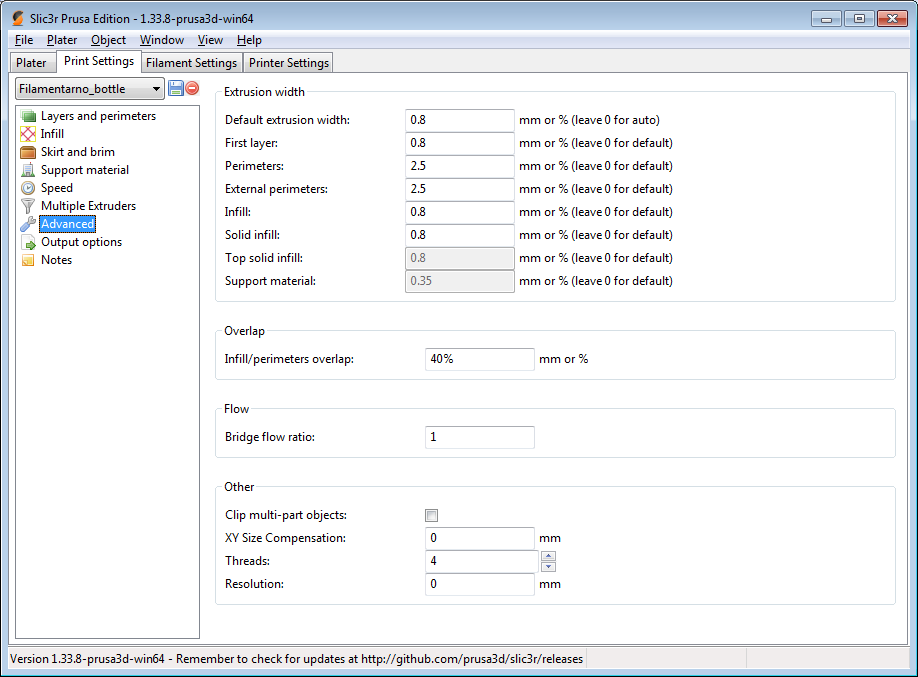
3D printer abs settings
How to 3D Print ABS Filament Like a Pro – Ultimate Guide & FAQ – 3D Printerly
ABS filament is known to be fairly tricky to 3D print successfully mainly due to the material not sticking so well to the build plate. I decided to put together an article that will show people how to 3D print ABS filament like a pro, so you can create some high quality 3D models.
To 3D print ABS, you should use a printing temperature between 210-270°C and a bed temperature between 80-120°C depending on the brand for the best results. ABS should be printed with your cooling fan off, with a print speed of around 40mm/s. Using an enclosure is ideal to control heat, but not essential.
This article is going to be a simple, yet in-depth guide on how to 3D print ABS filament just like the pros do, so stick around to see how it’s done and get your questions answered.
What is ABS Filament for 3D Printing & What is it Made of?
ABS or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a popular and durable thermoplastic material that can be used for 3D printing in the form of a 1. 75mm spool of filament. It has great mechanical and impact-resistant qualities, as well as great heat resistance. It used to be the most popular 3D printing material.
PLA has taken over ABS as the most popular 3D printed filament, though ABS definitely has properties that make it ideal such as being tougher and even lighter than PLA.
When looking at what ABS is actually made of, it is generally a combination of 50% styrene and the other 50% being butadiene and acrylonitrile, though it can still be made in different proportions. This combination of polymers is what gives ABS its properties and high levels of resistance.
What Printing & Bed Temperature Should You 3D Print ABS?
The best printing temperature you should use for ABS usually falls anywhere between 210-270°C. Filament brands will show you the temperature range for their specific spool of ABS. HATCHBOX ABS filament is 210-240°C, while OVERTURE filament is 245-265°C.
The best bed temperature for ABS falls anywhere between 80-120°C. You should use trial and error with different temperatures so you can figure out what works best for your brand of ABS and your specific 3D printer.
You should use trial and error with different temperatures so you can figure out what works best for your brand of ABS and your specific 3D printer.
A bed temperature of 100°C worked great for one user who bought HATCHBOX ABS filament, while another user got great results using 85°C with the same filament. It will depend on your surrounding environment and how your 3D printer bed heats up.
Let’s check the printing and bed temperature of some of the most popular brands of ABS filament.
HATCHBOX ABS
Printing Temperature: 210-240°C
Bed Temperature: 85-110°C
SUNLU ABS
Printing Temperature: 230-240°C
Bed Temperature: 85°C
OVERTURE ABS
Printing Temperature: 245-265°C
Bed Temperature: 80-100°C
JAYO ABS
Printing Temperature: 230-260°C
Bed Temperature: 80-110°C
NovaMaker ABS
Printing Temperature: 220-250°C
Bed Temperature: 80-120°C
When it comes to leveling your 3D printer bed, it’s a good idea to make sure the bed is heated to the operating temperature since the heat causes it to expand and change shape slightly, resulting in differences in heights across the bed.
What Printing Speed Should You Use for ABS Filament?
For ABS filament, the recommended printing speed falls between 40-60mm/s to get high quality 3D prints. Going above 70mm/s for ABS filament is likely to decrease your printing quality gradually, though you can still get successful prints at higher speeds.
ABS can’t be 3D printed as fast as a material like PLA since it doesn’t flow as well.
If you are wondering how fast you can 3D print ABS, you could reach speeds up t0 100mm/s and beyond with a 3D printer that is tuned for speed and stability. Delta 3D printers are built for speed
Does ABS Need a Fan? Can You Print ABS Without a Cooling Fan?
ABS filament doesn’t need a cooling fan to 3D print successfully. Using a low cooling fan setting can help with improving surface quality, but having it off usually leads to better strength. Enclosed 3D printers have a higher ambient temperature, so fans can be put on low settings and still work out great.
Sometimes, if sections of your ABS 3D prints have large overhangs, bridges, or short times per layer, turning on the fan for these layers can be very useful. This can be done by inserting scripts in your slicer to change fan settings on specific layers.
A minimum layer time of around 20-25 seconds should work well for ABS if you do have smaller layers that print a little too quickly, like the horn on a unicorn for example.
Shrinkage or warping is one of the key factors that people think about when it comes to using the cooling fans for ABS, but it is usually the surrounding temperature that has the biggest effect on warping or having the material shrink.
Many 3D printers that are optimized for 3D printing ABS do have cooling fans, like the Zortrax M200.
ABS Retraction Settings for 3D Printing
The best ABS retraction settings for 3D printing usually falls between a Retraction Distance of 3-7mm and a Retraction Speed of 30-45mm/s depending on whether you have a Bowden or Direct Drive setup. The default of 5mm distance and 45mm/s speed should work well enough, but you can test retraction for optimal results.
The default of 5mm distance and 45mm/s speed should work well enough, but you can test retraction for optimal results.
The video below shows you how you can dial in your retraction settings in Cura by using a Retraction Tower and seeing how the resulting prints come out. You test one setting at a time to see what works best for your specific printer and setup.
What Are Advantages of 3D Printing ABS?
- Very durable and impact resistant, so it can hold up well in load-bearing situations – great for functional objects.
- It doesn’t degrade as much as other filaments, so old prints keep their quality really well
- ABS has amazing heat-resistance, meaning you can use it in high temperature situations like outdoors or in a car.

- ABS has relatively good flexibility, definitely more so than PLA 3D prints.
- You can easily smooth ABS 3D prints using acetone, as well as weld parts together
- Has a good natural surface quality
- Great chemical resistance and mechanical properties
- ABS is good for functional objects that require strength and some level of flexibility or tensile strength.
What Are Disadvantages of 3D Printing ABS?
- ABS can be difficult to 3D print, especially for beginners due to warping issues
- Can release harmful gasses (ultrafine particles) when printed at high temperatures – known to be smelly
- Requires a heatbed unlike PLA filament
- Known to have trouble sticking to build platforms – Blue Painter’s Tape works well as a surface or glue stick
Best Things to 3D Print with ABS
ABS can print many things since it is quite a versatile material with great mechanical properties. The heat resistance and strength are the best aspects of ABS, so if those are the characteristics you are looking for, then you can print it with ABS.
Here are some popular items made from ABS:
- Lego toys
- Luggage cases
- Helmets
- Chairs
- Computer keyboards
- Wall sockets
- Containers
- Automotive parts
- Handles & holders
How Do You Smooth ABS 3D Prints?
Smoothing ABS 3D prints is done through a method called acetone smoothing, which is when you use acetone fumes to dissolve the outer surfaces of ABS, leaving a smooth behind. You simply pour acetone into an airtight container with the 3D print inside but separated from the liquid for 10-20 minutes.
Check out the video below by Josef Prusa to see how it is done, and the final results on your prints.
How to Paint 3D Printed ABS
The usual way to paint 3D printed ABS is to apply a primer to help the paint properly adhere to the object, sand and smooth the object by sanding, buffing, and polishing. Then paint it either with spray paint, an airbrush, or a paint brush. It’s a good idea to use multiple undercoats to make it more even.
Then paint it either with spray paint, an airbrush, or a paint brush. It’s a good idea to use multiple undercoats to make it more even.
You can get the best results by polishing your 3D prints between each coat of paint to really bring out the gloss. I’d recommend using some fine sandpaper at a grit of around 500 to get some great results.
Make sure you are using the correct equipment such as a NIOSH-approved respirator, safety goggles, nitrile gloves, all in a well-ventilated area.
Formlabs created these really helpful videos to illustrate how to prime and paint your 3D printed objects successfully.
The first video is for priming.
The second video is for painting.
The materials you’ll need are as follows:
- Primer
- Spray paint
- Clear coat spray
- Masking tape
- Flush cutters
- Sandpaper
- Needle files
- Polishing sticks
- A toothbrush/cloth
- Water
- Gloves
- Respirator
- Safety googles
The first thing you need to do is clean up the model after it comes off the print bed with your flush cutters.
You want to use low-grit sandpaper (50-100) to sand down any obvious support marks or imperfections, then use a higher grit sandpaper (200-350) to smooth out the surfaces. Wet sanding usually provides the best results for smoothing surfaces.
Use the cloth or a toothbrush to remove dust from the model, as dust can remain even after wet sanding.
Once your model is cleaned up, we want to prime the model, making sure to shake the primer well before spraying. It’s a good idea to add a few layers of primer and sand in between that to really clean up and get the model smooth.
After priming, some people will add 2-3 layers of an undercoat spray to cover up the color of the primer, usually in black or white depending on whether you want darker or lighter tones. You’ll get the best results by polishing and buffing between each layer of paint.
We can now start to apply the final layers of spray paint to the model, after applying masking tape to the areas that you want to be a different color. You want to apply the top coat in layers, ensuring that you wait a few minutes after each coat to see if the color is to your liking.
When you have your colors properly done, it’s a good idea to add 1-2 thin layers of clear coat spray to give your model that extra gloss and shine. Make sure you let your models rest for 5-7 days, so the paint can properly harden.
How to Fix ABS Prints Not Sticking to Bed
Making sure to level your bed is the first step to fix your ABS print is not sticking to the bed. Ensure your bed temperature is high enough in line with the recommendations. Use blue painter’s tape as a surface which your ABS prints can successfully adhere to. Using a raft can help greatly.
Some people have had great results by using a substance called ABS slurry, which is a combination of acetone and small bit of ABS filament, which dissolves in the acetone, creating a kind of thick mixture.
Rubbing this mixture on the print bed before an ABS 3D print is a great way of getting ABS prints to stick to the bed. I would definitely try experimenting with a few of these options, and I’m sure you’ll get your ABS prints to finally adhere to the build plate.
Using an enclosure around your 3D printer is a great way to regulate the temperature, which can positively affect your first layer and subsequent layers.
If your ABS prints aren’t sticking to the bed, you may also be using a printing temperature too low for the ABS to soften enough.
ABS layer separation also has very similar fixes in terms of controlling the temperature properly. If you find that you are getting layer separation in your ABS prints, try to optimize your printing and bed temperatures, as well as the ambient temperature by using an enclosure.
How to Print ABS Without Warping
To keep ABS prints from warping, you should enclosure your build area, increase the temperature of your build plate, decrease your printing temperature, make sure your build plate is flat, use extra adhesion methods such as hairspray, ABS slurry, or blue painter’s tape, use a raft or brim.
The main reason for ABS warping is through rapid cooling which causes the material to shrink and curl/warp around the outer model. It also occurs due to a poor adhesion to the surface, so if you can control those two factors, you should be able to print ABS without warping.
You can stop your ABS from shrinking by making sure there isn’t rapid cooling in the environment from things like drafts or your cooling fan.
Is 3D Printing With ABS Dangerous? Smell & Fumes
3D printing with ABS filament is known to emit toxic and smelly gasses such as styrene which is known to be a carcinogen or a possibly cancer-causing chemical. ABS is an oil-based material, so heating it to high temperatures can be dangerous to the respiratory system if you don’t have good ventilation or an enclosure.
For the many people who wonder how toxic ABS filament is, ABS is known to be significantly more toxic than other filaments like PLA and PETG, and it’s important to know that different filament manufacturers have differing standards when it comes to safety.
People have described the smell and fumes of ABS to be similar to that of burnt plastic. That arises from being a petroleum-based plastic.
I think in modern times, safety is being looked at more closely with there even being the introduction to non-smelly ABS filament.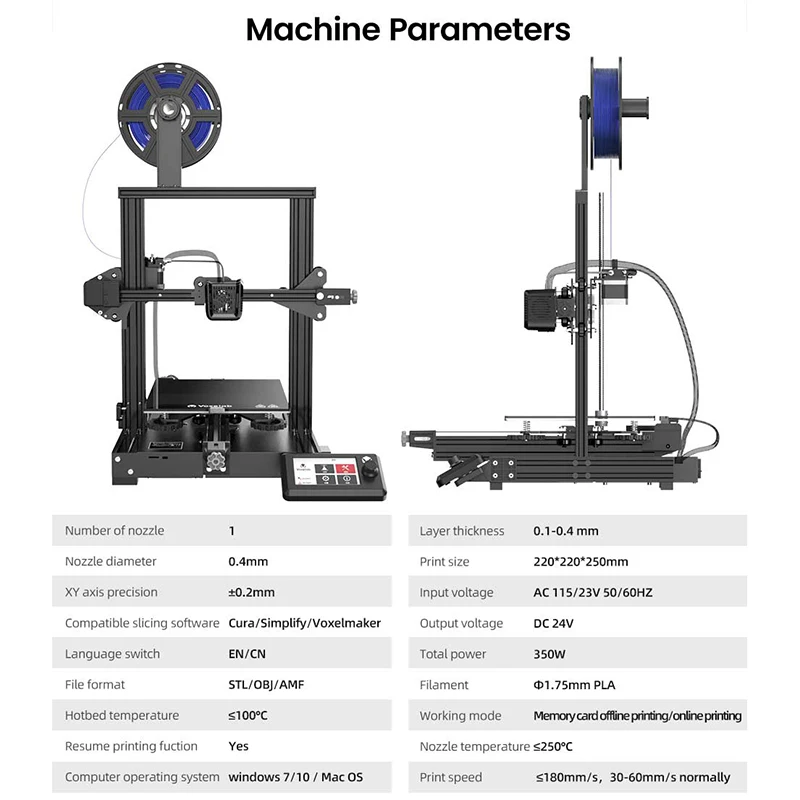
3D printing in general is known to release nanoparticles or ultrafine particles (UFPs) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the environment, so having good ventilation and not printing in occupied areas is recommended, especially for ABS.
UFPs are defined as particles with a diameter less than 100nm (nanometers) which can actually get into your lungs and bloodstream. They can cause respiratory issues and even cardiovascular conditions with constant exposure.
Styrene and formaldehyde are the main culprits for toxicity with ABS filament, both dangerous to people.
In terms of printing ABS indoors, it is safe if you have the proper ventilation channels with an enclosure to stop particles and emissions from spreading around. Using something like an inline carbon filter fan system with vents that lead outside.
How Strong is ABS Filament?
ABS filament is known to be a high strength filament with great durability. It also has a medium level of flexibility so it shouldn’t snap so easily like PLA filament.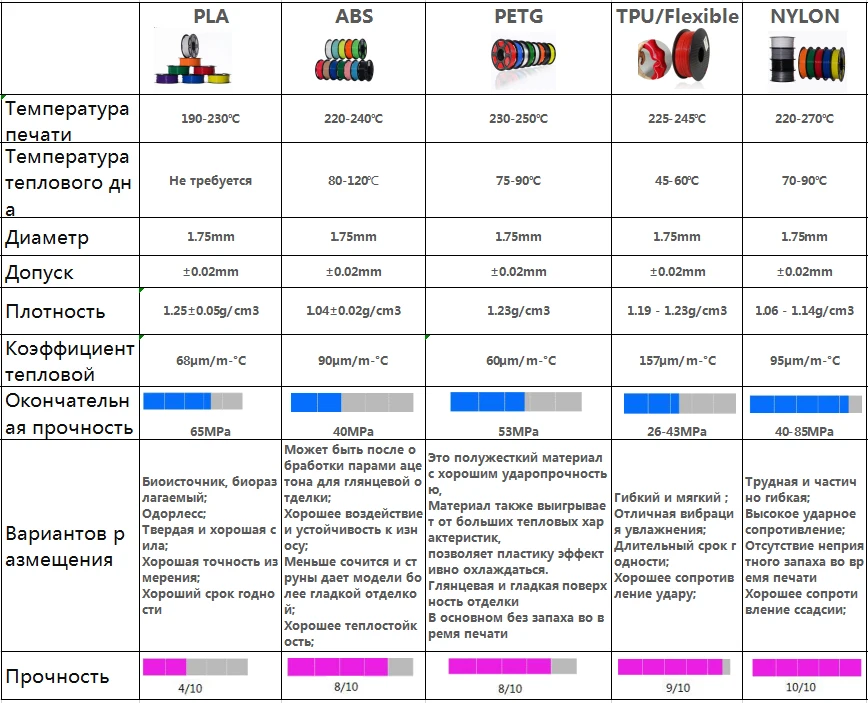 ABS can withstand a lot of impact and physical stresses. Legos are made of ABS plastic, as well as helmets and chairs.
ABS can withstand a lot of impact and physical stresses. Legos are made of ABS plastic, as well as helmets and chairs.
ABS plastic won’t break easily due to its strong mechanical properties, as long as it is printed with a good amount of infill and wall thickness.
Does ABS Need to Be Dried?
ABS filament doesn’t need to be dried to 3D print successfully, but drying it thoroughly should improve the print quality and give you smoother surfaces. Many people have seen differences in quality after drying their filament at around 65°C for 3-4 hours.
Does ABS Filament Absorb Moisture?
ABS filament does absorb moisture as well as all thermoplastics out there. Filaments absorb different levels of moisture depending on how they were manufactured and by how much humidity and moisture is in the surrounding environment. ABS is not as sensitive to moisture absorption compared to PLA or Nylon filament.
You can purchase a professional filament dryer solution like the SUNLU Upgraded Filament Dryer from Amazon. You can efficiently remove excess moisture from your filament in a matter of hours, giving you more success and better quality 3D prints.
You can efficiently remove excess moisture from your filament in a matter of hours, giving you more success and better quality 3D prints.
It’s very easy to set up since the filament dryer is fully assembled. You also have the added benefit of drying during 3D printing, for a moisture-free experience.
Can You 3D Print ABS Without a Heated Bed?
Some people wonder “does ABS need a heated bed” when it comes to getting a successful print.
ABS does usually need a heated bed to print properly, though some people have successfully printed it by using a strong adhesive on the bed. You can use blue painter’s tape and sand it with low grit sandpaper like 60 grit to improve the adhesion even without a heated bed.
The video below shows a user printing ABS without a heated bed. It looks like it can be a challenge, but definitely possible using the right methods.
Is ABS Easy or Hard to Print With?
ABS is known to be difficult to print with due to requiring a relatively high temperature and being prone to warping or shrinking.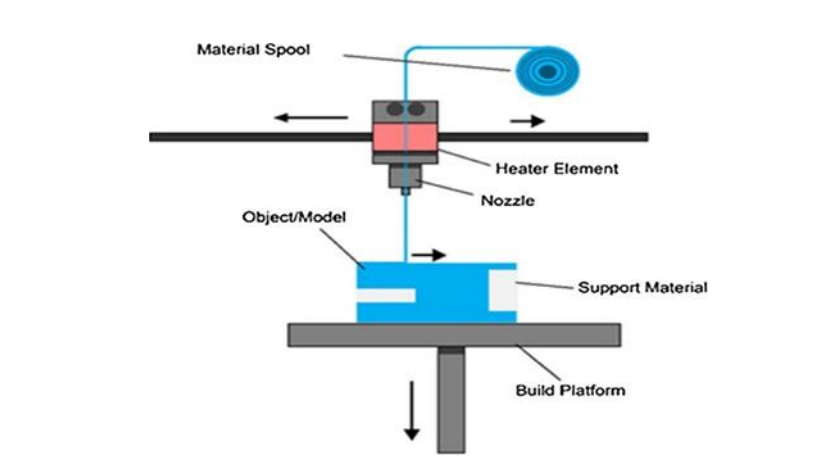 Beginners can have trouble with printing ABS successfully, but after dialing in your settings and having a good workstation, you can create some great ABS prints.
Beginners can have trouble with printing ABS successfully, but after dialing in your settings and having a good workstation, you can create some great ABS prints.
I would recommend beginners to start with PLA to understand how 3D printing works and how changing settings has an impact on the final print, then working up to printing with ABS.
Is ABS Filament UV Resistant?
ABS filament is not UV resistant and degrades under constant sun exposure. ABS 3D prints can still hold up well in the sun, but may become weaker and discolored after some time. It does have good heat resistance against the sun. I’d recommend getting ASA filament since it is a version of ABS that is UV resistant.
You can actually buy a UV-resistant varnish like the Krylon Clear Coatings Aerosol (11-Ounce) from Amazon. It not only dries in minutes, but is moisture-resistant and has a non-yellowing permanent coating.
Optimal Bed Temperature and Print Settings – Clever Creations
Ready to start 3D printing with ABS filament but aren’t sure where to start? You’re not alone. ABS is one of the more difficult materials to use in 3D printing and needs the right print settings and environment for the best results.
ABS is one of the more difficult materials to use in 3D printing and needs the right print settings and environment for the best results.
In this article, we’ll cover what ABS is, when you should use it, and what settings you should use in your slicer. We’ll also touch on post-processing ABS, and what upgrades you can add to your machine to make your ABS prints look better.
What is ABS Filament?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a petroleum-based thermoplastic used primarily in 3D printing and injection molding. ABS is used to make many different products, including electronics casings, car interior panels, lego bricks, and much more.
ABS is a strong, durable material that can withstand high temperatures. It’s also relatively easy to print with and has a low melting point, making it ideal for 3D printing.
In filament form, it’s one of the most popular 3D printing materials available and has several advantages over other filaments.
Why Use ABS Filament?
ABS is a heat-resistant filament that is often used when a 3D print needs to withstand environments with higher temperatures.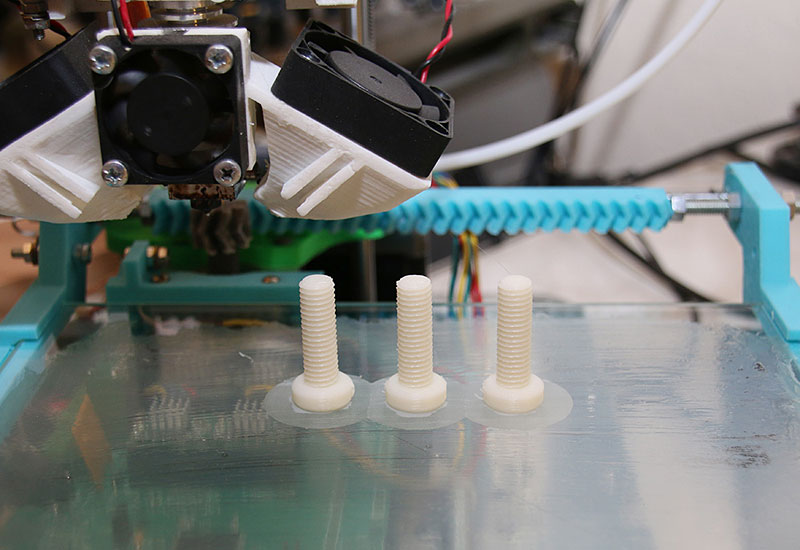 It is a good material to use for parts that need to stay in hot cars, outside, or near heat sources. It has a softening point around 100°C, which is much higher than PLA (60 – 65 °C) and even PETG (80 – 85 °C).
It is a good material to use for parts that need to stay in hot cars, outside, or near heat sources. It has a softening point around 100°C, which is much higher than PLA (60 – 65 °C) and even PETG (80 – 85 °C).
Recommended:
PLA vs ABS: Which Filament is Better?
With its high heat tolerances, ABS is one of the few 3D printing materials that can be placed in boiling water for sanitation. This makes it great for something that requires frequent sterilization like face shield mounts and other PPE items.
ABS is also a durable material that doesn’t easily break or shatter. This makes it ideal for 3D printed parts that need to withstand high impacts or be used in demanding environments.
Disadvantages of ABS
While ABS has its advantages over other 3D printing materials, it also has some drawbacks that make it unsuitable for some uses.
The biggest complaint with ABS is that it is difficult to print with. Even the best ABS filament has a tendency to warp and shrink, making it one of the more difficult materials to use in 3D printing.
ABS also has poor printing bed adhesion. It tends to lift off the build plate while printing, making it challenging to get good results unless you maintain a constant elevated temperature in the print chamber.
Image: Matterhackers via Youtube
Warping is a big issue with ABSYou will also encounter high levels of 3D printing fumes when printing with ABS. The fumes can be harmful to your health and should not be inhaled.
ABS prints are also prone to UV damage, moisture retention, and weak resistance against solvent-based chemicals. While the last is also seen as an advantage (it is what makes ABS so easy to smooth with acetone), it can also lead to a ruined ABS print if it comes into contact with a solvent unintentionally.
Printing ABS Without Warping
Enclosure
ABS needs to be printed at high temperatures and has a high shrinkage rate. This means that if the temperature of the 3D print drops during the printing process, the cooled parts of the print will start to shrink. This leads to warping, curling, and other print quality issues.
This leads to warping, curling, and other print quality issues.
To avoid this issue, it is best to keep an ABS print consistently above a certain temperature. A 3D printer enclosure is ideal for this.
A 3D printer enclosure is a box or heated chamber that surrounds your 3D printer and helps to keep the temperature of your ABS print stable during the printing process. This can be a challenge without an enclosure because drafts of cooler air cause temperature instability.
There are many different types of enclosures available on the market, from simple boxes to complex chambers with built-in heaters. The simplest way is to buy an off-the-shelf enclosed 3D printer, but you can also build a DIY 3D printer enclosure.
Image: Mikolas Zuza via Prusa3D
This IKEA LACK enclosure is a popular choiceIf you’re looking to build your own enclosure, there are a few things to keep in mind. The enclosure should be large enough to fit your 3D printer and should not be flammable. It should also be well-insulated to maintain a consistent temperature.
It should also be well-insulated to maintain a consistent temperature.
Print Bed Material
While you can print ABS on a number of different surfaces, the easiest and most consistent results come from printing directly onto a piece of glass attached to your heated bed. The smooth glass gives the bottom of your parts a smooth surface and distributes heat well.
A glass print surface works best when a thin layer of glue or melted ABS is spread across the build plate. A PVA glue stick is usually enough to keep most prints stuck to an even printing bed so long as the heated bed temperature remains consistent, but we’ve also listed some more powerful alternatives below for those really stubborn prints.
Bed Leveling
When the build plate isn’t fully level, ABS is more susceptible to bed adhesion issues than other 3D printing materials. Getting the printing bed as even as possible will result in much better prints overall and save you a lot of hassle with failed and warping parts.
When the build plate is uneven, some parts of the first layer print closer to the print bed than others, making it harder for the part to stay attached. Leveling the printing bed ensures that all parts of the first layer adhere consistently and within the right distance.
Automatic or assisted leveling systems are best for keeping the build plate consistently level. Our go-to solution for this is the BLTouch leveling sensor, but there are other solutions as well.
Recommended:
What is a BLTouch Sensor and How to Use It
If your 3D printer doesn’t have an automatic leveling system, you can use a manual leveling method like the 3-point leveling system. It is more time-intensive, but it works just fine with enough practice.
Bed Adhesion
First layer adhesion is incredibly important (and somewhat difficult to achieve) in order to prevent warping in ABS prints. There are many ways to ensure good bed adhesion, but one of the easiest ways to ensure a good bond with the build plate during printing is by using an appropriate adhesive on the bed.
The best bed adhesive for 3D printing with ABS filament is usually considered to be ABS slurry. It is possible to make this yourself and it produces a solid bond between your first layer and the print bed. ABS slurry is made up of ABS material dissolved in acetone. You can make it by cutting up your scrap pieces of ABS and letting them dissolve in acetone.
Another option is to use a PVA glue stick to help ABS adhere to the print bed. They are cheap, simple to use and don’t make a mess. Elmer’s has a variety of glue sticks well-suited for 3D printing.
Elmer's Extra Strength Glue Sticks, Washable, 8 Grams, 4 Count
4,601 Reviews
Check PriceImage: Geeetech
Glue-sticks are an essential component of any 3D printer accessory kitAlternatively, you can also use the acetone from your vapor smoothing setup, if you have one. Even though it can be harder to tell when this acetone reaches the right ratio of acetone to ABS.
3D Gloop! is a ready-made solution for ABS bed adhesion. It’s a glue specifically designed for use in 3D printing and with 3D printed parts. Not only can it glue 3D prints, but it can also adhere your ABS prints to the bed while printing. Simply brush a thin layer of it onto the build plate before you start your ABS print.
It’s a glue specifically designed for use in 3D printing and with 3D printed parts. Not only can it glue 3D prints, but it can also adhere your ABS prints to the bed while printing. Simply brush a thin layer of it onto the build plate before you start your ABS print.
They make a formula for both PLA and ABS, and while it is best to use the product designed for the material you are using, you can technically use the PLA gloop for ABS if that is all you have on hand.
Recommended Settings for 3D Printing ABS Filament
| Printer Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Print temperature | 220°C – 250°C |
| Bed temperature | 90°C – 100°C |
| Bed surface | Glass with glue |
| Print speed | 40-60 mm/sec |
| Cooling fans | First layers off – 0-30% after |
| Enclosure | Yes |
| Retraction | 2-3 mm (direct drive) / 4-5 mm (Bowden) |
| Layer height | 0. 2 mm 2 mm |
| Storage | Airtight container when not in use / usually okay to leave out while in use |
Nozzle Temperature
ABS filament prints hot, which is one of the reasons it can be difficult to work with. Most ABS brands work with a printing temperature range of 220°C – 250°C. However, it’s also not uncommon for ABS brands to have a recommended printing temperature with an upper end of 260°C – 270°C.
It is worth noting that basic extruders have difficulties with printing temperatures above 240°C. This is because at that temperature the PTFE tubing inside the extruder starts to melt. Even if the heater cartridge in the hot end can reach even the highest ABS temperatures, you run the risk of damaging the extruder if you try to print at them.
This is why many users upgrade their printer to an all-metal hot end if it does not come standard. It is one of the most popular Ender 3 upgrades and Ender 5 upgrades you can do to improve either of these budget 3D printers.
Bed Temperature
Most brands of ABS filament have a recommended heated bed temperature within the range of 90°C – 100°C. Unlike PETG and PLA, 3D printing with ABS filaments requires a heated build plate. If the bottom layers don’t stay warm enough throughout the entire print process, they will start to shrink. This detaches them from the build plate and leads to warping and print failures.
ABS slurry can help with bed adhesion. If you are using it, you don’t need to worry about the heated bed temperature as much. However, if you are not using ABS slurry, it is important to keep the heated bed at a temperature that will keep your prints from warping.
Print Speed
ABS works with the same standard print speed as most other 3D printing materials at 40-60mm/sec. This is slow enough to ensure that the print quality won’t suffer while still being fast enough so that it does not excessively slow down your ABS print.
Cooling Fan Settings
Since ABS needs a high bed temperature to print correctly, it’s important to keep the cooling fan off during the first few layers. This helps with layer adhesion and prevents the bed temperature from dropping.
This helps with layer adhesion and prevents the bed temperature from dropping.
You can turn the cooling fan on to about 30% after the initial layers print, but it usually isn’t necessary.
The cooling fan settings do change depending on whether or not the 3D printer is in an enclosure with a heat chamber. If it is, a low cooling fan setting of around 30% is more helpful in keeping the heat consistent.
Retraction
Retraction is a bit more forgiving with ABS than a stringy filament like PETG. Usually, you can get great ABS prints by setting a direct drive extruder to 2-3mm retraction and a Bowden extruder to 4-5mm retraction. These settings can change between different ABS filament brands and 3D printers, so adjust them as needed if you notice any stringing or blobbing on your ABS print.
Layer Height
ABS works well with the standard 0.2mm layer height for a 0.4mm nozzle. Even so, just like with other 3D printing materials, changing the layer height while printing ABS can affect how long the print takes and what the print quality looks like. A shorter print height produces more detailed prints with less noticeable layer lines, while a taller layer height reduces print times and quality.
A shorter print height produces more detailed prints with less noticeable layer lines, while a taller layer height reduces print times and quality.
Brim and Raft
Brims and rafts are common ways to avoid warping with ABS since they help with bed adhesion. It is best to use brims and rafts to print ABS when your part does not cover a lot of surface area on the printing bed in the first layer. An example is a figure with just the feet touching the print bed.
Rafts are best when those small contact points happen inside the print, whereas brims are best when parts on the outer perimeter of the print need stabilization.
Draft Shield
A draft shield is an experimental feature in some 3D printing software options like Cura. It essentially prints an out case around the print to protect it from cold air drafts. The shield and the print are separate pieces, so the shield can easily be removed from the print bed and discarded.
Image: The 3D Print General via Youtube
Don’t be afraid to use a draft shield when working with ABSThis is a good feature to try if you are consistently having trouble keeping your printing temperature stable when printing ABS.
ABS and Moisture Absorption
While ABS does absorb some moisture, it usually takes on much less than other printing materials like PETG. ABS also doesn’t degrade in water like PLA or PETG, so even if it does take on some moisture content, it is unlikely to ruin the structure of the material.
That said, even with ABS filament it is best to properly store it in a filament dry box. That way, you can avoid any moisture absorption that could cause printing problems.
Smoothing ABS
One of the biggest advantages of using ABS is its easy post-processing. Smoothing the layer lines is especially effective since ABS is a solvent-based material. As such, it reacts with solvent chemicals such as acetone. This makes it possible to use acetone to smooth the outer layers with acetone instead of sanding them.
This can be a huge time-saving tactic if you have several 3D prints to smooth. However, it is also somewhat dangerous depending on which method you use, and it requires working with acetone which is an irritant and requires protective equipment like gloves, glasses, and a respirator.
Cold smoothing is the safer option, but it takes more time to produce results. It requires putting a small amount of acetone in the bottom of the container, usually soaked up by napkins or paper towels, and putting your print on top of it on an elevated platform so that there is no direct contact. You then place a lid on the container and leave it until your prints are sufficiently smooth. This process can take anywhere from a few hours to a few days depending on the size of the model.
Image: SinkHacks
Acetone smoothing can create beautiful resultsVapor smoothing requires heating the acetone until it vaporizes, allowing you to smooth a part within seconds. However, it is extremely dangerous and we don’t advise trying it. Purchasing a smoothing station is a far better (and safer) alternative and will produce the same great results.
Recommended ABS filament brands
Our go-to ABS filament brands are Polymaker and Hatchbox. Both brands have a wide variety of colors and produce high-quality prints.
Polymaker ABS Filament 1.75mm Orange ABS, 1kg Heat Resistant ABS...
451 Reviews
Check PriceHATCHBOX ABS 3D Printer Filament, Dimensional Accuracy +/- 0.03 mm, 1...
9,148 Reviews
Check PricePrusament ABS is also a great option. It is a little more expensive than the Polymaker and Hatchbox brands. But it has a very high quality, great dimensional accuracy, and is easy to print with.
Troubleshooting ABS filament
There is a nasty smell during ABS printing
ABS printing gives off a strong odor that some people find unpleasant. The best way to combat the smell is to print in an enclosed 3D printer. This will help to contain the fumes and make them less concentrated.
The print is warping
Warping is one of the most common problems with printing ABS. There are a few things you can do to try and prevent it: use a brim or raft, print in a draft-free environment, and make sure the bed is level and clean. If you are still having trouble with warping, you can try using an ABS slurry.
The print is stringing or blobbing
If you are experiencing stringing or blobbing with your ABS prints, it usually means that the retraction settings are not set properly. Try adjusting the retraction settings for your direct drive extruder to 2-3mm and for your Bowden extruder to 4-6mm. You can also try decreasing the print temperature by 5-10 degrees Celsius.
I can’t get the first layer to stick
If the first layer of your ABS print isn’t sticking to the bed, you can try using an ABS slurry or increasing the bed temperature. If that doesn’t work, you can also try adjusting the bed level or angle.
Things to 3D print with ABS filament
ABS is a versatile printing material that can be used for a wide variety of applications. Here are some things you can 3D print with ABS:
- Prototypes
- RC car parts
- Functional parts
- Cosplay props and costumes
- Phone cases
- Tools
- Toy parts
- Camera mounts
- Household items
FAQ
Is ABS or PLA stronger?
PLA is better than ABS in both strength and stiffness. However, because of its low heat resistance, PLA is less ideal for prototyping purposes.
However, because of its low heat resistance, PLA is less ideal for prototyping purposes.
What do you use ABS filament for?
ABS filament can be used for a wide variety of applications, including Prototyping, RC car parts, functional parts, phone cases, tools, toy parts, camera mounts, and household items. Because of its ease of post-processing, ABS is also great for creating a 3D printed helmet or 3D printing cosplay armor.
Which is stronger, ABS or PETG?
PETG has increased strength and durability compared to ABS. It is also easier to print. The only reason to pick ABS over PETG is when you need increased temperature resistance or if you need to post-process your print by gluing or painting it.
Recommended:
PETG vs ABS: Which Filament Should You Use?
Are ABS fumes toxic?
The fumes from ABS printing are considered toxic. Additionally, they can be unpleasant to breathe in. The best way to combat the smell is to print in an enclosed 3D printer. This will help to contain the fumes and make them less concentrated in the surrounding air.
This will help to contain the fumes and make them less concentrated in the surrounding air.
What temperature should I print ABS?
ABS prints best at temperatures between 220°C and 250°C. However, the exact temperature you use will depend on the type of printer you are using and the brand of filament you are using. You can figure out the optimal temperature by using a temperature tower.
Does ABS filament need print cooling?
In general, it’s best to leave the fan off when printing ABS plastic because too much cooling can cause warping and other problems.
Can you print ABS without a heated bed?
No, you can’t print ABS without a heated bed. The reason is that the filament needs to be kept warm to prevent warping. Without a heated bed the ABS print would cool down too quickly and would not produce the proper results.
Final Thoughts
ABS is a durable plastic that has a great heat resistance and easy post-processing methods. It’s great for parts that need impact, temperature, or certain chemical resistances.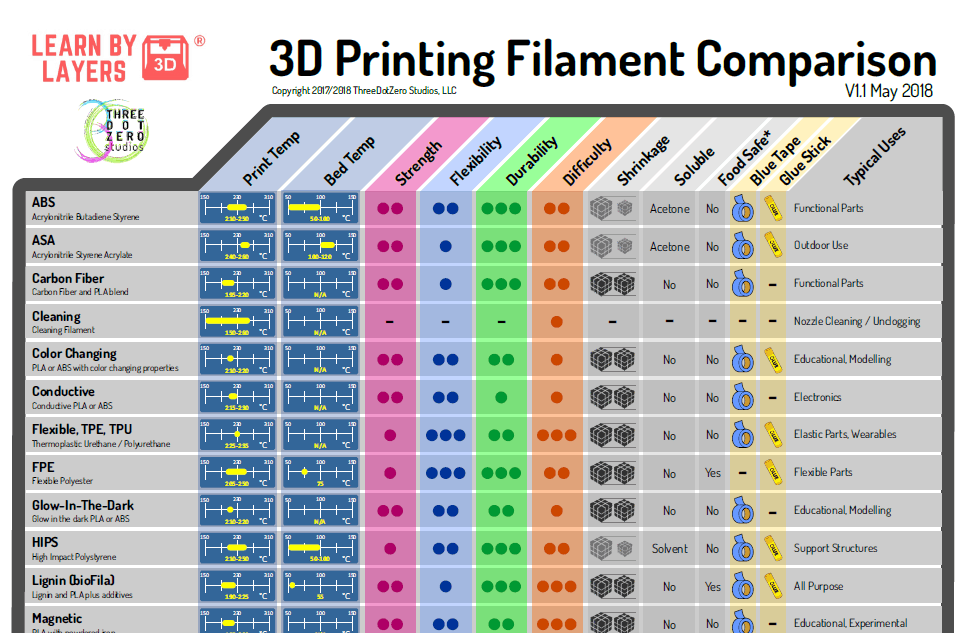 However, it’s also a difficult and frustrating material to print with.
However, it’s also a difficult and frustrating material to print with.
Its high printing temperature, shrinkage rate, and propensity to warp mean it usually takes a lot of trial and error to get the perfect settings for your printer and brand of ABS filament. Beyond your basic print settings, adding an enclosure, heated chamber, and all-metal hot end can make working with ABS much easier.
Do you still have questions about 3D printing with ABS? Let us know in the comments!
Blood, pain and ... glass.
Personal diaries
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
5
3D Print #21: Blood, pain and ... glass.
Prologue.
If you're looking for big projects, legendary filaments and supersonic printers... no, that's not it, don't even read it.
This story is about ordinary domestic violence with kitchen utensils by the recipient, and then about ordinary domestic violence with kitchen utensils over recipient .
Prerequisites for printing.
Half a year before printing.
- Throw it away - said the wife, looking at her husband trying to wire the handle of the French press holder.
After a couple of weeks, the handle of the metal cup holder completely fell off, and the glass flask of the French press almost broke, but it almost doesn't count. The glass holder flew into the trash can, and the flask hid in the darkest corner of the cabinet... where Dark energy flowed in a stream, filling it with energy for revenge for its companion thrown into the landfill. And she didn't care that the coaster died due to its own weakness and vulnerability to rust. She made plans for revenge, because where there is Dark Energy, evil always accumulates...
Present.
A week ago, my husband received a package from Uncle Liao with nozzles for his brand new 3D Printer, and they lay quietly on the table, did not touch anyone. But one day, looking into the kitchen cabinet for some trifle, the husband was attracted by the unhealthy shine of the French Press Flask, until that day she stood in the Darkest Corner of the cabinet and did not shine. But the Dark Energy finally decided to show itself... 'I have a 3D Printer, and I can print a coaster for her!' - thought the husband. Moreover, ABS plastic gathers dust in the corner, and 1 mm nozzles just came for faster printing ...
But the Dark Energy finally decided to show itself... 'I have a 3D Printer, and I can print a coaster for her!' - thought the husband. Moreover, ABS plastic gathers dust in the corner, and 1 mm nozzles just came for faster printing ...
The compass plunger in the teeth and howl 3D model ... for an experienced engineer and a novice 3D modeler, the creation of a cup holder model did not take much time, without artistic frills and the printer is already rustling on the table, evaporating toxins from ABS into the environment, and on it the table is born the embodiment of engineering and design thought called
to revive the French press...
But printing with a 1 mm nozzle had its own characteristics, the miel walls had an uneven structure, dips and roughness. In other places, strange snot appeared ... all this did not add attractiveness to the coaster, but the husband hoped that after processing with a file, acetone and such and such a mother, the model would take on a more elegant look . ..
..
... and when everything ... almost all the defects were removed, it was time to try on a new glass holder for the old flask ... the clothes turned out to be the wrong size, and the flask barely fit into the glass holder by 15% and got stuck like Winnie the Pooh in a rabbit hole... just like in a cartoon... and not here and not here... It was decided to squeeze the flask from the bottom... the thumbs pressed on the bottom of the flask, and the rest pulled the cup holder up by the edges... at the husband's (idiot) another thought flashed that you could try to soften the plastic with boiling water ... and another thought that the bottom of the flask could crack due to its small thickness ... and at that moment the flask decided to avenge the long days of seclusion, it was not in vain that it saved up Dark power... and its bottom cracked... the thumbs fell through, and the sharp edges of the bottom of the flask left deep wounds on the husband's thumbs. .. the First Blood was shed. nine0003
.. the First Blood was shed. nine0003
The revenge of the Dark Flask was a success, and if the physical pain was not strong and quickly passed, a band-aid was put on the wounds... Then the moral pain haunted the husband for a long time, the pain of failure... but the biggest pain is the temporary inability to use one's own hands - if you can type and use a mouse without thumbs, then you can wash the dishes, fasten a button .... yes, even cutting a piece of bread is quite difficult ... and my wife, as if evilly, drove away for a week with her children to relatives.
This is how you make children... you do... and in the hour of need there is no one around and you clench your will into a fist in general, clench your teeth, wash the dishes, fasten the buttons and cut off a piece of bread performing miracles of balancing act with your hands trying not to use your thumbs , and in general you try not to strain your hands, because every careless movement can cause bleeding. And without hands as without hands.
And without hands as without hands.
Results.
When working with glass, be very careful not to press too hard... better not to press at all. nine0003
For a 1 mm nozzle, you need to choose the optimal settings to improve print quality and print in 1 wall, because this is exactly what the nozzle was ordered for. Perhaps the Comrades will tell you why under-extrusion appears in one place and vertical snot in another.
ABS plastic, nozzle 1 mm, layer thickness 0.2, temperature 270, flow 100%. printing time 8-9 hours, sticking to the table on ABS juice.
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want to
5
Manual for 3D vacuum heat press
| Manual for vacuum 3D heat press in PDF format | Available in three colors A large number of colors are created for various needs of customers.
| 3D vacuum heat press | 1 |
| Power cord 220V | 1 |
| Silicone mug belt (11oz) | 3 |
| Replacement silicone membrane | 1 |
| Replacement silicone contour seal | 1 |
| Spare filter | 1 |
| Heat resistant gloves | 1 pair |
| Instruction video disc | 1 |
| User manual | 1 |
DEFINITION
3D vacuum heat press is a universal electro-mechanical device that is used for the manufacture of souvenirs by applying images to various objects, both with a flat and uneven surface, thanks to the use of vacuum discharge technology and high temperature.
PURPOSE
The 3D vacuum heat press can be used to print mugs, shot glasses, fully sealed plates, T-shirts, decorative stones, protective covers for various cell phones and tablets, ceramics, crystals, puzzles and more.
DESCRIPTION
3D vacuum heat press is a design consisting of a thermal chamber made using heat-insulating materials and heat-resistant plastic. nine0231 The heat source is two tubular electric heaters (TEH) located at the top and bottom of the thermal chamber and allowing to reach temperatures up to 230 degrees Celsius.
A vacuum pump with a silicone membrane is used to create a vacuum pressure. The vacuum pump capacity is 33 liters per minute, the maximum pressure is -640 mmHg (mmHg). Electric power supply of the 3D vacuum press 230 volts, power consumption 2800 watts.
The 3D heat press has two thermal sensors that allow you to maintain different temperature conditions and control the automatic shutdown of the heating elements. The operation of the press is controlled by a touch screen with audible alarm. nine0003
The operation of the press is controlled by a touch screen with audible alarm. nine0003
PACKAGING
High-density foam is used for packaging, which provides good impact protection.
|
|
|
| Size: 680x620x370 (mm) | Color box |
EQUIPMENT
| Device description in two languages - English and Chinese | High heat resistance gloves | |||
| Training disc | Spare filter element | |||
| High temperature silicone tube | High temperature silicone seal for vacuum plate | |||
| European power cord | High temperature silicone sheet 30x42 cm | |||
| nine0084 |
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
It consists in transferring an image printed on a special media to the surface of the product using vacuum pressure and high temperature.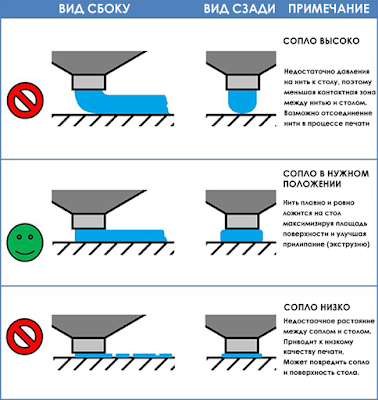 A product with a print pre-fixed on its surface made on special sublimation paper, with sublimation ink is placed in a 3D vacuum thermal press chamber heated to a certain temperature for a certain period of time (moreover, the temperature and time regime differs depending on the medium used). Thermal transfer can be carried out using vacuum pressure created by a vacuum pump and a silicone membrane, or using a silicone belt (when transferring the image to mugs). nine0003
A product with a print pre-fixed on its surface made on special sublimation paper, with sublimation ink is placed in a 3D vacuum thermal press chamber heated to a certain temperature for a certain period of time (moreover, the temperature and time regime differs depending on the medium used). Thermal transfer can be carried out using vacuum pressure created by a vacuum pump and a silicone membrane, or using a silicone belt (when transferring the image to mugs). nine0003
UNPACKING AND INSTALLATION
- Remove the vacuum heat press from the box and remove from the factory packaging.
- Place the vacuum heat press horizontally on a hard surface (table).
- Open the top cover and remove foreign objects from the press (cords, instruction discs, packaging residue, etc.).
Open the top cover and leave it in this position for 2-3 hours at room temperature (DO NOT POWER ON!). nine0003
Control 3 D Vacuum thermopress
Tempenser, thermal transfer time is set, the upper and lower heater is turned off, the time of timer is set. You can also set the current date and time. The 3D vacuum heat press is equipped with a speaker that will beep when the heat chamber is fully heated or the thermal transfer is finished. nine0003
You can also set the current date and time. The 3D vacuum heat press is equipped with a speaker that will beep when the heat chamber is fully heated or the thermal transfer is finished. nine0003
The 3D Vacuum Heat Press will automatically turn off when idle for more than 15 minutes.
Switching to degrees Celsius is done by simultaneously pressing "+" and "-".
POWER ON 3 D VACUUM HEAT PRESS
- Plug the power cord into the appropriate socket on the heat press.
- Insert the plug into the socket.
IMPORTANT! When choosing a power source, it is not recommended to use carriers and extension cords; if possible, the source of electricity should be directly from a 220-volt outlet. nine0003
Turn on the 3D vacuum thermopress using the
switch on the control panel Power Power
Delicacy
The heating area contains convex points.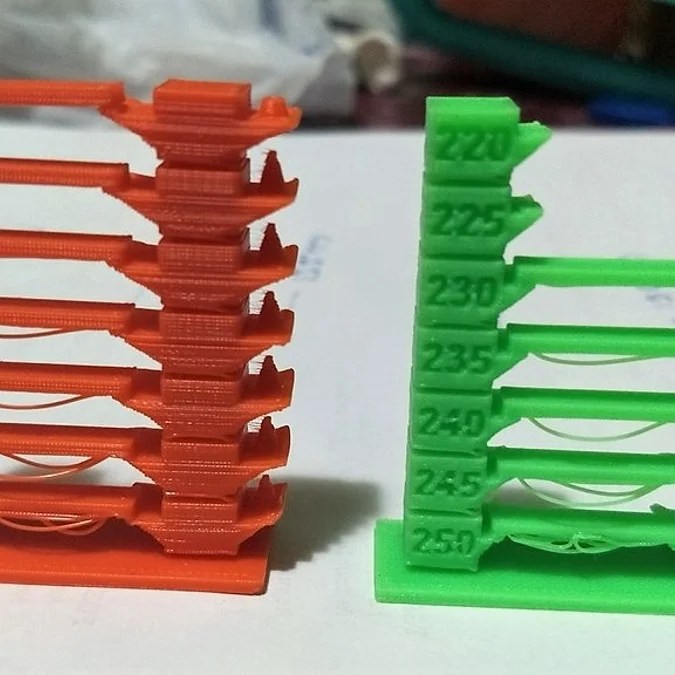 Due to the use of aluminum alloy, the temperature is evenly distributed.
Due to the use of aluminum alloy, the temperature is evenly distributed.
3D VACUUM THERMOPRESSER CONTROL
To set the image transfer time, use the “TIME SETTING” button by pressing it. After the time value starts flashing, set the value using the "+" and "-" buttons. If the change range of the time value is very large (for example, you need to change the value from 5 to 200 seconds), then you can save time by holding the "+" button, while the value will change faster in automatic mode. nine0003
To set the temperature, press the “TEMPERATURE” button on the display, the value will start flashing, use the “+” and “-” buttons to set the desired value in accordance with the temperature conditions given in this manual.
The heating elements are switched on by pressing the "HEATING" button. When pressed once, the upper heating element is turned on, when pressed again, the lower heater comes into action.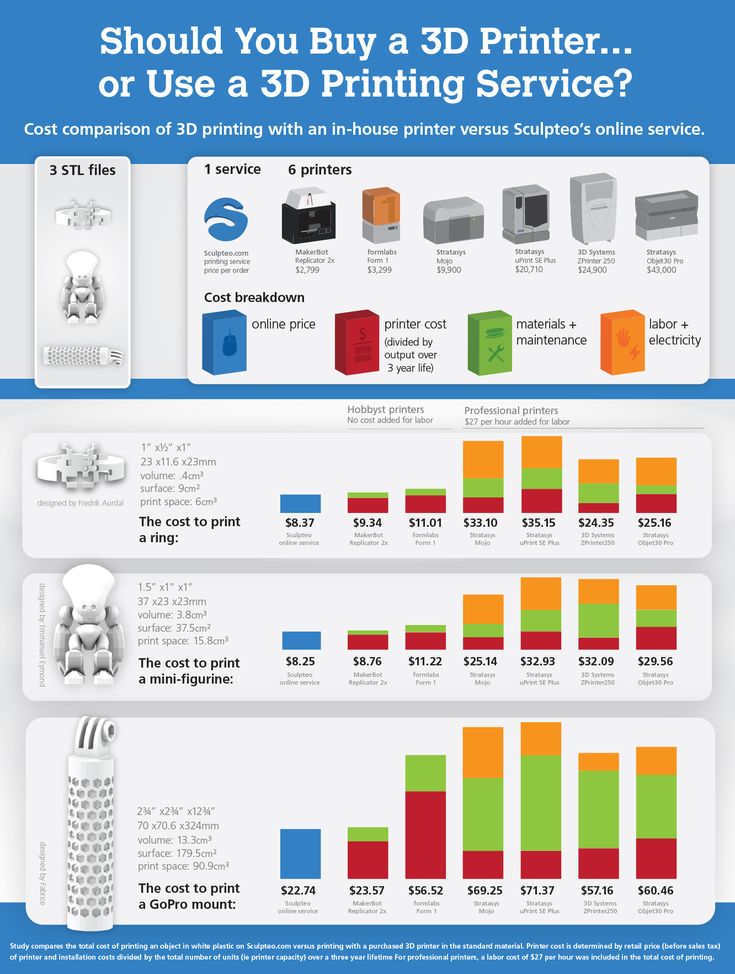
After the 3D vacuum heat press has reached the temperature necessary for transferring the image, place the product in the 3D heat press chamber and press (if necessary) the “VACUUM” button. This mode is used when transferring images to stones, plates, cell phone cases, etc. When transferring images to mugs, it is not necessary to use vacuum pressure . Next, start the timer by pressing the "TIMING" button. The system will notify you of the completion of the image transfer process by beeping. If you don't respond to the beep, the 3D vacuum heat press will turn off automatically after 15 minutes. nine0003
FILTER ELEMENT
When working with the press, it is necessary to periodically empty the filter element from accumulated condensate. If the filter capacity is overfilled, its work to neutralize harmful substances becomes ineffective.
Highly active carbon air filter effectively retains harmful substances during vacuum heat press operation. nine0003
nine0003
IMAGE TRANSFER ON MUGS
It is carried out by fixing the printed image with thermal tape on a mug intended for sublimation transfer. Printed on special paper using an inkjet printer with sublimation ink
Then a special silicone belt is put on the mug, which is included in the delivery.
Next, the mug is placed in the “large” chamber of the heat press upside down, where 12 mugs can fit. If it is not possible to arrange the mugs with belts attached to them so that the heat press lid closes completely, you can remove the lower grill located at the bottom of the heat press.
For sublimation heat transfer of 12 mugs, 14 minutes will be enough, while the transfer temperature will be 210 degrees Celsius, for one mug, the transfer time will be 8 minutes at the same temperature. In order to exclude heat leakage and, as a result, a temperature drop, it is necessary to remove the chrome grill located at the bottom of the heat press so that the mugs with a silicone belt rest directly on the bottom of the heat press and the press cover is hermetically sealed. nine0003
In order to exclude heat leakage and, as a result, a temperature drop, it is necessary to remove the chrome grill located at the bottom of the heat press so that the mugs with a silicone belt rest directly on the bottom of the heat press and the press cover is hermetically sealed. nine0003
| Number of mugs | Temperature | Transfer time |
| 12 cups | 210°C (410°F) | 14 minutes |
| 1 mug | 8 -10 minutes | nine0088
For even heating, mugs should be placed upside down in the heat press. Drawing the image can be made both on standard, and on non-standard mugs (Beer and cone mugs, coffee and tea cups).
Drawing the image can be made both on standard, and on non-standard mugs (Beer and cone mugs, coffee and tea cups).
IMAGE TRANSFER TO PLATES
The main difference between the resulting image and the classical method is the complete imprinting of the entire area of the plate, including its sides. Please note that the diameter of the finished image should be slightly larger than the diameter of the plate itself. This will prevent accidental shifting of the print during thermal transfer and, as a result, the appearance of unprinted edges. When preparing a design, it is desirable to take into account possible cuts in the image when fixing the print on the plate for a more uniform fit to its surface. After the image is fixed on the surface of the plate, we place it in the small chamber of the 3D vacuum heat press. nine0003
In order for the silicone membrane to completely press the imprint to the plate in places of sharp transitions (the border between the bottom and the side), it is necessary to put a plastic tube or a folded strip of paper.
Temperature-time conditions for image transfer on plates are as follows: temperature - 210°C (410°F), image transfer time - 7 - 9 minutes. In conclusion, I would like to note that for sublimation thermal transfer of images, it is necessary to use plates specially designed for this. nine0003
3D VACUUM THERMOPRESS SPECIFICATIONS
| Dimensions | 680x610x370 mm, 620x470x320 mm |
| Volume | 0.15 m³ |
| Net weight | 21 kg |
| Gross weight | nine0118 |
| Power input | 2800 W |
| Supply voltage | 220V ± 10%, 50Hz |
| Working format | 300x420x110 mm |
| Upper heating element power | 1300 W | nine0088
| Lower heating element power | 1300 W |
| Vacuum pump power | 150W |
| Max vacuum pump pressure | -640 mmHg or -0. |