3D printed shoes file
How 3D printing revolutionizes the footwear industry
3D Learning Hub
See all categories
Contents:
- Introduction
- Designers and 3D printing
- 3D printed footwear: try a new manufacturing process and new materials
- Are 3D printed shoes for everybody?
- 3D printed sneakers
- What about the future of 3D printed footwear?
Introduction
Designers and 3D printing
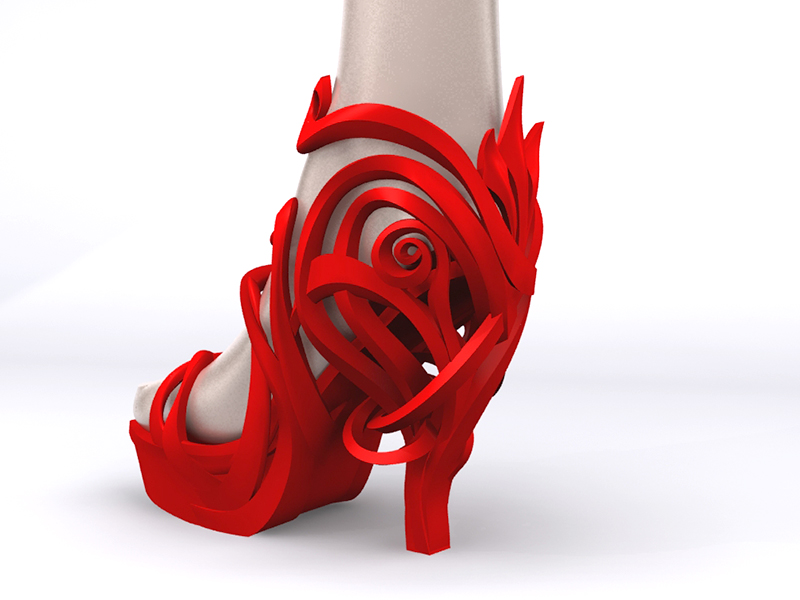
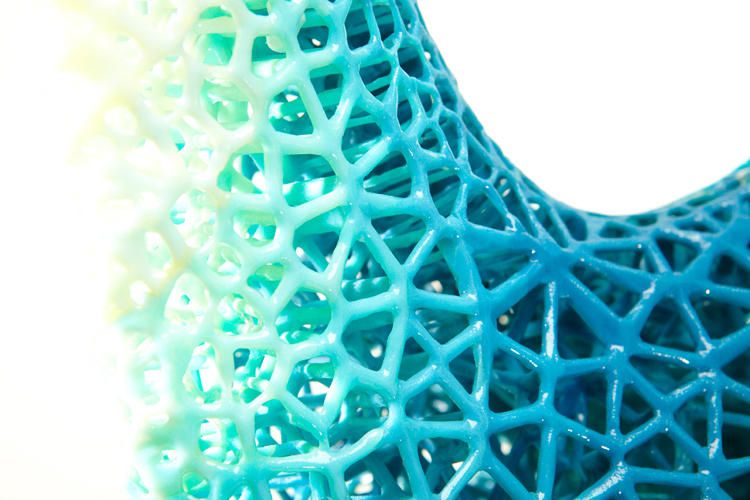
As we saw with the Virus Collection 3D printing allows designers to create clothes. But its utility in the fashion tech doesn’t end here because it’s also possible to create shoes with astonishing designs.
For example, Zoe Jia-Yu Dai, a designer based in Taiwan and specialised in footwear, created “Breaking the 3D Mould”, a shoes collection with 3D printed parts. This technology allows designers to go further with the design structures. It is a way to change the manufacturing process. It’s easier to create organic structures with additive manufacturing, than with a traditional process.
It is obviously a good way to create prototypes to work on the design of any shoe. Some designers only focus on the design of the shoes. Melissa’s shoes are a great example of the possibilities offered by the 3D printing technology when it comes to design. Check out our blogpost about Melissa’s footwear experiments.
Silvia Fado, a spanish footwear designer, uses 3D printing and laser cutting to do rapid prototyping. Inspired by engineering and architecture, Silvia Fado focusses on style but not only since she’s also interested in the movement of the body, the wearability of the shoes, and the comfort elements that are part of the shoes. She works on the aesthetic and on the functional value of footwear.
She works on the aesthetic and on the functional value of footwear.
3D printed footwear: a good way to try a new manufacturing process and new materials
Rethink your production
Like in other sectors, 3D printing can be used to develop new manufacturing processes. It can give more possibilities and opportunities to any company. For example: Feetz. It is an American startup run by Lucy Beard. They make custom shoes, easy to wear and with a nice style. On top of that, Feetz is also committed to protect the environment.
They developed their own 3D printer, using a Fused Filament Fabrication technique, and their own 3D printing material: a patented polymer. They wanted to rethink the whole manufacturing process, in order to make it more sustainable. Feetz uses recycled and recyclable materials, no water and reduced by 60% their carbon footprint. Moreover there is no material waste because with 3D printing you only use the quantity that you need.
Their use of 3D printing in their manufacturing process shows that it is possible to change the way the shoes industry affects the environment.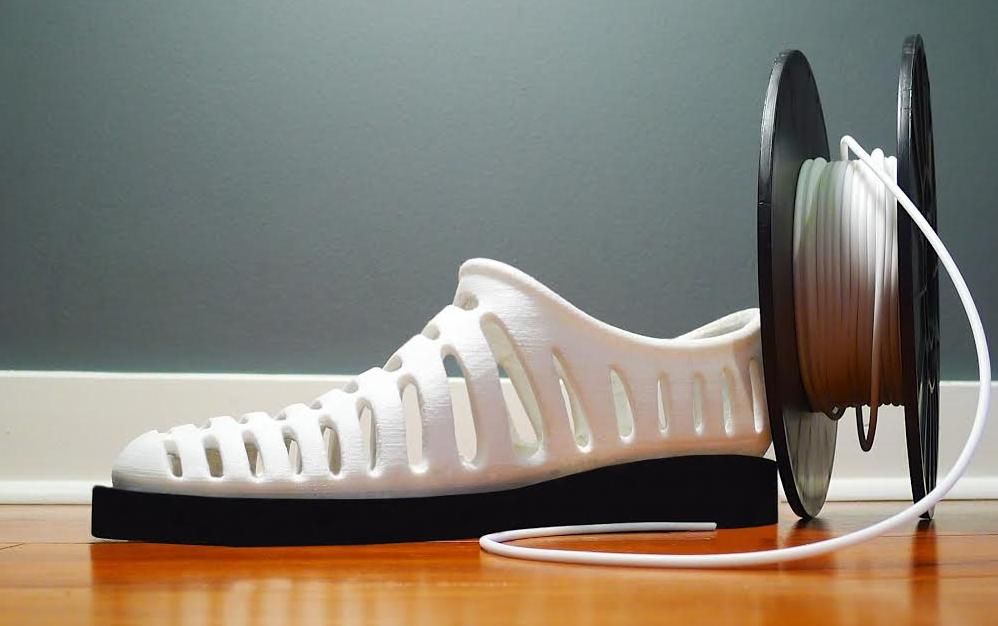
Try out high performance 3D printing materials
New high-performance materials are now available on the market and particularly adapted to the creation of shoe parts, such as midsoles.
The perfect example for that is TPU. Indeed, objects printed with Thermoplastic Polyurethane are offering advanced properties, which is perfect to get durable, strong, and flexible parts. With Sculpteo’s online 3D printing service, you will have the choice between two different TPU options for the creation of shoes or midsoles: Ultrasint® TPU 88A and Ultrasint® TPU01 a perfect 3D printing material choice if you need to produce parts requiring shock absorption, high elasticity, and energy return. For flexible lattices and complex parts, this TPU material is ideal.
Are 3D printed shoes for everybody?
It’s easy to get a pair of 3D printed shoes made with a 3D printing technology. For instance, Feetz collaborated with the designer Seth Aaron to launch a shoe line together, inspired by a Japanese, 1960s mid-century modern look.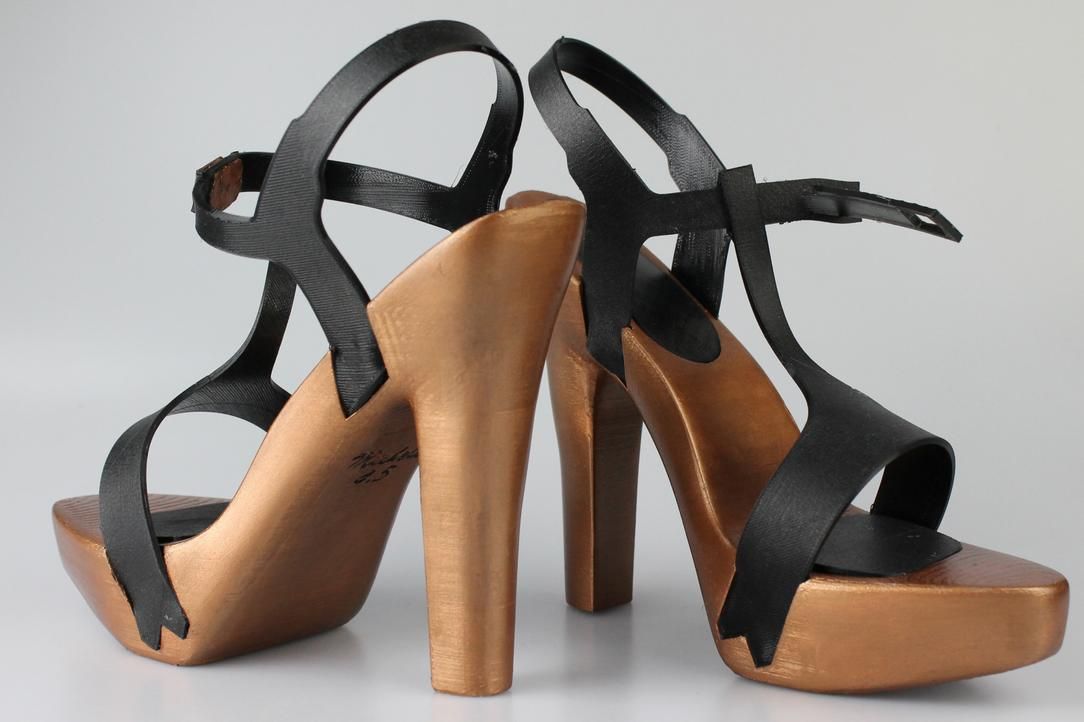 You can buy those shoes on their website.
You can buy those shoes on their website.
But you can also get custom made shoes, as they are offering different models from slides and sneakers for men and women, to wedges with a lattice design. To get your 3D printed shoes, you have to download their app to 3D scan your feet in order to get a 3D model. Then, you just have to choose the shoes among the different models that Feetz offers. They will make you a ready-to-wear pair of shoes based on the 3D model of your feet.
Continuum Fashion also launched ready-to-wear pairs of shoes, created thanks to 3D printing. With Additive Manufacturing, it is possible to give life to organic forms. The project shows that 3D printing shoes actually make sense to create ready-to-wear. Moreover, you can produce them faster than with traditional manufacturing.
3D printed sneakers
A running shoe can now be partially created with 3D printing technology. Actually, the midsoles of running shoes are particularly suitable for 3D printing. Big shoe manufacturers are using additive manufacturing. For example, brands like Adidas, Nike, New Balance and Under Armor have already printed sneakers. You can already customize your shoes thanks to Adidas, by choosing the look and the color of it, but you will soon be able to go further. Adidas already made a limited edition of FutureCraft 3D, using 3D printing. The brand now unveiled FutureCraft 4D, a footwear with a midsole created in partnership with Carbon 3D, using a new process called Digital Light Synthesis (formerly known as CLIP). Thanks to digital light projection, oxygen-permeable optics and liquid resin, this process can produce a durable and resistant polymeric goods. These Futurcraft 4D shoes will offer a personalized support for athletes and are allowing mass customization. New Balance Zante Generate is another similar project, these sneakers have a partially 3D printed midsole. It is a pair of running shoes with a flexible midsole that offers a good support. Nike also uses 3D printing a lot for prototyping and they are proud to say that they use Selective Laser Sintering to create their prototypes.
Big shoe manufacturers are using additive manufacturing. For example, brands like Adidas, Nike, New Balance and Under Armor have already printed sneakers. You can already customize your shoes thanks to Adidas, by choosing the look and the color of it, but you will soon be able to go further. Adidas already made a limited edition of FutureCraft 3D, using 3D printing. The brand now unveiled FutureCraft 4D, a footwear with a midsole created in partnership with Carbon 3D, using a new process called Digital Light Synthesis (formerly known as CLIP). Thanks to digital light projection, oxygen-permeable optics and liquid resin, this process can produce a durable and resistant polymeric goods. These Futurcraft 4D shoes will offer a personalized support for athletes and are allowing mass customization. New Balance Zante Generate is another similar project, these sneakers have a partially 3D printed midsole. It is a pair of running shoes with a flexible midsole that offers a good support. Nike also uses 3D printing a lot for prototyping and they are proud to say that they use Selective Laser Sintering to create their prototypes.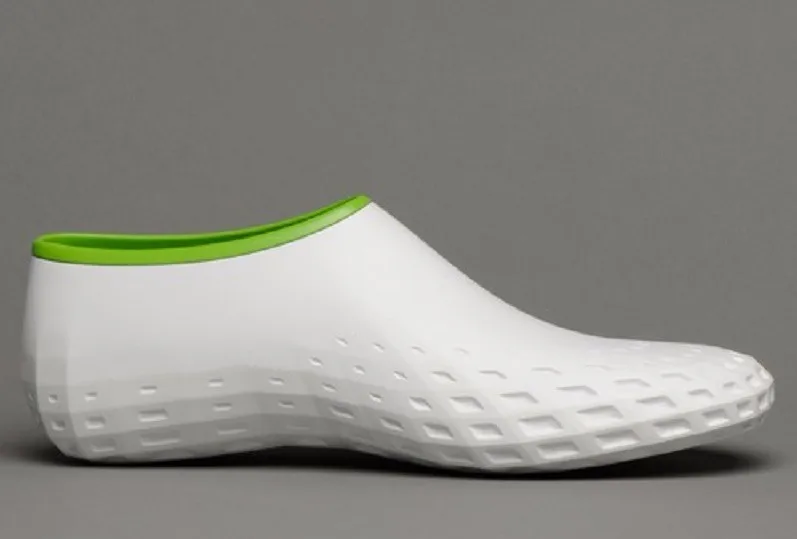 Indeed, you can work and rework on a shoe design very easily thanks to rapid prototyping. They made a partnership with HP, who released the HP Multi Jet Fusion, and will certainly work on new projects soon.
Indeed, you can work and rework on a shoe design very easily thanks to rapid prototyping. They made a partnership with HP, who released the HP Multi Jet Fusion, and will certainly work on new projects soon.
Rethinking the manufacturing process
Nike also uses 3D printing a lot for prototyping and they are proud to say that they use Selective Laser Sintering to create their prototypes. Indeed, you can work and rework on a shoe design very easily thanks to rapid prototyping. They made a partnership with HP, who released the HP Multi Jet Fusion, and will certainly work on new projects soon. Indeed, Nike, is using additive manufacturing to prototype its products, and in 2017, their use of 3D printing was estimated to provide a 10% cost efficiency. With their partnership with HP, mass production could be on its way with the use of these powerful 3D printers. These big leaders of the footwear industry have to start using additive manufacturing in order to keep on being competitive and improve their processes on a different level: it can be for product development, customization, or mass-production.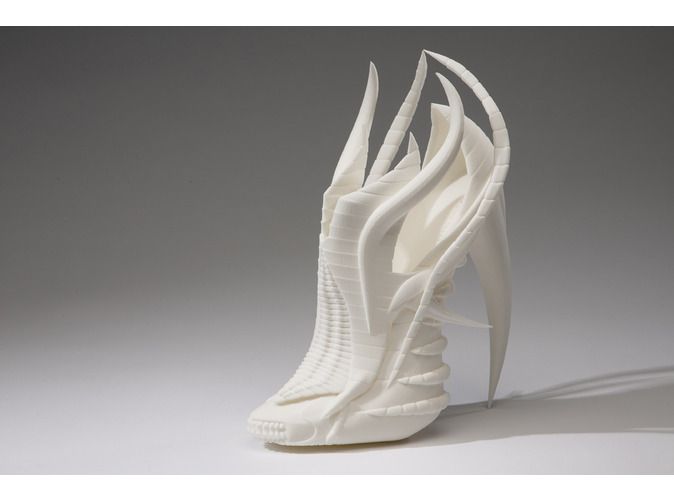
Fully 3D printed shoes?
There is still a lot of work to get the fully 3D printed shoe. Nevertheless, some product developments are going in this direction: Olivier Van Herpt is using 3D scans and 3D printing to create new shoe structures, making them unique, lightweight and quite resistant. These 3D printed shoes have a unique style but are custom-made, meaning that they guarantee you the perfect fit. But Olivier Van Herpt is not the only person working on fully 3D printed shoes. Some other creators like Nicholas Unis are starting their footwear business with fully 3D printed products.What about the future of 3D printed footwear?
3D printed footwear can easily be integrated to your daily life, for example Phits, with their 3D printed insoles, are a good example. Some projects are really accessible to anybody, and could be developed more widely. Personalized pairs of shoes are now accessible to everybody and mass customisation will gain ground in the upcoming years.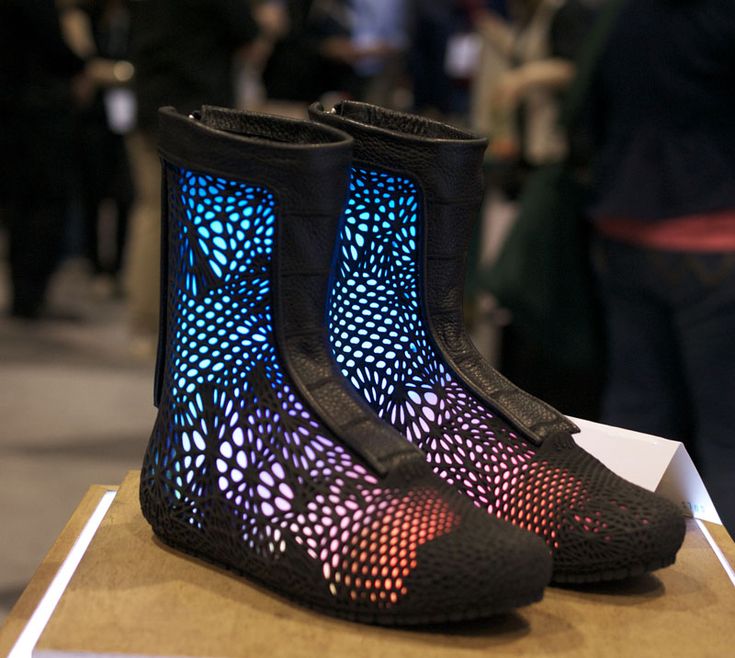
Indeed, 3D printing is a great way to get shoes perfectly adapted to your feet. Big brands are making partnerships with major actors of Additive Manufacturing such as HP, and are including the 3D printing process in the production of some of their models. 3D printed shoes, thanks to brands like Nike or Adidas are now entering the mass production era.
Designers will continue to work with 3D printing as it allows to create incredible designs with a lot of freedom. For example, Zoe Jia-Yu Dai is definitely not going to stop working with 3D printing. As she’s interested in men and children’s footwear, new projects could be launched really soon.
The footwear industry is more linked to 3D printing than you might think. All these examples show that there are different ways to create shoes. It can be to push design boundaries or to change manufacturing methods by finding an ecological way to produce, or even to get shoes or insoles made to measure for more comfort. Reasons to create 3D printed shoes are numerous, and it could be pushed further in the upcoming years!
Do you want to start your 3D printing business in the footwear industry? Well, here is our first advice: Choose the right 3D software.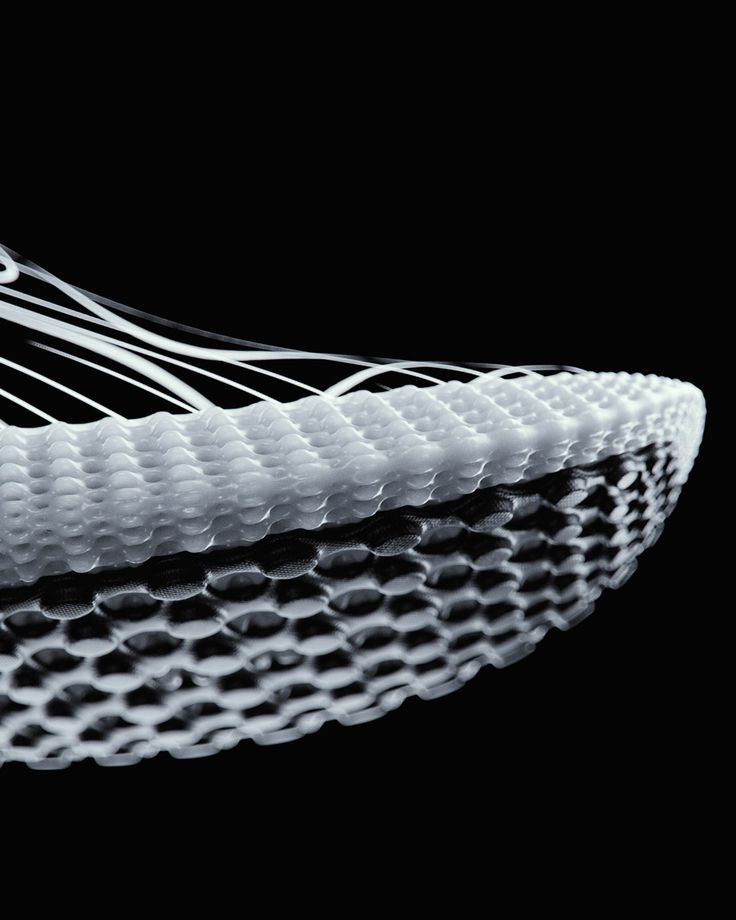 Getting the perfect shoe design software will help you start your best project.
Getting the perfect shoe design software will help you start your best project.
You have a 3D model and you want to prototype a pair of shoes, or anything else? You can upload a model on our online 3D printing service.
You want more news about the latest innovations in the 3D printing industry? Don’t hesitate to subscribe to our weekly newsletter.
Related Topics
- Return to Top
Get the latest 3D printing news delivered right to your inbox
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter to hear about the latest 3D printing technologies, applications, materials, and software.
▷ shoe stl file 3d models 【 STLFinder 】
shoe horn
thingiverse
This is the Shoe Horn STL file
STL file
prusaprinters
Be the first one on your block to prank people with the 3d printing equivalent of a rickroll! Print instructionsUnassociated tags: can you make an STL?, Do you have the STL?, Is there an STL?, STL file Category: Other Summary Has someone showed you. ..
..
STL file
thingiverse
Has someone showed you an insanely complicated 4000 hour plus IRL sculpture and asked if you have an STL file of it? How about classical architecture that took 80 years to build? Or someone elses patented invention? Well now you can give them the STL...
Doll House STL File
cults3d
Doll house STL file
abeille,bee stl file
cults3d
bee stl file 3d
8266 Base STL file
thingiverse
8266 Base STL file
my first stl file
thingiverse
my first stl file
bird stl file
pinshape
bird relief 3d stl file
rooster STL FILE
pinshape
cock,rooster stl file for cnc frlief
house, house STL file
cults3d
house, House STL file for 3D printer
STL file for Mechanisms
grabcad
STL files for Mechanisms Class UNO
Earrings stl file
cults3d
This stl-file is made with fusion 360.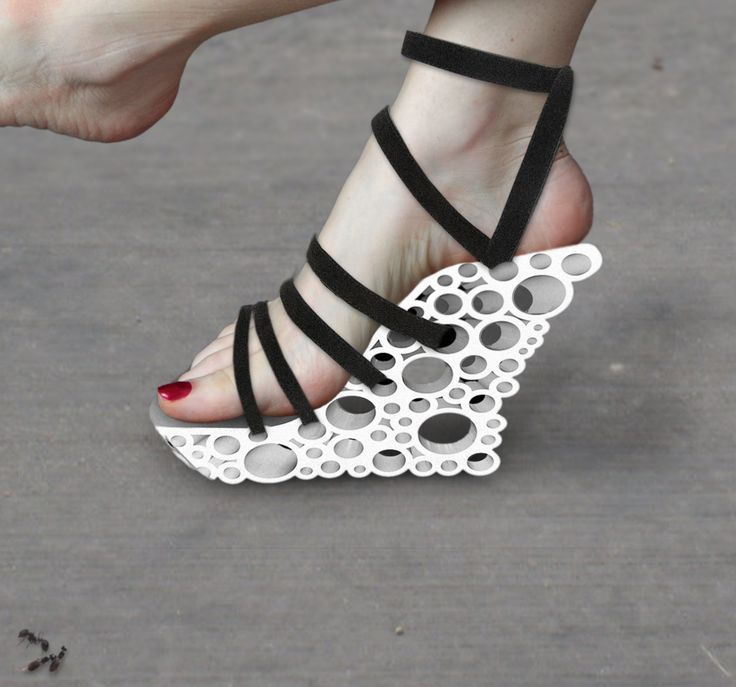
Cow, STL cow file
cults3d
Cow, cow STL file for CNC, Router, Printer 3D
wings,wings STL file
cults3d
wings,Ailes STL file for 3D printer, CNC, router
scorpion stl file
pinshape
scorpion stl file for cnc or 3d printed
Retailed base stl file
thingiverse
The original stl file gave me issues so I fixed it here you are.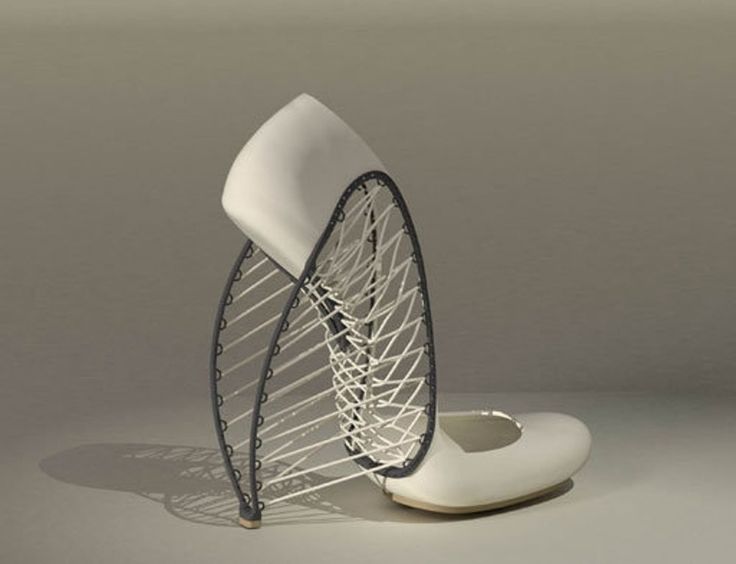
Stitch Marker STL File
thingiverse
This is a remix so that it is easier to obtain the STL file from the original creator since many people were asking for it.
$100 bill .stl file
thingiverse
This is a .stl file. I loaded it in HeeksCNC and cut it with a desktop CNC router. ...It will also print hollow.
stl file 3D model
cgtrader
3D design in stl format
Valve Connector .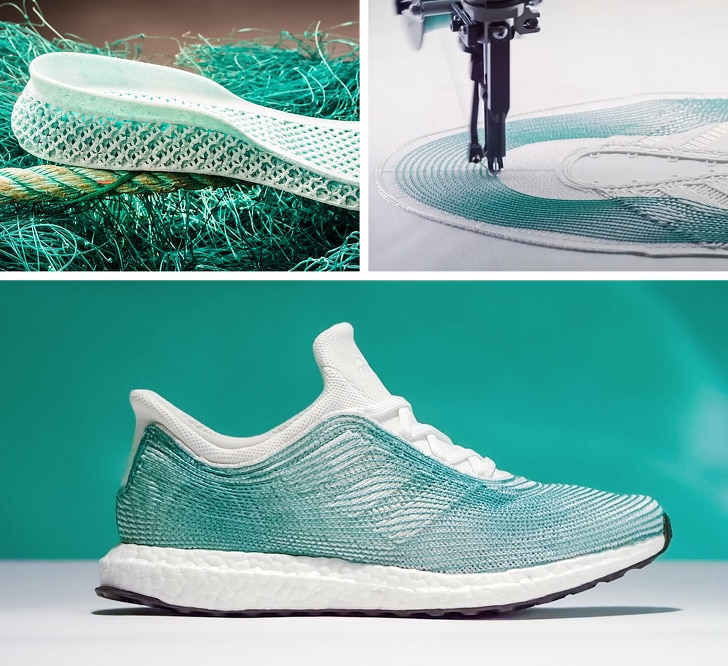 STL File
STL File
sketchfab
Valve Connector .STL File download Visit www.3dscanningservices.net to check out our complete selection 3D scanners, 3D printers and 3D software. In addition to 3D equipment sales, we also specialize in providing 3d scanning, reverse engineering,...
Turbine Blade .STL File
sketchfab
Turbine Blade .STL File for download Visit www.3dscanningservices.net to check out our complete selection 3D scanners, 3D printers and 3D software. In addition to 3D equipment sales, we also specialize in providing 3d scanning, reverse engineering,...
The cursed STL file
thingiverse
This is an STL file that I designed in Blender, but no matter what, I can not print this part without it having a shift layer at some point. ...this part will not be useful for you but I want you to print it and tell me in the comments if you could...
...this part will not be useful for you but I want you to print it and tell me in the comments if you could...
japanese landingcraft (stl file)
sketchfab
Includes all necessary STL files to print the model on your own 3D printer. (No physical model included with your order.) Minimum printbed needed is 15 x 15 cm and 15 cm high. Scale is for 28mm Miniatures (approx 1/48) you can rescale it: Example...
Lighter File STL
thingiverse
Lighter File STL 125.235 points 253.762 facets dimension in mm 9.78 X 16.88 X 50.82 inch 38 X 66 X 2 follow me YOUTUBE: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCegptSyuzQWuU1Fow04_MKw?view_as=subscriber FACEBOOK:.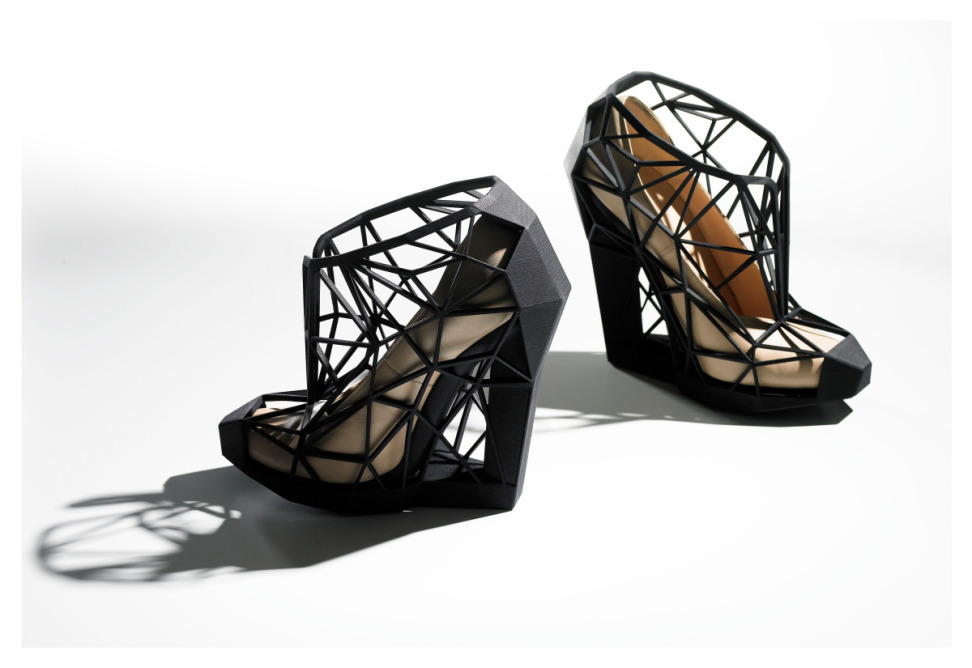 ..
..
sugarskull now stl file
thingiverse
little sugar skull in honour of halloween...my second ever sculpt changed from obj to stl
Hulk - 3d STL file
cults3d
Hulk, 3d STL model fore printing. ...It is my wersion of this hero.
bee stl file
pinshape
bee insect 3d file for cnc or 3d printer
STL Printing file, Printable File helmet
cults3d
3D STL Printable Print file helmet This is a one-piece 3D printing file, ready to print at home or at your local 3D print vendor.
Dae file to Stl file for Ladder
thingiverse
Convert the dae to stl. ... I didn't scale this very accurate,may need to resize a little bit.
doll house Bed STL File
cults3d
doll house Bed STL File
3D printing for shoes
Application
Subscribe author
Subscribe
Don't want
9
Then they released the first sneakers with a printed sole - Futurecraft 3D. Around the same period or a little earlier, on popular portals with 3D models, you could download and print your own sandals, of course, more for fun.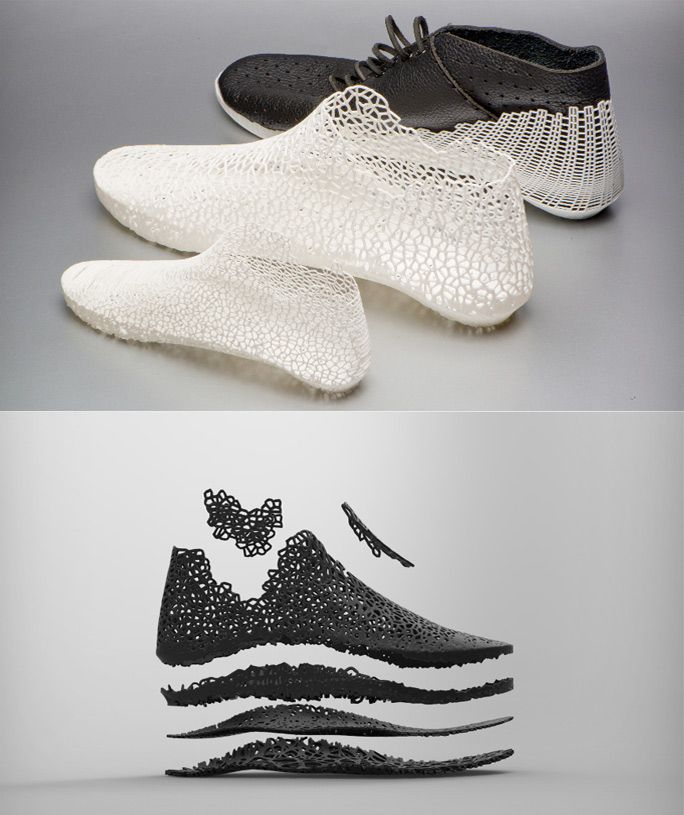 Those. 3D printers have been used in shoe manufacturing for a long time. But few people know how things are in the real Russian shoe production and how long 3D printing technologies have been used.
Those. 3D printers have been used in shoe manufacturing for a long time. But few people know how things are in the real Russian shoe production and how long 3D printing technologies have been used.
RALF RINGER is a Russian company specializing in the production and sale of men's, women's and children's shoes under the brands Ralf Ringer, Piranha and Riveri. Production facilities are located in Moscow, Zaraysk and Vladimir.
RALF RINGER purchased its first 3D printer back in 2017.
The production of soles is a complex technological process, which includes the production of expensive aluminum tooling, in other words, molds. The cost of a mistake is about 10,000 euros. Therefore, to reduce risks, it is important to make the most accurate layout possible. Previously, RALF RINGER carried out this process on 6-axis CNC machines, or on powder printers. Both methods did not suit them: in the first case, it was expensive equipment, in the second, expensive materials.
RALF RINGER bought a HERCULES STRONG 3D printer in 2017 to make sole models.
The cost of making a model immediately decreased by 15-20 times, and the manufacturing time was reduced to a day.
Then heels began to be printed. It is very important for the heel to "stand" correctly on the plane, the comfort when walking depends on it. All the main elements, such as the heel itself, the main insole / half insole, arch support, hard heel counter, must be perfectly fitted. It is important to note that the feel of the foot - depending on the deflection - changes significantly for every millimeter of values. Therefore, in addition to aesthetics, functional indicators were selected - material, filling density, wall thickness.
Now, before opening the molds for the RALF RINGER heel, they print a functional model of the heel , attach it to the shoe and carry out all the necessary fitting and technological operations before the mass launch.
Having received a functional heel model, they thought about obtaining a functional flexible sole model. For the production of such a functional model, it was decided to print molds with a short life cycle .
The RALF RINGER team has developed special technologies for designing and printing molds, selected materials and technological modes of casting.
As a result, they received polyurethane and fully functional soles prior to mold making.
The main challenge for RALF RINGER today is to improve sole manufacturing accuracy and extend the life cycle of molds.
In addition, the company has its own large-scale production and equipment mainly of Western assembly, so the question of spare parts and tooling regularly arises.
With the help of 3D printing, the company learned how to produce some technical parts of machines, which allows saving on maintenance and quickly responding to wear parts.
________________________________________
Subscribe to our social networks and get the latest information:
Our website - https://imprinta.ru/blog
VK - https://vk.com/imprinta
TG - https ://t.me/imprinta_llc
Even more interesting articles
35
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
0003
Read more
one
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
The PLAZ company specializes in the development and production of unmanned aerial systems...
Read more
204
Subscribe to the author
Subscribe
Don't want
Sadness has come.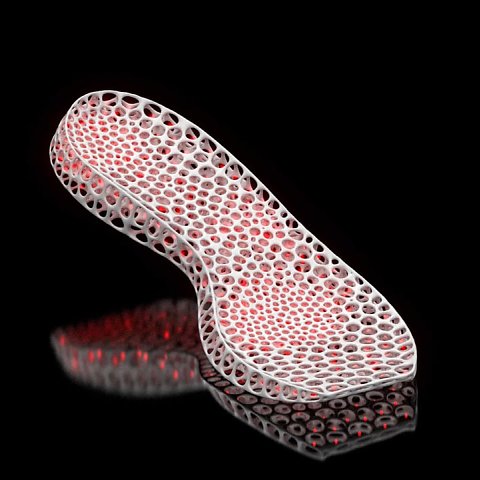 The screwdriver began to discharge quickly. Time to change batteries.
The screwdriver began to discharge quickly. Time to change batteries.
Look...
Read more
copy or original? On the nuances of regulation of 3D printers in different countries hits
The widespread use of home 3D printers has raised a question for lawyers: what to do with intellectual property rights when users print objects at home and should printed objects be considered copies?
Take, for example, a construction helmet. Today, there are various technologies, such as 3D scanners, with which it is possible to digitize almost any object and print it on a 3D printer using special software and material.
The resulting object is externally identical to the original, but due to the use of a different material will have different physical and chemical properties.
Can it be considered a copy in this case?
In early 2017, Adidas announced plans to start producing sports shoes using 3D printing. In April, the first 300 pairs of Futurecraft 4D sneakers were unveiled to the public, featuring a 3D printed mesh midsole made with innovative Primeknit technology.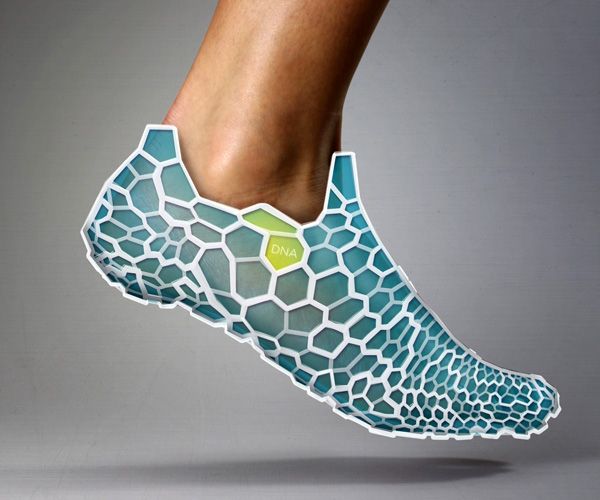
A few months later, Reebok presented the world with a video in which a 3D printer, like a Michelin chef conjuring up an original dessert, printed a sneaker from a material specially developed for the occasion by BASF. These sneakers were to be marketed under the Liquid Factory brand.
A few months have passed since these presentations, but it is unlikely that anyone today will point you to the place where you can purchase this innovative product. It's simply not for sale.
And strangely enough, the same technologies that created the hype around these shoes of tomorrow are at the same time hindering their entry into the mass market. The technology used by Adidas allows only six sole pads to be printed at a time, a process that takes 8 to 10 hours. Mass production at such speeds is out of the question.
Today, Adidas is pinning its Futurecraft 4D hopes on Carbon, which is bringing to market a form of 3D printing known as digital light synthesis. With it, Carbon promises to reduce the time it takes to produce Futurecraft 4D to 20 minutes.
These sports shoes from both companies are specially designed for 3D printing (which is not the case with the construction helmet mentioned above) and, accordingly, each new pair printed will be considered an original.
This September, it was announced that 3D printer distribution startup Just3DPrint (Just Print It Inc.) had lost the last of its three defamation lawsuits filed in a Philadelphia court earlier in February against the website 3dprint. com and its parent company 3DR Holdings (https://3dprint.com/186206/just3dprint-loses-lawsuit/). The plaintiff alleged that as a result of articles where his sale of copyrighted items was presented as wrongful, he suffered losses in the amount of $100 million, and sought to be reimbursed.
The articles dealt with a 3D SadFace (or anti-smiley) model. The copyright owner uploaded it to Thingiverse, only to find it was being offered for sale at startup Just3DPrint's ebay store. After several complaints, the Just3DPrint online store was closed and the whole scandal was described in detail by the website 3dprint.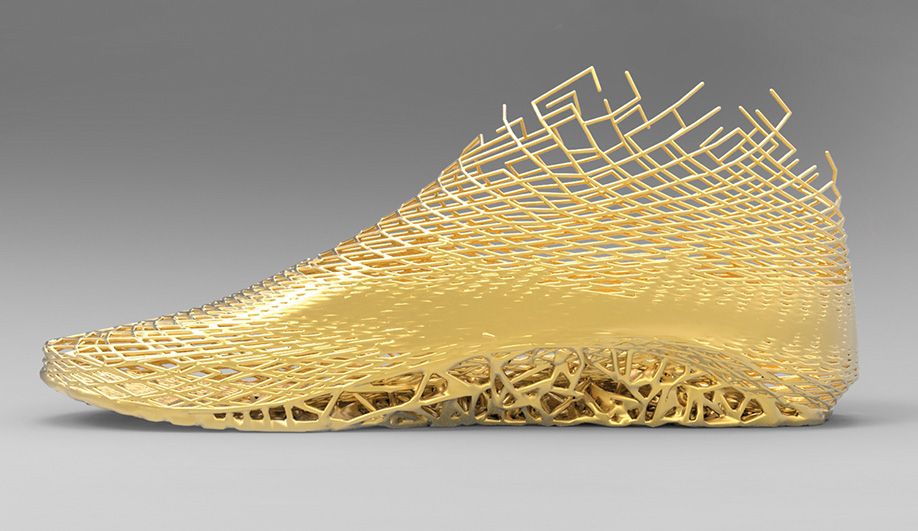 com, defining the startup's activities as illegal.
com, defining the startup's activities as illegal.
This is one of many cases where startups exploit gaps in copyright laws to their advantage. But the legislative process in this area does not stand still, and in each country it goes in its own way.
Russia
In Russian law enforcement in the field of 3D printing, three options arise: created by technical means without the use of existing intellectual property objects.
In the first case, when a 3D model is obtained as a result of scanning or converting a two-dimensional image, the model will be protected by copyright as an electronic copy of the object used for scanning. Although the question of extending patent protection to 3D models of objects, the creation of which implemented patented solutions, can be answered in two ways.
Chapter 72 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation refers to the use of patented solutions in the context of their implementation in a product or product, which 3D models are not.
But at the same time, a 3D model containing information about a patented solution makes it possible for anyone to manufacture a product or article in the most simple way.
Accordingly, the distribution of such models, including via the Internet, is contrary to the interests of patent holders.
In the second case, the model was developed in a graphics editor by a designer, it is an independent work, and the rights to it belong to its author.
In the third - when scanning or converting images that are not intellectual property, the created models are not protected by copyright. But at the same time, a 3D model can be registered as an industrial design and receive independent protection in a new capacity.
Unfortunately, there are no cases in Russian legislation yet when a model is created as a result of complex calculations, when scanning a group of objects and developing information about the relative position of thousands of points in space. It is logical that the creator of such a model is interested in legal control over this information.
However, in such cases, the neighboring law of the database manufacturer may apply.
Due to the fact that the law allows free use without the consent of the copyright holder of objects of copyright and patent rights for personal purposes, it is likely that the interpretation of the rules for personal use will narrow and undergo certain changes in the foreseeable future.
USA
There are several forms of intellectual property in the USA. For example, patents, which are further divided into use patents and design patents, carry with them a low level of risk for users of 3D printers. And that's why.
Usually the owner of a patent, upon discovery of an infringement of his rights, demands to correct the situation and thereby not bring the case to court. Moreover, he understands that in cases with 3D printing, where the rights were violated by private users for their own needs, and not for the purpose of obtaining material gain, any litigation will be economically unreasonable, and potential compensation will not even cover legal costs.
Patent infringement litigation in America typically lasts at least three years and costs over $3 million. In addition, it is not easy to identify the infringer due to the tradition in the online 3D printing community to go online under false names.
In the case of copyrights, the risk may be higher, although they only apply to the original, not copies. It should be borne in mind that, unlike patents and trademarks, which must be applied for, copyrights come into force from the moment a unique work is created and are valid not only throughout the life of the author, but also for 70 years after the day of his death. .
The country also has a Digital Millennium Copyright Act, under which websites created to download any copyrighted product (for example, YouTube) are not liable for copyright infringement by users.
Instead, they are required to create a mechanism for copyright holders to act upon copyright infringement. As with patent law, this law provides a guarantee to those who download files for 3D printing from the Internet that the copyright owner will not go directly to court, but will first notify the user of copyright infringement.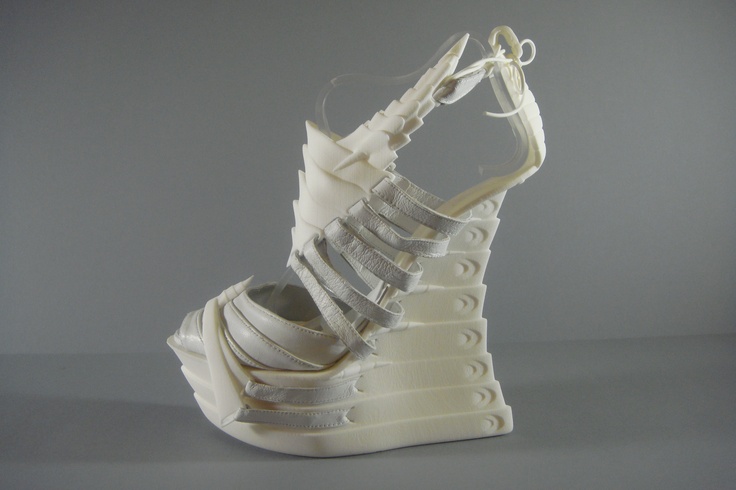
Unlike patent law, where damages must be proven as well as infringement, intentional copyright infringement can result in compensation of up to $150,000.
The risk of copyright infringement is comparable to the risk of trademark infringement. But the cost of legal proceedings and the amount of evidence required for the court play into the hands of individual violators here.
Asia (Hong Kong)
In October 2014, 28-year-old Japanese man Yashitomo Imura was sentenced to two years in prison by a court for manufacturing firearms using a 3D printer and distributing this technology via the Internet (https://3dprint.com/ 20019/sentence-imura-3d-printed-gun/ ).
As is often the case with new technologies, users are so overwhelmed by the benefits they bring that they forget the legal responsibilities that come with using them.
An example of this is the story of the once popular Napster file hosting service, which, by distributing audio files, violated the copyrights of artists and was eventually closed.
In Hong Kong, the Hong Kong BitTorrent HKSAR v Chang Nai Ming case (http://www.bileta2007.co.uk/papers/images/stream_6/WeinsteinS_WildC.pdf ) was widely publicized in 2007. Chan, distributing films through the BitTorrent network, violated licensing rights and ended up in jail for this.
In Hong Kong, intellectual property is governed by the Copyright Law (Chapter 528), which covers both the original object and the computer modeling (CAD) file required to 3D print it. It is believed that even if such a file is in the public domain, but is protected by various licenses, then its use to copy an item implies copyright infringement.
Patent law in Hong Kong is governed by the Patent Law (Chapter 514) and stipulates that registration of a patent in any other geographical area does not imply its validity in Hong Kong. Similarly, the law treats trademarks and registered designs.
At the same time, Asian jurisdictions are actively discussing the need for clarifications and additions caused by the widespread use of 3D printing.