3D print abs cooling fan
User Guides
User GuidesAdvanced Guide to printing PC-FR Filament
LEARN ABOUT PC-FR 3D PRINTING, WITH OUR COMPREHENSIVE USER GUIDE.
Read More...
Monday, 6 April 2020 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (8832) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesPC
Tags: PolyCarbonateHow to 3D PrintUser GuideTroubleshootingPC-FR
Advanced guide to printing ASA Filament
LEARN ABOUT ASA 3D PRINTING, WITH OUR COMPREHENSIVE USER GUIDE.
Read More...
Wednesday, 23 October 2019 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (67663) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesASA
Tags: FilamentHow to 3D PrintUser GuideTroubleshootingASA
Advanced Guide to printing PolySmooth Filament
Learn about PolySmooth 3D printing with our comprehensive user guide.
Read More...
Tuesday, 8 October 2019 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (11606) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesPVB
Tags: FilamentHow to 3D PrintUser GuideTroubleshootingPolySmoothPVB
Advanced guide to printing PETG Filament
LEARN ABOUT PETG 3D PRINTING, WITH OUR COMPREHENSIVE USER GUIDE.
Read More...
Monday, 20 May 2019 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (133188) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesPETG
Tags: FilamentHow to 3D PrintUser GuideTroubleshootingPETG
Starters guide to moisture, drying and filament storage
Stop moisture from ruining your 3D printing filament and learn how to dry and protect your filament.
Read More...
Thursday, 25 October 2018 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (26319) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial Guides
Tags: Filamentbeginnersmoisturefilament dryingfilament storage
Starters guide to 3D Printing: Orientation
Orientate your models to minimize support material, maximize strength and achieve the best surface finish.
Read More...
Wednesday, 5 September 2018 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (26621) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User Guides3D Printer Guides
Tags: How to 3D Printbeginnersrotating 3d printsorientationoptimizing 3d print
Advanced Guide to printing Polycarbonate Filament
LEARN ABOUT PC 3D PRINTING, WITH OUR COMPREHENSIVE USER GUIDE.

Read More...
Wednesday, 22 August 2018 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (32392) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesPC
Tags: PolyCarbonatePCHow to 3D PrintUser GuideTroubleshooting
Starters guide to 3D Printing popular filaments
Learn how to print PLA, PETG, ABS, ASA Nylon, PolyCarbonate and more with our simple and intuitive beginners guide!
Read More...
Friday, 15 June 2018 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (12144) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesPLAPETGABSPCASANylon (PA)TPU
Tags: PCHow to 3D PrintPLAUser GuideTroubleshootingABSPETGNylonIntroduction
Advanced Guide to printing ABS Filament
LEARN ABOUT ABS PRINTING WITH OUR COMPREHENSIVE USER GUIDE.
Read More...
Monday, 4 June 2018 / Author: Matt Tyson / Number of views (83976) / Comments(0)/
Categories: User GuidesMaterial GuidesABS
Tags: How to 3D PrintUser GuideTroubleshootingABS
Need Help?
Dont know where to start? Or which filament will suit your application?
We have a broad range of support options including Telephone Support
Contact Us
How Much Cooling (Fan Speed) Does ABS Need? (Solved!)
Last Updated: September 2, 2022
Regardless of the type of filament you use, it’s undeniable that getting the temperature of the plastic correct is one of the pillars of 3D printing, where print temperature, bed temperature, cooling fan speed, and even the ambient temperature of the room play significant roles.
On the other hand, while the print and bed temperature variables are often straightforward to configure correctly by following the manufacturer’s recommendation, getting the cooling fan speed right is usually a bit trickier as it’s a parameter that shows variance based on the scenario.
Today, we will be covering the topic of cooling and fan speed, specifically for printing ABS filament as optimally as possible and avoiding issues related to the plastic cooling down way too slowly or way too quickly, such as warping.
So, how much cooling does ABS need for the 3D printing process?
For the most part, ABS is a type of filament that does not require any cooling or requires minimal cooling, as cooling can cause the plastic to solidify too quickly and prevent the layers from adhering, causing the problem known as layer separation or delamination.
Moving on, we will analyze the optimal cooling speeds for printing with ABS in more detail, discuss the effects of cooling on ABS plastic, and take a quick look at the signs that indicate you may be using too much or too little cooling.
Table of Contents
How Much Cooling (Fan Speed) Does ABS Need?
As there is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to finding the optimal amount of cooling for printing with ABS plastic, a successful configuration mostly comes down to identifying the purpose of your model and applying a suitable fan speed value.
Provided that you are printing ABS in an enclosure that allows you to keep the ambient temperature stable and protect the model from drafts, you can print most models with zero or minimal (10-20%) cooling with success.
On the other hand, as you may predict, there are some exceptions to this rule where more cooling can be required to stabilize the plastic before the upcoming layers start piling on.
The first exceptions to the rule are the nightmare of every 3D printing enthusiast, known as overhangs and bridges, which will require some assistance in the cooling department to hold on to the rest of the model and not start drooping.
The second exceptions are small layers that don’t take too much time to print, which will also require some cooling due to the lack of time to cool down naturally before the upcoming layer.
In the case of these exceptions, we recommend setting the cooling fan speed to a starting point of 20% and incrementally (increments of 5% should do) working your way up until you don’t face any problems.
As always, to find the optimal level of cooling for your purposes, we highly recommend running test prints with distinct fan speed values before entirely committing to the final product.
What Are the Effects of Cooling on Printing with ABS?
Since cooling impacts the temperature of the plastic directly, which essentially determines how the plastic behaves, it’s possible to observe severe changes in factors such as layer adhesion and surface resolution.
The main impact of cooling on printing with ABS will be the strength of adhesion between the model’s layers – since how fast the cooling fan runs effectively decides how quickly a layer cools down and solidifies from its melted state, which is one of the primary deciders for the adhesion strength.
Since ABS is notorious for layer adhesion issues caused by excessive cooling, blasting the cooling fans throughout the print will make it irrefutable that the layers won’t have enough time to bond before solidifying, which causes the issue we know as layer separation.
As layer separation will drastically damage the durability of the model and cause visible defects through the appearance of cracks, it will most likely render your print unusable regardless of the use case.
On the other hand, another impact to consider is the surface resolution of the model, as the chance of the model deforming due to more layers coming on top of the plastic that’s still in its fully melted state is directly related to the absence of cooling.
While ABS can usually naturally cool down to a state where it’s suitable to add the next layer without issues, you are likely to see such deformations on layers on the smaller side that don’t have enough time to cool down naturally until the next layer comes.
What Are the Signs of Too Much Cooling on ABS?
Configuring the speed of the cooling fans in a way where they cause ABS to cool down way too quickly is problematic for the health of the printing process, causing issues such as:
- Weak layer adhesion, which can lead to layer separation (delamination)
- Problems with model durability that make it prone to cracking or breaking
- Warping on the first few layers of the model
- Bridges (if applicable) are likely to be very weak and prone to breakage without too much force
- Overhangs (if applicable) are very likely to be weak and prone to breakage without too much force
What Are the Signs of Too Little Cooling on ABS?
Applying too little cooling while printing with ABS also comes with its own set of problems, which we have listed below:
- The appearance of stringing and blobbing on the model
- Deformation of smaller layers that don’t get enough time to cool down correctly
- Bridges (if applicable) drooping due to not cooling down quickly enough
- Overhangs (if applicable) drooping due to not cooling down quickly enough
Wrapping Up
While it may be slightly challenging due to the amount of effort and time that goes into it, correctly configuring the cooling while printing with ABS filament is vital for the health of the printing process.
To quickly recap, we can say that ABS is one of the few types of filament that does not require cooling for a successful print, and in fact, the presence of cooling can have adverse effects on the model by causing the layers to solidify before they can form strong bonds.
On the other hand, when printing smaller layers and overhangs, it may be a good idea to apply a small amount of cooling, as such layers may not have enough time to naturally cool down to a level where it becomes suitable to add the next layer on top.
Happy printing!
Mike Davies
Mike started his 3D printing journey with the Anet A8 when it first came out back in 2017, and has been obsessed with 3D printers ever since. Nowadays, he primarily uses his Ender 3 to print functional parts that make his life more convenient whenever possible.
Ender 3 ABS 3D Printing Tips
3DPrintStory 3D printing process Tips for 3D Printing ABS on Ender 3
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS, ABS) is an industrial thermoplastic that finds applications in a wide variety of applications. If you are familiar with LEGO bricks, you are already using ABS. It is especially known for its high impact resistance and is one of the most popular materials for 3D printing.
If you are familiar with LEGO bricks, you are already using ABS. It is especially known for its high impact resistance and is one of the most popular materials for 3D printing.
While printing with ABS plastics is notoriously difficult, after a few tries and getting your 3D printer set up correctly, you will definitely end up with some great 3D models. Products made of ABS plastic after treatment with acetone have a smooth and glossy surface, which makes them aesthetically similar to parts obtained by injection molding.
In this article, we'll look at tips to help you get great ABS 3D printing results on the popular, inexpensive Ender 3 3D printer.
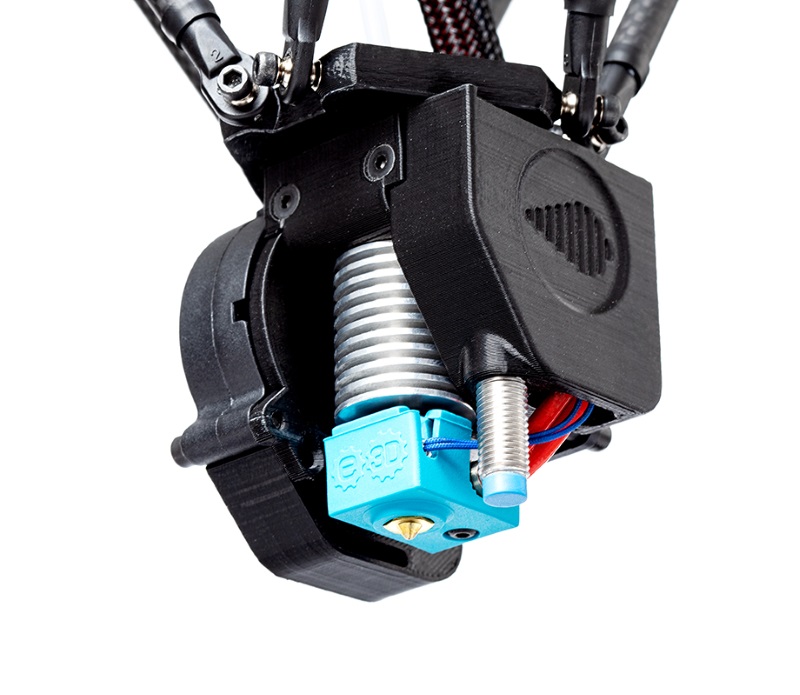
Ender 3 motherboard cooling
Make sure the motherboard fan is on by default. If not, then read on.
At first glance it may seem that motherboard cooling and 3D print quality are completely unrelated things, but when it comes to ABS with Ender 3, this is the first thing to check and fix.
The default installation for some reason turns on the electronics cooling fan only when the partial cooling fan near the hotend is turned on. The fact is that when 3D printing ABS, the cooling fan of the part must be turned off. We will discuss why this is so. And this, in turn, means that the board fan will also be turned OFF. This causes the electronics to heat up, affecting the performance of the 3D printer.
The fact is that when 3D printing ABS, the cooling fan of the part must be turned off. We will discuss why this is so. And this, in turn, means that the board fan will also be turned OFF. This causes the electronics to heat up, affecting the performance of the 3D printer.
The fix is very simple. You just need to connect the part cooling fan wires and the hot end wires as shown in the picture above.
Ender 3 Quality Print Table Surface
Ender 3 comes standard with a heated print bed. This is important for 3D printing with ABS plastic. The heated bed promotes good adhesion of the first layer and maintains an elevated temperature in the 3D printing area, which significantly reduces the likelihood of deformation when printing parts from ABS plastic.
Standard Ender 3 has a surface similar to Buildtak. Thanks to this coating, the first layers of ABS at the end of 3D printing can be easily removed even without the use of an additional layer of glue or hairspray. You can also look into using PEI-coated sheets, which also work well for good surface adhesion.
You can also look into using PEI-coated sheets, which also work well for good surface adhesion.
If you are using Creality Glass or any other glass surface, hairspray or glue will greatly improve the adhesion of the first coat.
As with the Ender 3 Pro, the default table cover is a flexible magnetic surface. This is a great option for 3D printing PLA plastics, but be aware that these coatings lose their magnetic properties at temperatures above 80° C. For greater safety, glass is recommended.
If you've tried everything and still can't get good first coat adhesion, your table may be damaged. But this is not a cause for concern. You can always just switch to Creality Glass or any other glass surface. Also, consider upgrading the table adjustment springs. You can also consider the option of automatically correcting the position of the extruder, but this is already a more complicated way.
Suitable slicing settings for 3D models
If you're already printing with PLA, you're already halfway there. ABS printing is very similar to PLA, only a few settings need to be changed for optimal results.
ABS printing is very similar to PLA, only a few settings need to be changed for optimal results.
- Nozzle temperature: ABS material melts at temperatures between 220 and 240°C. The higher temperature allows the part to cool gradually, reducing the chance of any defects. It is recommended to set the table temperature of the Ender 3 3D Printer between 100 and 110°C.
- Cooling Fan 3D models: ABS tends to deform when cooled quickly. For this reason, it is necessary to turn off the partial cooling fan near the hot end. This allows the ABS to cool gradually, reducing the chance of warping.
- Brim or raft: The use of additional bases of the first layers helps to mitigate the effects caused by thermal shrinkage and will also provide better adhesion of the first layer in the table.
To check the quality of the slicer settings, we recommend choosing one of the test 3D models for printing.
Enclosure for Ender 3
And finally, for high-quality 3D printing with ABS plastics, you should think about an enclosure or, at least, isolated corners, in which there will be no drafts.
Ender 3 is an open frame 3D printer and is not ideal for printing ABS plastics, because during 3D printing, the model is affected by all sorts of external factors, such as wind and overly curious pets.
But most importantly, the housing helps keep the ambient temperature high enough to prevent warping and delamination of the layers by reducing the effects of thermal contraction. It retains the heat from the heated table and also prevents any external influences.
Even a cardboard box can be used as an enclosure (not recommended due to safety and flammability, but even this option will help). The main job of the case is to maintain a uniform, high ambient temperature so that the ABS cools naturally.
We hope that the features of 3D printing ABS plastics on the Ender 3 mentioned above will help you. Good luck in the world of 3D printing and DIY experiments!
Nozzle Best Circular Airflow Model
How to upgrade the blower unit of a 3D printer and maximize print quality?
One of the parameters of the 3D printer that affects the quality of the model is the cooling of the filament. Airflow is responsible for lowering the temperature of the plastic. It is proposed to increase the capabilities of the cooling unit by installing powerful fans and upgrading the air duct.
Airflow is responsible for lowering the temperature of the plastic. It is proposed to increase the capabilities of the cooling unit by installing powerful fans and upgrading the air duct.
Why do I need airflow for a 3D printer?
The principle of FDM printing is to heat the plastic to a softening temperature and extrude it through a nozzle onto the worktable. Further, the polymer solidifies, the layers at the same time are connected, forming a homogeneous three-dimensional object. But the heated plastic has fluidity, and if the previous layer does not have time to cool down to the curing temperature, the model begins to lose its desired shape. The heat of the heated nozzle also has its effect: the already cooled layer softens again when the extruder moves directly above it.
Temperature deformation is especially noticeable on miniature and thin-walled objects. This is due to the following points:
- small parts are constantly exposed to heat coming from the nozzle;
- thin model elements heat up faster.

To prevent the temperature rise of already finished layers and to cool the last of the printed ones faster, 3D printers are equipped with airflow.
What is a cooling unit?
The blower unit consists of the following components:
- fan;
- air duct.
Fan speed and start times are set in the slicer. The duct creates a directional flow, providing cooling to the desired area.
Important! Slicer airflow settings are set by default. But for each type of plastic and the shape of the 3D part, it is recommended to set special parameters, which makes it possible to maximize the quality of the model.
There are no universal values, each user of a printing device selects them empirically.
How can I improve print quality with airflow?
To set the cooling of the model as correctly as possible, consider the following:
- Type of plastic.
 ABS and PETG have a high melting point and require less airflow. Large objects sometimes print with the fan turned off. Parts made of PLA, especially small ones, may require 100% airflow; when printing several figures at the same time, the fan speed can be reduced to 60-70%.
ABS and PETG have a high melting point and require less airflow. Large objects sometimes print with the fan turned off. Parts made of PLA, especially small ones, may require 100% airflow; when printing several figures at the same time, the fan speed can be reduced to 60-70%. - Model size. When printing large-sized objects, the plastic has time to cool down so much that when the next portion of plastic comes from the extruder, the previous layer does not heat up to the critical fluidity temperature. Accordingly, the formation of a part with a small surface area should occur with blowing, the intensity of which will be the higher, the smaller the size of the print area.
- The shape of the feature. Here, the wall thickness, the presence of supports and the density of filling are taken into account. Models with small, thin, openwork elements are printed, be sure to turn on the fan. The same requirement applies to parts with less than 30% infill. The higher the percentage of filling, the less airflow is allowed.

Important! When setting the fan operation mode in the slicer, all the above conditions are taken into account. Experienced users recommend keeping statistics on settings and print results. So by trial and error, over time, the maximum quality of the final result is achieved.
It is not always possible to achieve the desired result by changing the software settings of standard equipment. The maximum effect is achieved by installing high-power fans and other designs and replacing air ducts.
The best airflow models for a 3D printer nozzle
Three airflow options are most often used to modify the plastic cooling system:
- Direct (one-sided) with an improved air duct and a more powerful fan.
- Double-sided.
- Circular.
Either one is suitable for improving the print quality of a 3D model.
Straight
The simplest option is to replace the stock fan with a "snail" or the same, but more powerful, and leave the standard air duct. But another solution is also proposed: the installation of an improved duct. It has a reshaped spout, which allows for a more directed air flow, and a seat for a fan.
But another solution is also proposed: the installation of an improved duct. It has a reshaped spout, which allows for a more directed air flow, and a seat for a fan.
By redirecting the air jet, more precise cooling of the target area is achieved with minimal impact on nozzle temperature. And due to the installation of a productive fan, a wide adjustment of the blowing speed is provided.
Double ended
Dual outlet ducting is another way to improve your airflow system. But separating the air stream into two significantly reduces the power of each. This means that a stronger air blower is needed (the standard one will definitely not cope). Most often, seats for two fans are formed in the duct box - one for each outlet. Double-sided blowing does not have a noticeable disadvantage of one-sided blowing, when, depending on the direction of movement of the extruder, there is a different cooling intensity of the plastic.
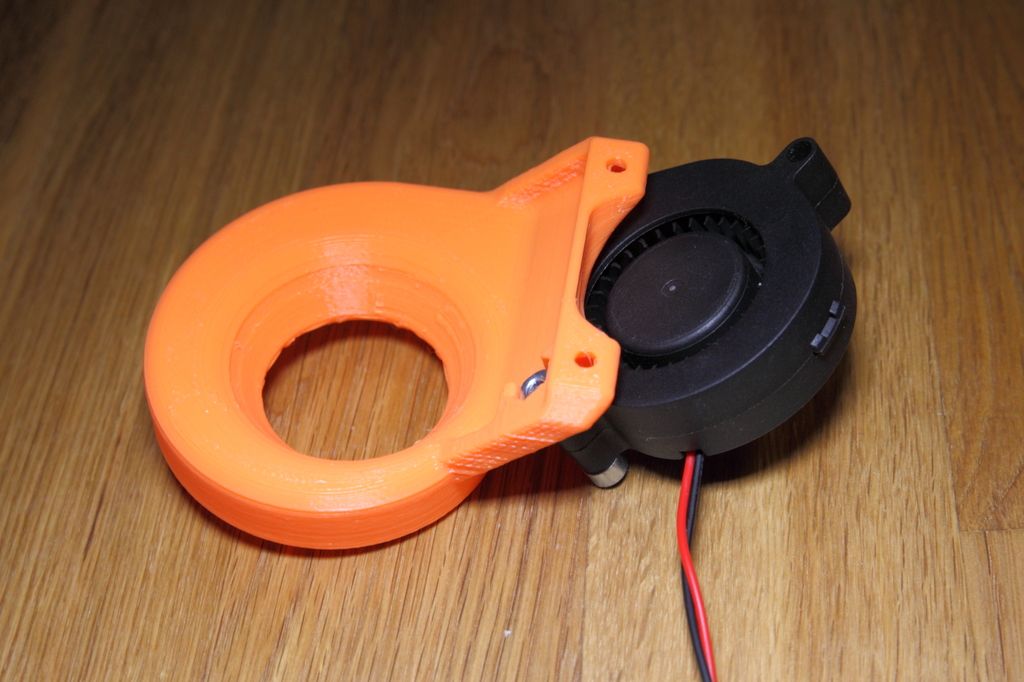
Circular
Circular, or annular, cooling is a uniform blowing of the zone from all sides. The air flow is directed in such a way that it does not affect the nozzle. The standard fan also needs to be replaced here. Instead, they put one or two more powerful ones, for the installation of which a seat is provided on a modified duct box.
The air flow is directed in such a way that it does not affect the nozzle. The standard fan also needs to be replaced here. Instead, they put one or two more powerful ones, for the installation of which a seat is provided on a modified duct box.
Users of 3D printers who have applied this solution note the following drawback: the circular air duct greatly obstructs the view, making it difficult to control print quality.
Important! Any increase in fan power results in increased noise during fan operation. The same can be said about installing two coolers at once. Experienced users recommend paying attention to expensive models of well-known brands, whose developers have made every effort to reduce the noise of their devices.
***
Changing the blower setting has an effective effect on 3D print quality. When software settings are not enough, you should pay attention to the modernization of the cooling unit. Users offer different solutions, tested on their own experience.