3D food printing ppt
Top 9 3d food printing ppt THE BEST
You have a question 3d food printing ppt but have not got the exact and detailed answer you want, when you follow this article of wechoiceblogger.com, you will surely get the answer to the 3d food printing ppt question. most detailed and accurate. The results that we have listed in the top articles about asking 3d food printing ppt will definitely give you the answer you want right after.
1.3D food printing – SlideShare
Contents
- 1 1.3D food printing – SlideShare
- 2 2.3D Food printing – SlideShare
- 3 3.A 3D Food Printing Process for the New Normal Era: A Review – MDPI
- 4 4.3D Food Printing: Create food as you imagine – FoodTech Pathshala
- 5 5.A PRESENTATION ON “3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY”. What is 3D …
- 6 6.3D Food Printing Market – SlideServe
- 7 7.3D Printing and its Application Insights in Food Industry – FutureBridge
- 8 8.3D Food Printing Presentation – [PPTX Powerpoint] – VDOCUMENT
- 9 9.
Make Ppt over introduction and history of 3D printing from the…
- Author: www.slideshare.net
- Post date: 13 yesterday
- Rating: 5(1460 reviews)
- Highest rating: 5
- Low rated: 2
- Summary:
See Details
2.3D Food printing – SlideShare
- Author: www.slideshare.net
- Post date: 19 yesterday
- Rating: 1(353 reviews)
- Highest rating: 4
- Low rated: 1
- Summary:
See Details
3.A 3D Food Printing Process for the New Normal Era: A Review – MDPI
- Author: www.mdpi.com
- Post date: 14 yesterday
- Rating: 2(1296 reviews)
- Highest rating: 4
- Low rated: 1
- Summary: Three-dimensional food printing technology can be applied to various food ranges based on the advantages of designing existing food to suit one’s taste and …
4.
 3D Food Printing: Create food as you imagine – FoodTech Pathshala
3D Food Printing: Create food as you imagine – FoodTech Pathshala- Author: foodtechpathshala.com
- Post date: 1 yesterday
- Rating: 4(1662 reviews)
- Highest rating: 4
- Low rated: 1
- Summary: 3D food printing is a cutting edge technology which provides highly customized and personalized food with plenty of attractive 3-dimensional shapes.
See Details
5.A PRESENTATION ON “3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY”. What is 3D …
- Author: slideplayer.com
- Post date: 5 yesterday
- Rating: 4(1642 reviews)
- Highest rating: 4
- Low rated: 2
- Summary: 3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid. … Download ppt “A PRESENTATION ON “3D PRINTING TECHNOLOGY”.
See Details
6.
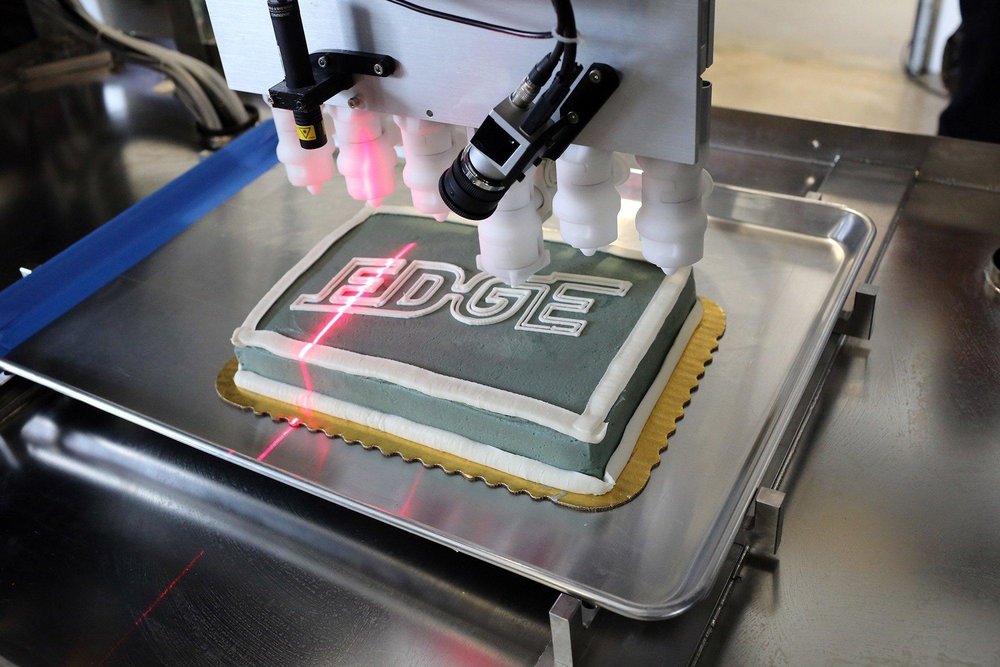 3D Food Printing Market – SlideServe
3D Food Printing Market – SlideServe- Author: www.slideserve.com
- Post date: 22 yesterday
- Rating: 2(1352 reviews)
- Highest rating: 4
- Low rated: 1
- Summary:
See Details
7.3D Printing and its Application Insights in Food Industry – FutureBridge
- Author: www.futurebridge.com
- Post date: 10 yesterday
- Rating: 5(1033 reviews)
- Highest rating: 5
- Low rated: 2
- Summary:
See Details
8.3D Food Printing Presentation – [PPTX Powerpoint] – VDOCUMENT
- Author: vdocument.in
- Post date: 12 yesterday
- Rating: 5(1520 reviews)
- Highest rating: 5
- Low rated: 1
- Summary: PowerPoint Presentation 3D FOOD PRINTING Knowledge and Attitudes of Millennials in the GTA Researchers: Ankita Singh, Anjali Sharma, Jason Szymanski, …
See Details
9.
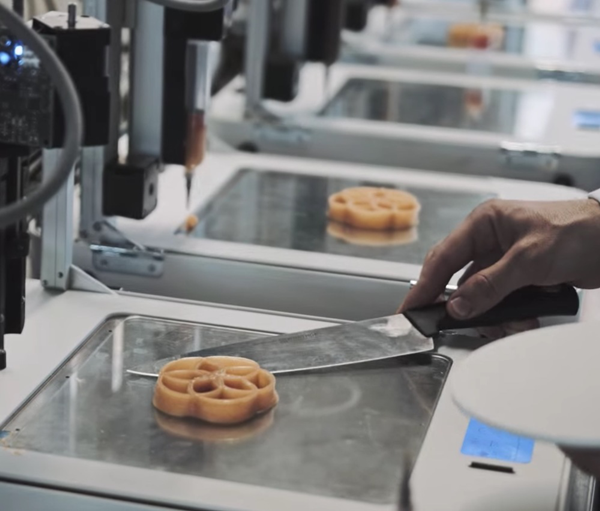 Make Ppt over introduction and history of 3D printing from the…
Make Ppt over introduction and history of 3D printing from the…- Author: www.coursehero.com
- Post date: 8 yesterday
- Rating: 1(1575 reviews)
- Highest rating: 4
- Low rated: 1
- Summary: Answer to Make Ppt over introduction and history of 3D printing from the… … aviation, locomotive, food, fashion, and automotive industry.
The answers to the 3d food printing ppt question above of wechoiceblogger.com have helped you get the correct information, right? Please share this article with your friends and family to let them know more new knowledge. Wishing you a day full of joy and luck!
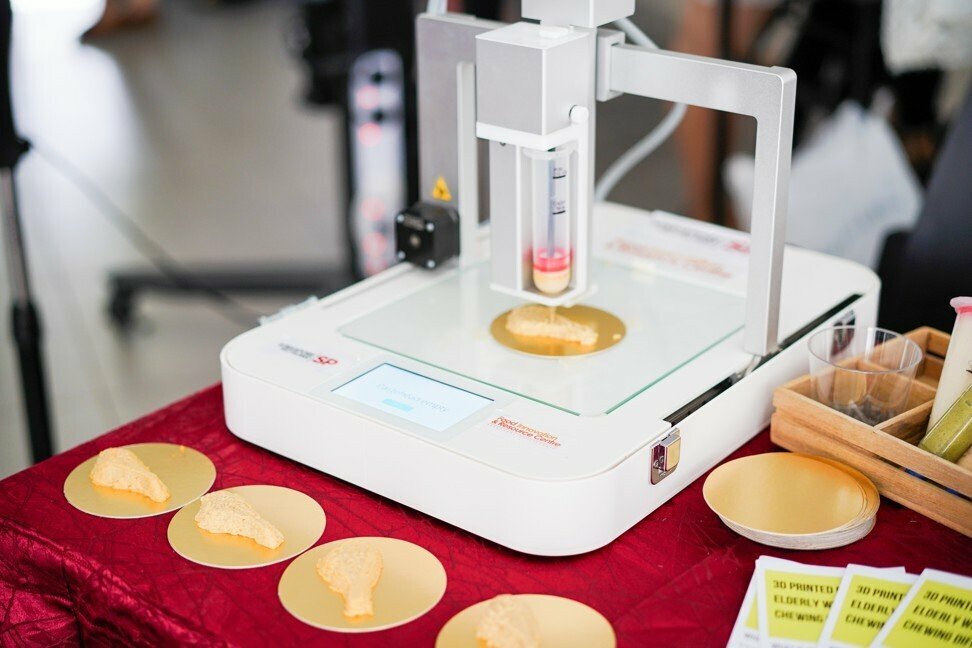
Top Food -3D Food Printing: Create food as you imagine
3D Printing, which is a kind of Additive Manufacturing Technology, has now
entered in the field of food processing and has also drawn attention of many researchers.
In 21st century where everything has been computerized, why should making of food continue with traditional cooking methods?
Though traditional methods have their own advantages but still they are tedious and time consuming.
That is where 3D food printing comes in the picture to offer us highly customized and personalized food with plenty of attractive 3-dimensional shapes.
One of the major advantages of additive manufacturing over subtractive manufacturing is that it brings down the reduction in material wastage to almost zero level.
How does it work??
A 3D printer can be regarded as a robot that is instructed by a digital file of 3D graphic model.
This graphic model of an object is generally created using Computer Aided Design (CAD) software such as Auto Cad, Solid Edge, Solid Work etc.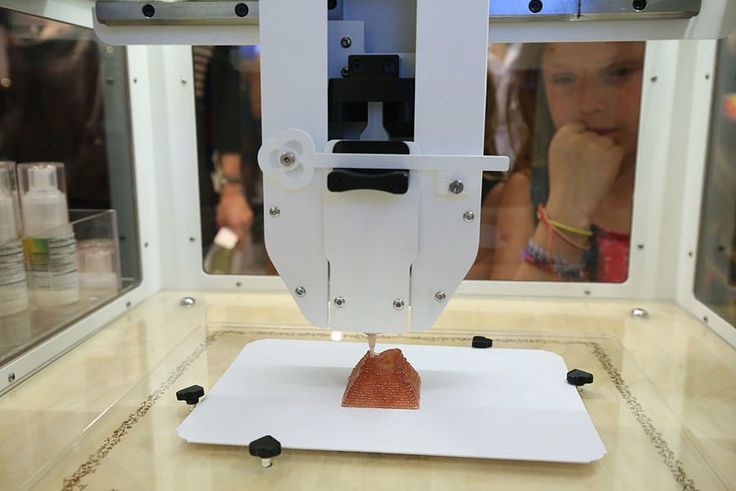
The CAD drawing is converted to the standard tessellation language (STL) format. This STL format file is transferred to computer system that operates the 3D printer.
The same computer also has a pre-installed slicing software which is sort of specific coding. Its function is to break the 3D model into 2- dimensional layers.
The printer is instructed by the slicing software to construct these 2D layers one on the top of other until the 3D object is created.
Another important aspect of this process is feeding the right kind of material in the right form and at appropriate temperature.
It becomes very easy when you want to make something from plastic by a 3D printer.
The most common plastic used in 3D printing is ABS filaments (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) in wired form. But it becomes the most difficult when material is food stuff.
Food Formulation
Food formulation is the most complex and difficult aspect of producing edible 3D printed objects.
This is where a food technologist or a food engineer plays a vital role in making a successful 3D food product.
The formulation of food ink should be in such a way that after printing, it must gain physical stability and at the same time, it should be nutritionally rich and tasty.
One who formulates the food for 3D printing should have a precise and thorough knowledge of rheological, nutritional, and biological properties of particular food material.
Customization or personalization is one of the characterized advantages of 3D food printing. It allows us to formulate the nutritional value of the product according to the deficiency of micronutrients in a particular age group.
Each 3D printer is designed for a specific type of material. So when we talk about food material 3D printing, it can be classified into three categories:
- Extrusion-based Printing
- Inkjet Printing
- Binder Jetting
In extrusion-based printing, the material (solid or paste with low viscosity) is loaded into a plastic or metallic syringe.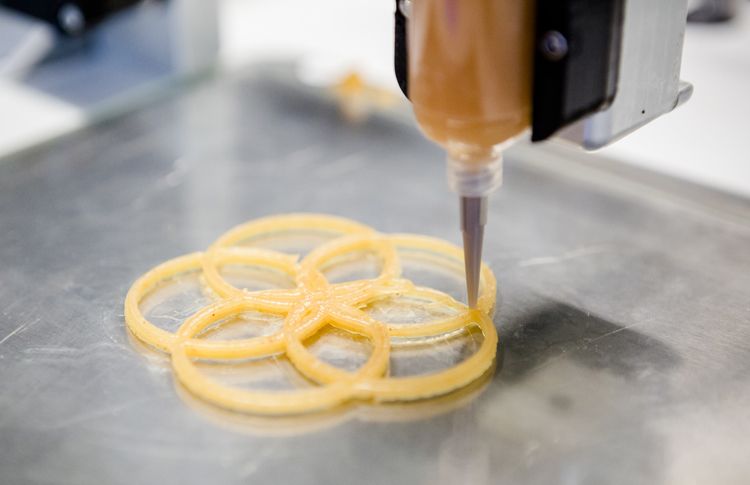 And then, it is pushed out through a micro nozzle at constant pressure.
And then, it is pushed out through a micro nozzle at constant pressure.
Application of constant pressure can be done in one of these three ways: pneumatic, piston-driven or screw-driven.
First two techniques can be used for low viscous material whereas the last one is desirable for higher viscosity material.
The 3D printer deposits the melted filament by layer, each layer on top of the others, to build the object in 3D.
When one layer is complete, the tray holding the object lowers very slightly and the extrusion process resumes, depositing a new layer of melted filament on top of the previous one.
Deposited layers are fused together as the melted plastic quickly solidifies to form a solid three-dimensional object.
This type of printing method is used for dispensing macromolecules such as hydrogel or polymer. Some of the edible hydrogel are polysaccharides, protein and lipids.
Inkjet Printing
An inkjet printer dispenses low viscosity (generally liquid) material in the form of stream of droplets falling through micro nozzle connected to thermal or piezoelectric head.
In the case of the thermal head, the print head is electrically heated to establish pulses of pressure. These pulses of pressure push the low viscous material in the form of droplets from the nozzle.
In case of piezoelectric head, the material is made to fall continuously in the droplet form by vibrating it at certain frequency.
This method is not suitable for creating complex 3D shapes because it uses only liquid materials.
Binder Jetting
In binder 3D printing, the inkjet nozzle applies a fine dry powder and a liquid glue, or binder, that come together to form each printed layer. Binder printers make two passes to form each layer.
Binder printers make two passes to form each layer.
The first pass deposits a thin coating of the powder, and the second pass uses the nozzles to apply the binder.
This method allows us to use combination of liquid and powdered materials.
Powder materials used are Sugars and starch mixtures.
And, the liquid binding agents could be corn syrup, soy sauce etc.
Reference
A Review of 3D Food Printing Technology
3D Printing of Food in food industry
3D Printed Chocolate by Cadbury Australia
In a world premiere, CADBURY DAIRY MILK launched the very first CADBURY DAIRY MILK milk chocolate 3D Printer, in celebration of World Chocolate Day on July 7, 2019.
LINK
How Hershey’s is Using 3-D Printers to Make Chocolate Kisses
3D printing technologies - online presentation
Similar presentations:
3D Printing Technologies and Trends
Additive technologies
Master class on 3D printing.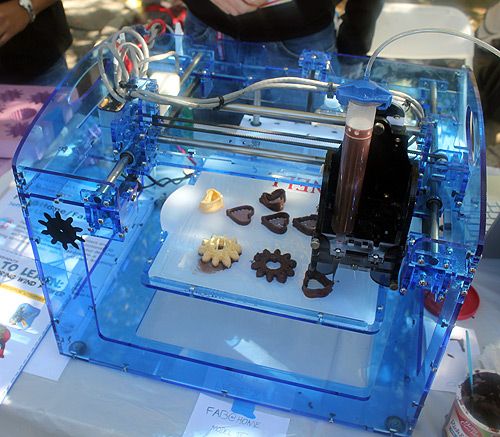 Picaso 3D
Picaso 3D
3D printing technologies at the enterprise "3D Techno"
Additive manufacturing technologies
3D Printing Technologies
Additive technologies: 3D printing
Additive technology
3D printing
3D printers
3D printing technologies
The history of 3D printers
The technology
for making
three-dimensional objects with
digital data was first
developed by Charles
Hull in 1984. In 19086 he received his patent 9
invention and named this technology
Stereolithography.
T I 3D PRINTING
E
X FDM - fused deposition
H SLA - stereolithography
O SLM - selective laser
L
PAYSED
O
DLP
-
Digital
LED
g
and Printing
Slender Fronts
FDM
technology involves the creation of
three -dimensional objects for
consistent layers
,
repeating contours
.
Stereolithography
SLA - technology
additive production of models,
prototypes and finished products
from liquid photopolymer resins
.
Resin curing 9
is produced by
irradiation with ultraviolet
Selective laser melting
SLM is an additive manufacturing method
that uses
high power lasers
(typically ytterbium
fiber lasers) to create
three-dimensional physical objects
by melting metal powders.
Digital LED
printing
DLP - technology
involves
the use of
liquid plastic,
which cures
exposed to
UV light.
C for 3D
• Acryl
Printers
s
Chocolate
Other materials
K
I
H
E
M
A
T
I
K
A
Cartesian 3D printers
CoreXY and H-Bot
Delta printers
P
P
and
m
and
H
E
H
and
E
3D printers
Quick prototyping and mechanical engineering
Medicine
Architecture
Design and clothing production
Medicine
from
fast-growing
directions
3D printing
–
medicine. In 2011 there was a
In 2011 there was a
triumph
in
regenerative medicine: a printer filled with
biogel with stem cells,
"printed"
in
3
hours
a human kidney. Although
transplantation
organs
is still
far away,
scientists
are already
now
developing technologies for transplanting
3D-printed blood vessels,
Construction
Construction using 3D printing
is a serious competitor 29025 approaches. The United Arab Emirates
, Thailand, China and Russia
are already using modern
mobile printers for printing houses
directly at their location.
The printing method is the same as in other areas of application
- layer-by-layer extrusion.
Cement,
construction waste
,
former
in use
building materials,
fiberglass, etc. are used as materials.
Byt
3D printers gradually enter the manufacturing industry
food products, clothes, shoes, unique souvenirs, toys, furniture - a total of
things that people use in everyday life.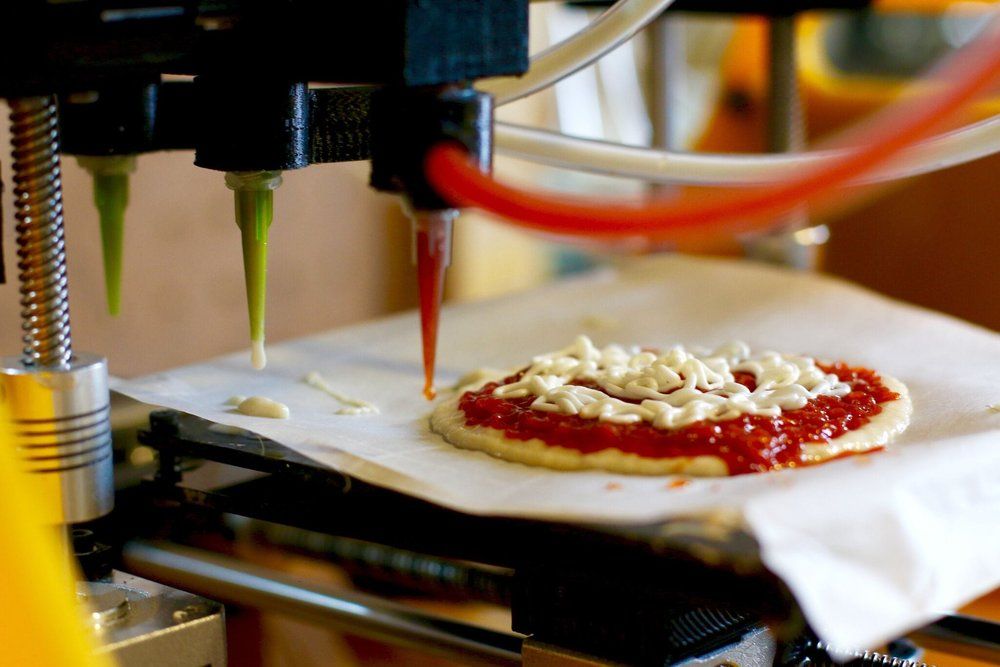
To print a wide range of household products, a person only needs a
printer and various materials for it.
3D food printer fills with ingredient cartridges and prepares the most delicious multi-ingredient dishes
according to recipes stored on a memory card.
The future: 3D printing perspectives
3D printing technology will soon enable
create
elements
for
construction of
research bases on the Moon and Mars. NASA has already
successfully tested titanium nozzles for rocket engines printed on the
3D printer.
Prospects for the exploration of the nearest planets dictate
a reduction in the cost of transporting cargo and
materials.
So,
experts of NASA
called the use of 3D printing in space the only
option
for possible planetary exploration.
Print landing pads, solid
buildings and roads on the Moon can be made from local
soil, and on Mars from basalt and regolith. More
More
Moreover, in the polar regions of Mars, water and low temperatures
will help
build
habitable
"Martian igloos" - multilayer ice
shelters from radiation and winds
P
O
C
T
R
OY 2 A
3D PRINTER
• WHICH 3D PRINTER DO I NEED?
• KINEMATICS
• SELECTION OF PARTS
• MANUFACTURE OF NECESSARY PARTS. nine0025 • PREPARATION OF ALL COMPONENTS
• ASSEMBLY OF THE BODY AND ALL MECHANICAL ASSEMBLY.
• WHICH FIRMWARE TO CHOOSE?
• CONNECTING ALL ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS
• Repeater Firmware
• DOWNLOAD AND DEBUG FIRMWARE
• REPITERHOST
• FIRST PRINT
Conclusion
Using 3D printing in everyday life
will reduce the cost of manufacturing
products;
cut
production timeline
;
develop a product of any size and shape; nine0025 exactly, without marriage, reproduce the item. Can
confidently
say
that
3D printing application provides a bright and comfortable future.
English Russian Rules
Professions of the future in agriculture. Food 3D printing engineer
Similar presentations:
Transport Process Technology
Organization of work and calculation of technical and economic indicators of the part machining section
Lifting machines. (Lecture 4.1.2)
Safe work at height
Well logging
ICE cooling system
Operation of oil and gas wells. Course of lectures in slides
Safety requirements when performing work at height
Project on technology "Rolling pin" (grade 6)
Switchgear designs. (Lecture 15)
MBOU "Zagorskaya
Secondary School
Week of Science
Professions of the future in agriculture
. 3D printing engineer
food
8b class
Modern
production technologies
physical
-
will free
labor
in
genetics,
millions
agricultural
automated
people 90.
from
heavy
Cultivation of
agricultural products will be transferred from fields to mini-farms on the roofs of
high-rise buildings. Mastering the cultivation of organisms
out of one
cells in test tubes - will solve the problem of slaughtering livestock. With the introduction of
modern technologies in agriculture, new
professions will appear: agro-cybernetic, GMO agronomist, 3D printing engineer
food products
,
operator
automated agricultural machinery
, agricultural ecologist.
3D Printing Engineer
food
Object synthesis technologies continue to impress, especially in the field of
food production. This branch of 3D printing is considered the most unusual
and amazing. Oddly enough, today even meat can be printed using 3D printers
. The heart of the machine is a syringe, layer by layer it
lays down a viscous liquid, forming an object of a given shape. They are loaded with
paste-like or gel-like food mixtures and due to extrusion (method
of squeezing pasty materials through a hole) materials are obtained
ready meals or products.