3D printing growth projections
Three Areas Holding Back The $10.6B 3D Printing Industry
Market research firm SmarTech Analysis recently released its data for the additive manufacturing (AM) industry. It determined that, in 2021, the 3D printing sector reached $10.6 billion in revenue, excluding the revenues associated with hardware maintenance contracts and post-processing equipment. The firm further projects that AM is expected to grow to over $50 billion by 2030.
The 3D printing industry is projected to reach over $50 billion by 2030, according to one market ... [+] research firm.
Image courtesy of SmarTech Analysis.This growth is closely pinned to the trend that large manufacturers will increasingly use the technology for mass production. However, in order for AM to reach wide-scale adoption, it will need to advance significantly in three crucial and interrelated areas: throughput, factory integration, and quality control. Fortunately for the industry, these are all also issues that are being actively addressed.
3D Printing Throughput
Due to its roots as a prototyping technology, 3D printing was never designed with mass production in mind. Instead, its ability to create complex shapes has been limited to one-off parts or small batch manufacturing. For that reason, firms across the 3D printing industry have been working to develop systems that can make many parts as rapidly as possible, a concept known as throughput.
Among the leaders in this regard is HP, which spent years researching the technology before finally unveiling technologies capable of rapid production both in plastics and metals. The 2D printing giant has ported its expertise in inkjet printheads over to 3D printing with a technology called Multi Jet Fusion (MJF). MJF is already being used to produce large batches of polymer parts for everything from eyewear to grocery bots.
Legor Group in Italy is using HP Metal Jet to 3D print functional stainless steel accessories for ... [+] the jewelry and fashion markets.
MORE FROMFORBES ADVISOR
This is just the beginning for the company, which is now rolling out its Metal Jet technology. A form of what is called “metal binder jetting,” Metal Jet deposits a liquid binder onto metal powder, creating a component that must then be sintered in a furnace. Customers as large as Volkswagen are investing in the technology with a plan to mass produce up to 100,000 metal components annually for consumer vehicles.
However, HP isn’t the only company in this quickly evolving space. A widely publicized startup called Desktop Metal is working to speed up metal binder jetting. GE, too, is working on its own version of the technology. Altogether, these companies are ushering in an era in which low-cost metal powders can be used to 3D print large numbers of parts in a single job, potentially changing the cost structure for metal 3D printing altogether.
This means that they will be taking on the established leaders in metal 3D printing, which typically rely on zapping high powered laser beams at expensive metal powders. These companies are working on increasing throughput, as well, by adding up to 12 lasers to their machines.
These companies are working on increasing throughput, as well, by adding up to 12 lasers to their machines.
3D Printing Factories
While a fleet of 3D printers may be capable of manufacturing at volume, that doesn’t mean that they’ll necessarily fit into an existing factory operation. In large part, this is due to the fact that they lack mass production-level software.
Now, a handful of startups have emerged to take on the challenge of developing AM-specific software for manufacturing execution systems (MES). These tools make it possible to both manage a fleet of 3D printers and connect them to a company’s existing production software. They typically aid in the entire order-to-fabrication workflow. This means order quoting and tracking, print file preparation, print job monitoring and data collection, printer fleet queuing, quality control, and shipping.
MES software necessarily connects to a business’s existing software tools. This includes product lifecycle management (PLM), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and general IT software. While PLM might include a company’s preferred 3D modeling software, ERP will be made up of everything from payroll programs to tools for tracking overall finances.
While PLM might include a company’s preferred 3D modeling software, ERP will be made up of everything from payroll programs to tools for tracking overall finances.
MES platforms are now working to take all of the software that a manufacturer might already be working with and inserting 3D printing into the mix. However, they’re not just limiting themselves to AM. Many MES developers are looking to connect with other production equipment, such as CNC machines. Then, with the help of machine learning, the entire workflow can be improved automatically as data from each order and each machine job feeds back into the work cycle. Artificial intelligence is significantly adding to the capabilities of MES software.
3D Printing Quality Control
Perhaps the biggest obstacle to widespread AM adoption is quality control. This is because, with additive, each part is distinct. Every point on the build platform may be slightly different and even the slightest variation in a printing parameter may change the microstructure of the printed object.
In turn, an object printed at one angle will not be the same as one printed at another. And, because parts are built up layer by layer, it is difficult to validate the internal geometries of an item once printing is complete. As a result, the only true way to assure the quality of a printed object is with a CT scan, typically a cost-prohibitive method for inspecting multitudes of parts.
Fortunately, not only are newer CT scanning systems with lower price tags coming onto the market, but there are other tools that are being used to ensure the quality of printed parts. Among them is computer simulation. Companies like ANSYS have developed software that can anticipate any defects that occur during the printing process and compensate for them. Hexagon is taking this one step further by predicting issues at the microscopic level.
Meanwhile, firms like Sigma Labs and Additive Assurance have created hardware to monitor the build chambers of metal 3D printers to detect errors. Increasingly, these tools will enable active feedback so that the machines can quickly correct issues during the print process. When connected with MES software and 3D printing simulation, the equipment can learn from past errors and address them before they even happen in the future.
Increasingly, these tools will enable active feedback so that the machines can quickly correct issues during the print process. When connected with MES software and 3D printing simulation, the equipment can learn from past errors and address them before they even happen in the future.
Altogether, these areas are advancing at incredible rates, in large part because manufacturers see the value in being able to produce objects from digital files on demand. As companies as large as Ford, GE, and Siemens look to 3D printing to produce quality end parts, they are driving the entire additive market to bend to their needs. To reach a whopping $50 billion by the end of the decade, the 3D printing industry has to be capable of making millions of parts for those customers.
3D Printing Market Size, Growth
The global 3D printing market size was valued at USD 15.10 billion in 2021. The market is projected to grow from USD 18.33 billion in 2022 to USD 83.90 billion by 2029, exhibiting a CAGR of 24. 3% during the forecast period. Based on our analysis, the global market exhibited an average growth of 20.2% in 2020 as compared to 2019.
3% during the forecast period. Based on our analysis, the global market exhibited an average growth of 20.2% in 2020 as compared to 2019.
Rapidly increasing digitization, increasing adoption of advanced technologies such as Industry 4.0, smart factories, robotics, machine learning, and others fuel the demand for online 3D printing for simulation purposes. These technologies increase the chances of broader adoption and greater utilization of this technology across industries, including aerospace, automotive, healthcare, among others. For instance,
- Aerospace companies are exploring this 3D printing for manufacturing various hardware parts of their products. For instance, Boeing leverages industrial 3D printing to manufacture the interior parts of its plane, whereas, NASA uses it to build rocket engines and parts of the satellite.
- Automotive industry is expected to show a huge adoption of this technology. Rapid tooling incorporated with additive manufacturing has become the priority of many automotive manufacturers.
 Customization of the automotive interior is another major application of this technology in the automotive industry.
Customization of the automotive interior is another major application of this technology in the automotive industry.
COVID-19 IMPACT
Supply Chain Disruption and Halts on Production Units Negatively Impact Printing Industry Amid Lockdown
Post outbreak of the COVID-19 crisis, industrial hubs, manufacturing sectors witnessed an immediate supply chain disruption and halts on production. As a result of the fast-spreading pandemic, the overall industrial production across the globe experienced a sharp decline. It was demobilized, reflecting supply chain disruption, and reviving financial market conditions. The crisis forced market players across the globe to reduce their operational expenditure. Fewer operation expenditures restricted the investments of market players in this technology in 2020, impacting the 3D printing market growth.
The temporary closures of the factories in major economies such as China, Southeast Asia, the U. K., Germany, and others have impacted the production plants of the 3D technology industry and operations of suppliers resulting in short-term supply shortages. Manufacturing capacity was observed to be restored to normalized levels by the end of July 2020. The short-term disruptions in supply shortages have resulted in logistics challenges, including delays in delivering services to end-use industries. Such a situation affected the company’s ability to meet the technology demand of the end customers. For instance,
K., Germany, and others have impacted the production plants of the 3D technology industry and operations of suppliers resulting in short-term supply shortages. Manufacturing capacity was observed to be restored to normalized levels by the end of July 2020. The short-term disruptions in supply shortages have resulted in logistics challenges, including delays in delivering services to end-use industries. Such a situation affected the company’s ability to meet the technology demand of the end customers. For instance,
- Stratasys, one of the well-known companies in the market, experienced dip in sales in the early months of COVID-19 pandemic. However, later, the company started rebounding as it picked up new manufacturing contracts.
However, the study conducted by the ‘Society of Manufacturing Engineers’ states that 25% of the manufacturers in the United States plan to change their supply chains in response to the pandemic. The study also found that they prioritize investing in this technology post-COVID-19 out of other technologies such as robotics, 5G, digital security, and artificial intelligence. This shows that the increasing investments of manufacturers in 3D technologies are likely to uplift the growth of the market in the forthcoming years.
This shows that the increasing investments of manufacturers in 3D technologies are likely to uplift the growth of the market in the forthcoming years.
LATEST TREND
Request a Free sample to learn more about this report.
Advancement in 3D Hardware and Software is Generating New Revenue Streams for Market Players
Techno-savvy start-ups and established market players are upgrading and developing new technologies. The advancements in hardware have led to faster and reliable 3D printers for production applications. Polymer printers are one of the most used 3D printers.
- According to a 2019 report by Ernst & Young Global Limited, 72% of the enterprises leveraged polymer additive manufacturing systems, whereas the remaining 49% used metal additive manufacturing systems. The statistics show that developments in polymer additive manufacturing would create new market opportunities for market players.
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) and powder bed fusion technologies such as Multi Jet Fusion offered by HP Inc. are expected to be the most preferred industrial 3D technologies by the manufacturers due to their ability of volume manufacturing and high productivity. Similarly, resin-based technologies such as digital light processing (DLP) and Stereolithography (SLA) are more likely to have a growing demand from the dental and consumer goods industry.
are expected to be the most preferred industrial 3D technologies by the manufacturers due to their ability of volume manufacturing and high productivity. Similarly, resin-based technologies such as digital light processing (DLP) and Stereolithography (SLA) are more likely to have a growing demand from the dental and consumer goods industry.
Similarly, software developments are gaining pace in the 3D industry driven by the demand to streamline operations. The technology has been extensively used in the manufacturing process, which has surged the need for software that can help manufacturers to increase production volumes and enhance their additive manufacturing processes efficiently.
DRIVING FACTORS
Substantial Investments of Governments and Tech Giants to Foster Market Growth
Many countries across the globe are experiencing massive digital disruptions in advanced manufacturing technologies. The United States is a potential user of 3D technology. In 2018, the United States Department of Defense included this technology as an important capability in their budget. Even tech software giants such as Autodesk, Microsoft, and HP have launched products aimed at additive and 3D printing manufacturing.
In 2018, the United States Department of Defense included this technology as an important capability in their budget. Even tech software giants such as Autodesk, Microsoft, and HP have launched products aimed at additive and 3D printing manufacturing.
Similarly, China is making significant efforts to maintain the competitive index of the manufacturing industry in the global market. Chinese manufacturers foresee this technology as both a risk and opportunity for the Chinese manufacturing economy, and hence they tend to invest in the research and development of this technology.
Whereas India is looking forward to this technology as an opportunity to increase its share in global manufacturing competitiveness. The market in India is supported by active government initiatives such as the ‘Make in India’ Initiative.
Korea has established an independent roadmap for research and development of this technology and provides national support to execute it. The government of Korea is introducing tax incentives and accelerating industry regulatory agreements to encourage the adoption of this technology.
The U.K. government has developed an independent 3D technology strategy; however, it is witnessing some uncertainties in the U.K. manufacturing sector due to Brexit. Germany is expected to define new strategies for the technology as Germany has a well-established Industry 4.0 infrastructure.
RESTRAINING FACTORS
High Initial Investments to Restrict Market Growth
High initial investments are observed to be the most significant restraint for adoption of this technology. This investment encompasses investment in hardware, software, materials, certification, additive & manufacturing education, and training for the employees. The capital costs and resources required to set up a 3 dimensional system are quite expensive than traditional printing methods.
However, with the introduction of the industrial Desktop 3D printer, the manufacturers are helping the end-customers cut the high initial costs. Desktop printers are easy to use and handle and also are less expensive than the 3 dimensional system.
SEGMENTATION
By Component Analysis
Wider Adoption of the Software to Make Designs of Objects and Parts to Fuel its Growth Rate
On the basis of component, the market is divided into hardware, software, and services.
Adoption of hardware for manufacturing 3D printed material is maximum and is likely to maintain its dominance during the forecast period. The demand for hardware is increasing as major key players are enhancing their product portfolio and launching new technologies to serve high demand from several industry verticals. Companies are investing in research & development activities, which have a positive impact on the market growth.
The software is expected to grow at a high CAGR during the forecast period. The 3D printing software is widely used in different industry verticals to design the objects and parts to be printed. As manufacturing companies are shifting away from traditional manufacturing methods, the adoption of 3D software has grown to print iterations of different manufacturing parts.
By Technology Analysis
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Technology to be at Forefront
Based on technology, the market has been divided into FDM, SLS, SLA, DMLS/SLM, Polyjet, Multi Jet Fusion, DLP, Binder Jetting, EBM, CLIP/CDLP, SDL, and LOM.
Among these, fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) technology captured the maximum share in 2021. The growth of FDM is mainly due to the ease of operation and advantages associated with the technology. FDM technology is highly used in making durable, strong, and dimensionally stable parts.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS/SLM) technology is expected to grow at a high CAGR during the forecast period. The technology promotes the production of high-quality metal components, which makes them suitable for the manufacturing industry since they enable the creation of complex geometries of metals of extremely small sizes.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is expected to show significant growth in coming years. SLS finds a wide variety of vertical applications, including aerospace, defense, automotive, and others. Polyjet, Multi Jet Fusion, DLP, Binder Jetting, EBM, CLIP/CDLP, SDL, LOM technologies are expected to witness a significant rise in adoption in the upcoming years.
SLS finds a wide variety of vertical applications, including aerospace, defense, automotive, and others. Polyjet, Multi Jet Fusion, DLP, Binder Jetting, EBM, CLIP/CDLP, SDL, LOM technologies are expected to witness a significant rise in adoption in the upcoming years.
By Application Analysis
To know how our report can help streamline your business, Speak to Analyst
Prototyping to Capture Maximum Market Share Due to its Widespread Acceptance Across Various Vertical Industries
This technology has application in prototyping, production, proof of concept, and others.
Due to widespread acceptance of the prototyping process across various vertical industries, the prototyping represented the largest market share in 2021. Prototyping helps businesses to achieve greater precision and produce consistent end products. This technology helps to manufacture 3 dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) models and prototypes.
The production is expected to witness strong growth during the forecast period. While manufacturers are shifting their traditional manufacturing units toward advanced manufacturing processes, the adoption of this technology to produce complex and low-volume parts is expected to grow during the forecast period.
By End User Analysis
Automotive Industry to Lead Market Owing to its Maximum Use in Producing Prototype Equipment
Automotive, aerospace and defense, healthcare, architecture and construction, consumer products, education, and others are some of the end-users of 3D printing.
The adoption of this technology in the automotive industry is expected to hold a maximum share in 2021. For decades, the automotive industry has been using this technology to produce prototype equipment and small custom products in a short time span. The technology is being widely used for the construction of lightweight components for automobiles and OEMs.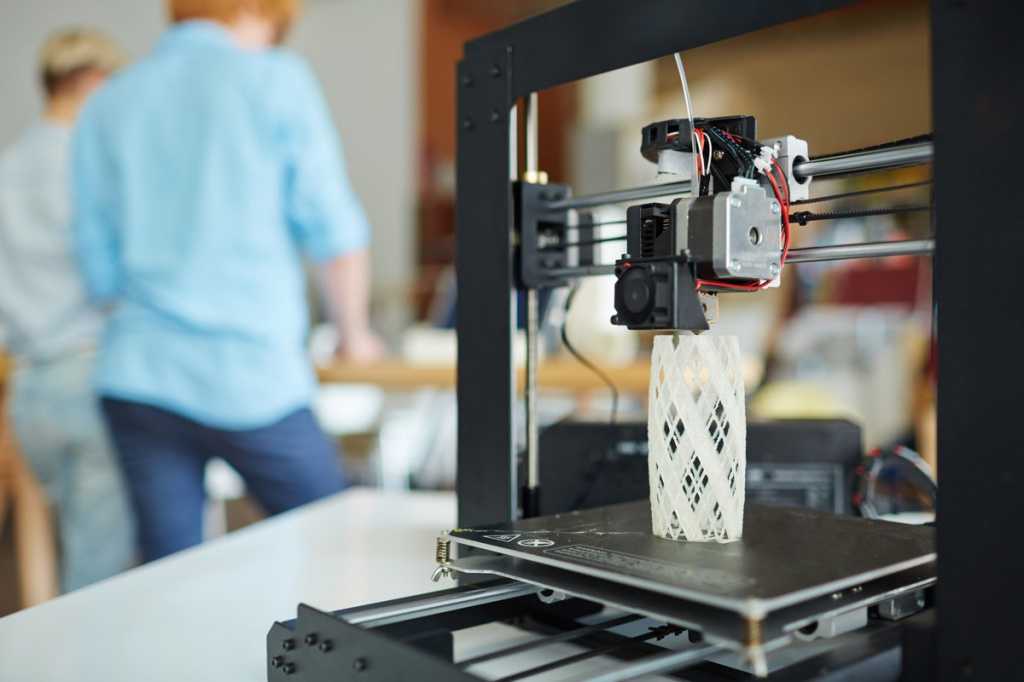
Additive manufacturing has tremendous potential for the aerospace industry, where light, solid, and geometrically complex parts are required — and normally manufactured in limited quantities. Aerospace and defense companies are heavily using this technology to produce lightweight components.
Additive processing in the healthcare industry helps create artificial tissues and muscles that mimic normal human tissues that can be used in substitution operations. These skills are anticipated to lead to vertical acceptance of 3DP in healthcare and the sector's development.
On the other hand, architecture and construction, consumer products, education verticals are anticipated to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
REGIONAL INSIGHTS
North America 3D Printing Market Size, 2021 (USD Billion)
To get more information on the regional analysis of this market, Request a Free sample
Geographically, the market is divided into five major regions such as North America, South America, Asia Pacific, Europe, and the Middle East & Africa. They are further categorized into countries.
They are further categorized into countries.
Globally, North America accounted for the maximum share in the global market mainly due to rising expenditure on advanced manufacturing technologies by developed countries such as Canada and the U.S. Also, various government agencies, such as the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), have identified major R&D investments that can greatly contribute to space applications and create new technologies that drive business expansion.
Europe holds the second-highest market share in the global market. The demand for this technology is high among small and medium-sized industries that require high-speed, reliable, and inexpensive prototypes for manufacturing purposes. The regional market is expected to showcase strong growth in the adoption of this technology in the manufacturing and semiconductors industry.
Asia Pacific is anticipated to grow at the highest CAGR during the forecast period. An increasing interest in the development of a sustainable 3D printing environment has been backed by APAC manufacturers and the implementation of several policies and legislative proposals by governments in the region. Given the massive government funding for the industry, China is possibly the main force behind adopting this technology in Asia.
Given the massive government funding for the industry, China is possibly the main force behind adopting this technology in Asia.
To know how our report can help streamline your business, Speak to Analyst
The Middle East & Latin America is expected to showcase high growth during the forecast period. The rapid adoption of 3D technology in the region is mainly due to technological advancements and improvements in the manufacturing industry.
KEY INDUSTRY PLAYERS
Companies are Focusing on Partnership and Collaboration Activities for Safer Internet Environment
The prominent players of the market are focusing on offering advanced and innovative solutions catering to the growing needs of industries. These key players are investing in R&D to provide innovative services and materials. They are entering into strategic partnership and collaboration to provide next-generation solutions. These companies are offering consumer-centric solutions to help in boosting business growth. Similarly, the key players are keen on offering a vast range of 3-dimensional materials to grow across every industry application.
Similarly, the key players are keen on offering a vast range of 3-dimensional materials to grow across every industry application.
February 2022 – Imaginarium partnered with Ultimaker to introduce desktop & industrial 3D printer range in the India market. This partnership would help Ultimaker to expand its business in India, where additive manufacturing is anticipated to reach a point of breakthrough in the coming years.
November 2021 – 3D Systems is planning to enhance additive manufacturing innovation through partnerships and launch of products. The company launched new 3-dimensional printing tools and collaborated with the U.K.-based startup Additive Manufacturing Technologies (AMT) to present novel 3-dimensional printing workflows and improve AM software, which is ideal for automotive components.
List of the Key Companies Profiled:
- 3D Systems Corporation (U.S.)
- The ExOne Company (Germany)
- voxeljet AG (Germany)
- Materialise NV (Belgium)
- Made in Space, Inc.
 (U.S.)
(U.S.) - Envisiontec, Inc. (Germany)
- Stratasys Ltd. (U.S.)
- HP, Inc. (U.S.)
- General Electric Company (GE Additive) (U.S.)
- Autodesk Inc. (U.S.)
KEY INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS:
- March 2022 – South Africa’s Department of Science and Innovation (DSI) launched a pilot project to build around 25 houses by utilizing 3D printing technology to combat the shortage of housing in the country.
- March 2022 – 3DGence, a European manufacturer, launched a new industrial FFF machine, INDUSTRY F421, which is well-suited with high performance materials. Additionally, the firm has also introduced AS9100, a new high-temperature filament, which is made using polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and certified for use in defense and aerospace sectors.
REPORT COVERAGE
An Infographic Representation of 3D Printing Market
View Full Infographic
To get information on various segments, share your queries with us
The global 3D printing market research report highlights leading regions across the world to offer a better understanding to the user. Furthermore, the report provides insights into the latest industry growth trends and analyzes technologies that are being deployed at a rapid pace at the global level. It further offers drivers and restraints, helping the reader gain in-depth knowledge about the market.
REPORT SCOPE & SEGMENTATION
ATTRIBUTE | DETAILS |
Study Period | 2018-2029 |
Base Year | 2021 |
Estimated Year | 2022 |
Forecast Period | 2022-2029 |
Historical Period | 2018-2020 |
Unit | Value (USD billion) |
Segmentation | By Component, Technology, Application, End-User, and Region |
By Component |
|
By Technology |
|
By Application |
|
By End-User |
|
By Region |
|
The 3D printing market will grow by 25% annually
2020 has been a major shake-up for the entire global industry, and for each of us, but there is good news: the global crisis has helped highlight the benefits of 3D technologies. There is a clear understanding that additive manufacturing can quickly cope with the difficulties associated with plant downtime and logistical collapse, and can become a catalyst for business growth.
There is a clear understanding that additive manufacturing can quickly cope with the difficulties associated with plant downtime and logistical collapse, and can become a catalyst for business growth.
Italian startup Isinnova was among the first to use 3D printers to make medical devices to help patients with COVID-19© AFP
Together with IQB Technologies, who prepared this material, we will see how the 3D printing market is growing, what analysts predict and what trends determined the state of the 3D industry in 2020.
Growth of the market for 3D printing products and services in 2020-2024 in billion US dollars. Source: Wohlers Associates © Statista 2020
According to Verified Market Research, the global 3D printing market was valued at $8.08 billion in 2017, with a growth potential of up to $49..74 billion by 2025 at a compound annual rate of 25.5% over the period 2018-2025. According to analysts, the main driving forces behind the global additive manufacturing market are:
- benefits of new production and logistics management models
- growing demand for customized products
- reduction in production costs
Fortune Business Insights, in a report published in October 2020, predicts an increase in market size to $51. 77 billion by 2026 with an average annual growth of 25.8%.
77 billion by 2026 with an average annual growth of 25.8%.
The field of 3D printing of medical devices has exploded this year. Technavio, in its latest study (November 2020), estimates that this market segment will grow by $1.572 billion over the period 2020-2024 at a CAGR of 13%. Manufacturers and service providers around the world are appreciating the speed and cost-effectiveness of 3D printing, as well as the ability to manufacture patient care devices on site, without the need for vendors.
In the spring of 2020, Rusatom - Additive Technologies (RusAT LLC) produced prototypes and started 3D printing of Venturi valves for artificial lung ventilation devices. The need for emergency aids and other medical equipment has skyrocketed due to the COVID-19 outbreak, and thousands of manufacturers around the world have jumped into their rapid production on 3D printers. Photo: Petr Kovalev, TASS
Impact of COVID-19to the 3D printing market: global forecast until 2025
Given the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the global 3D printing market will grow from $11. 4 billion in 2020 to $30.2 billion by 2025. It is expected that the compound annual growth rate in the period 2019-2025 will reach 18%. Such an assessment (less optimistic than the above) is given in the forecast of Research and Markets, published in July this year. According to analysts, the market decline in 2020 will be more than 19% compared to projections made before the coronavirus outbreak. The main reason for the decline is that while the volume of 3D printer work was high in 2020, many projects were done for free during this difficult period.
4 billion in 2020 to $30.2 billion by 2025. It is expected that the compound annual growth rate in the period 2019-2025 will reach 18%. Such an assessment (less optimistic than the above) is given in the forecast of Research and Markets, published in July this year. According to analysts, the market decline in 2020 will be more than 19% compared to projections made before the coronavirus outbreak. The main reason for the decline is that while the volume of 3D printer work was high in 2020, many projects were done for free during this difficult period.
Experts expected 3D printer sales to stagnate in 2020, but double-digit growth is expected through 2025
The 3D printing market will continue to generate revenue in 2020, although not as big as originally predicted before the pandemic. Losses incurred in the first half of the year are expected to be offset to some extent by revenues generated in the second half. Growth is likely to be possible in the coming years thanks to backorders in all end-use industries, as well as the arrival of new customers who did not think about using 3D printers before the pandemic.
Consumables sales will follow the same trend as 3D printer sales, with more investment in new types of materials
3D printer materials revenue will follow a similar trend over the forecast period. Large volumes of printing were in demand in the first quarter of 2020, however, in most cases, materials were provided free of charge. The focus will be on the use of new materials for 3D printing in the next five years, however, positive results will be noticeable only after the forecast period.
Overall, the AM market will remain resilient during the pandemic and beyond
That being said, the 3D printing market as a whole will see a reduction in potential revenues that could be generated, but the picture of the impact of the coronavirus pandemic will be much better than in other industries. An encouraging fact for the 3D printing industry can be considered a return to the previous rapid growth rate, which is expected as early as next year. It will be useful to know about this for new participants in the sector who plan to enter the market in the next few years.
It will be useful to know about this for new participants in the sector who plan to enter the market in the next few years.
Additive Manufacturing in 2020: Top 5 Trends
How has the field of additive manufacturing changed? The authoritative Internet portal 3dnatives.com has published an overview of the trends that determined the state of 3D printing in 2020. Despite COVID-19, the industry has developed strongly and a number of impressive developments have been introduced. So, we can identify five key trends in the development of the industry in the past year.
1. The COVID-19 pandemic shook up the 3D printing industry
Due to the pandemic and a critical shortage of necessary diagnostic tools and supplies, scientists at the University of South Florida have 3D printed a nasopharyngeal swab. Products can be printed on a portable 3D printer right at the test site. In a short time, 100,000 of these tampons were printed.
In 2020, the consequences of the spread of the coronavirus affected almost all spheres of life. One of the most vulnerable areas in the first few months of the pandemic was medicine, when there was a sudden shortage of equipment to fight COVID-19. 3D printing technologies have been rapidly introduced into the production of patient care equipment around the world. In a matter of days, it was possible to create critical healthcare devices, such as protective masks or ventilators, and later devices for taking a swab for coronavirus. Hospitals purchased 3D solutions for in-house manufacturing, universities also hosted equipment, and manufacturers quickly became providers of healthcare services.
One of the most vulnerable areas in the first few months of the pandemic was medicine, when there was a sudden shortage of equipment to fight COVID-19. 3D printing technologies have been rapidly introduced into the production of patient care equipment around the world. In a matter of days, it was possible to create critical healthcare devices, such as protective masks or ventilators, and later devices for taking a swab for coronavirus. Hospitals purchased 3D solutions for in-house manufacturing, universities also hosted equipment, and manufacturers quickly became providers of healthcare services.
Thus, 3D printing technology has shown greater flexibility compared to other manufacturing methods. This industry does not depend on complex supply chains that have not worked due to the cessation of imports of goods from China and Southeast Asia.
More globally, this market has been affected by the pandemic, but it has started to grow faster than expected. Market research agency Context, which studied the impact on the 3D printing industry, noted: “Demands for 3D printers across all price ranges have increased as they were intended to be used to create medical-related objects, including personal protective equipment. and devices for taking swabs. While this could not fully offset the loss of demand from market sectors that were closed (such as consumer goods, education, dentistry and automotive), the technology's flexibility, its ability to adapt to supply chain disruptions, and its prospects for future adoption were clearly demonstrated. across multiple industries." Indeed, representatives of many sectors have realized that 3D printing technologies can solve supply chain problems and are a smart investment for the future.
and devices for taking swabs. While this could not fully offset the loss of demand from market sectors that were closed (such as consumer goods, education, dentistry and automotive), the technology's flexibility, its ability to adapt to supply chain disruptions, and its prospects for future adoption were clearly demonstrated. across multiple industries." Indeed, representatives of many sectors have realized that 3D printing technologies can solve supply chain problems and are a smart investment for the future.
For the additive manufacturing community, the coronavirus pandemic meant the cancellation of almost all events. The industry needed new ways to meet and meet, so remote online events have become very popular this year. Formnext, the world's premier trade show for additive manufacturing, has also moved online. In fact, the digital format has allowed many companies to reach a larger audience at a lower cost compared to offline events.
2. 3D printing continues to transform into manufacturing technology
Porsche has used SLM Solutions' new generation NXG XII 600 additive metal printing system to create an E-Drive powertrain housing for the front axle of a sports car. As a result of topological optimization, it was possible to reduce the weight of the part due to lattice structures, implement functionally integrated cooling channels, increase the stiffness coefficient, and reduce assembly time due to a reduction in the number of elements. The NXG XII 600 is a revolutionary system aimed at mass production. It is equipped with twelve 1000-watt lasers and will make it possible to produce up to 10,000 kg of metal products per year.
As a result of topological optimization, it was possible to reduce the weight of the part due to lattice structures, implement functionally integrated cooling channels, increase the stiffness coefficient, and reduce assembly time due to a reduction in the number of elements. The NXG XII 600 is a revolutionary system aimed at mass production. It is equipped with twelve 1000-watt lasers and will make it possible to produce up to 10,000 kg of metal products per year.
3D printing technologies prove time and time again that they should not be seen as just a means of prototyping. They can be used for high volume production and production of final parts. In Sculpteo's latest State of the 3D Printing Market report, 50% of those surveyed confirmed they have used the technology to produce end products. In addition, for the first time in five years, the share of rapid prototyping has decreased.
For high-volume production, scalability and repeatability are key factors. Over the past few years, full-cycle additive manufacturing has been industrialized to provide the right conditions for these challenges. Huge progress has been made in the field of hardware, but there are also changes in the field of software and systems for post-processing. Many manufacturers of such systems, such as PostProcess Technologies, DyeMansion and AM-Flow, have raised millions of dollars in development of their solutions. But the post-processing stage is only part of the equation, and much of the work in 2020 has been centered around software.
Huge progress has been made in the field of hardware, but there are also changes in the field of software and systems for post-processing. Many manufacturers of such systems, such as PostProcess Technologies, DyeMansion and AM-Flow, have raised millions of dollars in development of their solutions. But the post-processing stage is only part of the equation, and much of the work in 2020 has been centered around software.
3. Additive manufacturing software becomes a must
The software is required for several stages of 3D printing: placement on the platform, preparation of the platform, fixing files, as well as for production planning. In 2020, companies such as AMFG, MakerOS, and 3YOURMIND have emerged as important MES (manufacturing management software solutions) providers.
In addition to a growing number of workflow solutions, integrated CAD tools are also evolving. For example, Netfabb is a manufacturing automation software that supports the optimization of manufacturing processes, reducing production time and minimizing production costs for 3D printing.
And finally, the Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) segment continues to develop. An increasing number of software products are using generative design or topological optimization to optimize the performance, cost, and reliability of additively manufactured parts.
4. Materials create new use cases
Growing production of key 3D printing materials. Source: Wohlers Associates according to Senvol Database
This year, materials are once again among the many milestones, and the number of suppliers has doubled in the past two years. High performance polymers with unique properties such as PEEK, PEKK and Ultem have been introduced to the thermoplastic market. Polypropylene, one of the most widely used plastics in the world, has become more compatible with 3D powder printing technologies. Polypropylene is excellent for high-cycle applications where high strength is not required due to characteristics such as high fatigue resistance, semi-flexibility and lightness.
The composites segment is also growing rapidly. Arevo, which aims to transform the manufacturing of composite materials through digitalization and automation, raised another $25 million in funding this summer. Startup Arris Composites is developing proprietary technology to enable mass additive manufacturing of high-strength, lightweight composite parts.
Last but not least, the metal 3D printing industry remains a growing market, estimated at $1 billion in 2020. According to forecasts, its volume will increase annually by more than 27% over the next few years.
Given the unique requirements placed on powder materials, the market for additive manufacturing powders and their supply chains are constantly evolving. Indeed, the process of making powders for 3D printers is still quite specialized and costly, but it is necessary for the industrialization of metal 3D printing and the production of certified parts. Powders for additive manufacturing must meet special requirements for structure, purity and particle size distribution.
Additive metal manufacturing has a greater environmental impact than traditional methods, so organizations and manufacturers need to develop sound strategies for this technology over the next few years if they are interested in a sustainable future for this material.
There is a growing demand for aluminum powder in the 3D printing market. According to a report funded by Equispheres, demand in this segment will rise to over 69$5 million in 2023, representing a CAGR of 36.5%.
5. Technology adoption by industries is changing
Growth graph illustrating the rate of adoption of 3D printing in various industries. Photo: AMFG
The adoption trends for additive technologies in 2020 have been very encouraging. In sectors such as medicine, aerospace, and automotive, 3D printing has seen a boom that has been going on for several years. At the same time, in the oil and gas industry, construction and electronics, the integration of additive manufacturing was slower.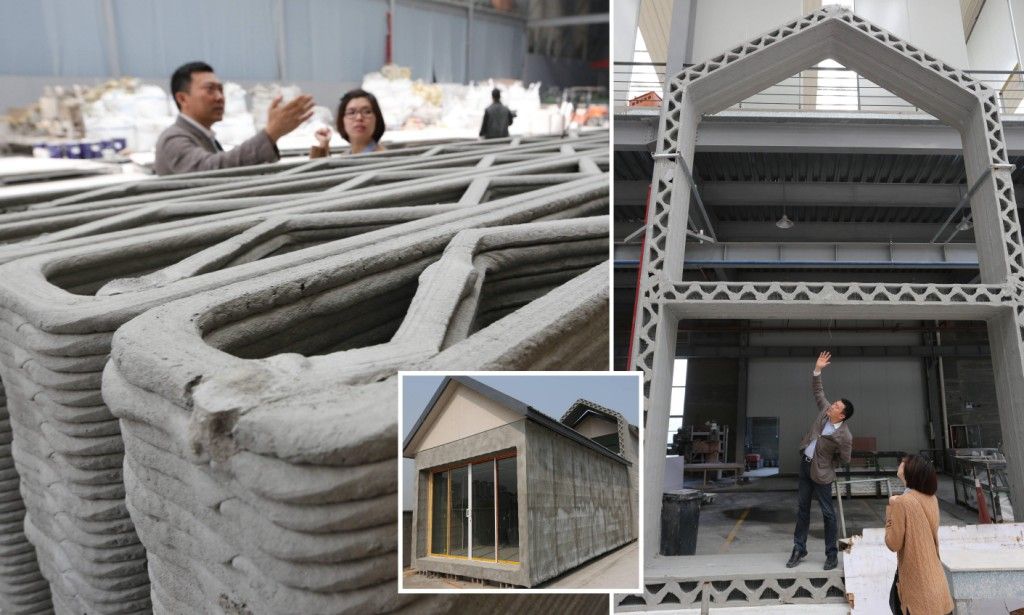 In 2020, there are many new applications in these three industries.
In 2020, there are many new applications in these three industries.
Following the introduction of robotic 3D printers, activity in the construction industry has skyrocketed this year. Danish manufacturer COBOD unveiled a three-story residential building with 3D printed walls in Wahlhausen, Germany. This 380 square meter facility will be the world's first commercial residential building. ICON has developed a gantry 3D construction printer for its proprietary Lavacrete material. In addition, in the latest joint project with NASA, the company said that its solution is well suited for construction on the Moon and beyond the Earth.
In terms of space technology, Relativity Space, which has developed a fully 3D printed rocket engine, has received $500 million in funding. It also proves that 3D printing technology has a future in space exploration. Relativity's long-term goal is to modernize humanity's industrial base on Earth and build it on Mars. For now, the company plans to launch its first rocket into orbit in early 2021.
Terran 1 rocket prototype 3D printed by Relativity Space. Photo: Relativity Space
The number of tasks solved by 3D printing in the oil and gas industry is growing. By the way, at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, researchers are building the first 3D printed nuclear reactor. The lab hopes to commission the first nuclear reactor of this type in 2023, enabling the nuclear industry to build better and more sustainable energy systems.
In conclusion, I would like to note that the electronics industry is also changing due to the additive manufacturing of micro- and nano-objects. Startups like Voltera are demonstrating the benefits of 3D printing in terms of creating smaller, thinner, and more precise components than can be achieved with traditional manufacturing methods.
Brief totals:
- In 2020, 3D printing technologies were rapidly introduced into the production of equipment for emergency care of patients around the world, clearly showing their advantages during production downtime and supply disruptions
- 50% of professional users use additive technologies to produce final products
- Over 25% cumulative annual growth rate of the 3D printing market through 2025
- 3D printer sales are forecast to double in the next five years
- The development of new materials and the expansion of their applications remain the most promising trend in the industry.
 The number of material suppliers has doubled in the last two years
The number of material suppliers has doubled in the last two years
Article published with permission from IQB Technologies. Author: Semyon Popadyuk. The review uses materials from Wohlers Associates, Research and Markets, Fortune Busness Insights, Technavio, marketwatch.com, 3dnatives.com.
Do you have interesting news? Share your developments with us, and we will tell the whole world about them! We are waiting for your ideas at [email protected].
main trends and expert forecasts
Analytics and business
Experts recommend
Author: Semyon Popadiuk
Author: Semyon Popadiuk
What 3D printing trends do additive manufacturing experts think will be especially relevant in 2022?
3D Printing Industry, one of the leading online publications in the 3D industry, asked researchers, senior executives, technical experts and investors to share their vision for 3D printing this year.
The message is clear: the potential of 3D printing in various industries, including aerospace, automotive and medical, is still growing.
The pandemic has boosted the industry as weak links in the supply chain have been identified, advanced additive technologies have once again topped the agenda. Increasing demands on materials, as well as an increase in demand for higher performance materials, are evidence of manufacturers' confidence in 3D printing. At the same time, attention to the problems of sustainable development suggests that the industry keeps pace with the times.
The discussion touched upon trends such as consolidation, manufacturing, automation, the expansion of the manufacturing ecosystem (including post-processing), as well as advances in software such as digital threads, simulation, and the growing use of artificial intelligence.
Become a qualified 3D technician! The iQB Technologies training center offers courses on working with hardware and software products for preparing models for 3D printing and processing 3D scanning data
Bart Van der Schueren, CTO Materialize
Additive manufacturing has proven its worth for many different applications and business models. Over the past two years, due to supply problems, it has received special attention. This has accelerated the adoption of the technology, but at the same time poses challenges for users and the entire 3D industry as a whole. As the boundaries between traditional manufacturing and 3D printing disappear, the two ecosystems are beginning to merge and form a more integrated manufacturing environment.
Over the past two years, due to supply problems, it has received special attention. This has accelerated the adoption of the technology, but at the same time poses challenges for users and the entire 3D industry as a whole. As the boundaries between traditional manufacturing and 3D printing disappear, the two ecosystems are beginning to merge and form a more integrated manufacturing environment.
© Materialize
This digitized unified manufacturing environment allows for greater efficiency and repeatability, greater scale and control, but requires a common resource, namely data. Data will play an increasingly important role in 3D printing. It's not just about access to data, it's also about how organizations and users can collect, use and protect their own data.
Smart manufacturing is based on the ability to analyze data to form actionable strategies. They allow to improve and expand production and, as a result, create better products. Combining data from different processes and levels makes it possible to optimize and automate production. This requires an AM software platform that can connect to all systems and datasets in and out of the production environment.
This requires an AM software platform that can connect to all systems and datasets in and out of the production environment.
At the same time, organizations must be able to protect their intellectual property. In the case of additive processes, this is relevant both from the point of view of the design of parts and the process itself. With 3D printing, the material and product are created at the same time. Given this side of the issue, data obviously plays a more important role in 3D printing than in traditional manufacturing.
But even in the presence of large amounts of data, optimization first requires knowledge of people in specific areas of specialization, and only then does it make sense to automate the process. In other words, if you're using a lot of data to automate and scale inefficient production, you still won't get good results. The main thing is to combine the right technology with the right experience.
Read more in the article Trend 2022: smart data is increasingly relevant for additive manufacturing
Brian Thompson, VP CAD & General Manager, PTC
Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM) will continue to evolve and software will become a critical enabler for industrial additive manufacturing. We will continue to overcome the fragmentation associated with point solutions and strive to create an interconnected ecosystem that combines hardware, software products and materials.
We will continue to overcome the fragmentation associated with point solutions and strive to create an interconnected ecosystem that combines hardware, software products and materials.
We expect an increase in activity and interest in the field of post-processing products printed on metal 3D printers. Now technologies are being actively developed that complement the printing process itself. This means that metal 3D printing technologies are becoming more mature, at least in a few niche markets.
Hybrid manufacturing (where the same machine performs both additive and subtractive processes) remains a hot topic, especially among manufacturers interested in combining a 3- and 5-axis milling machine with a 3D printer, which would eliminate the need for separate post-processing equipment.
We are already seeing great strides in predicting deformations in metal printing. However, there is also expected to be an increase in interest in modeling tools to address the strain problems inherent in polymer 3D printing. We are also looking forward to products that increase the predictability of resin printing.
We are also looking forward to products that increase the predictability of resin printing.
Download the free brochure 3D Plastic Printing: Technology and Applications
Finally, we anticipate an increasing focus on digital filament technology across the entire value chain, from concept to post-processing and quality control. In our practice, there was a demonstration project: it included not only an innovative heat exchanger (an achievement in itself) created using flagship CAD technologies, product lifecycle management and industrial Internet of things (order fulfillment and monitoring), but also augmented reality capabilities that allow “send” the part to a specialist anywhere in the world! By September 2022, it is unlikely that there will be manufacturers able to fully implement this practice, but this is what we are aiming for.
Avi Reichental, co-founder and CEO of Nexa3D
This year, the pandemic will continue to largely determine development trends. Over the past two years, weaknesses in a complex and fragile supply chain have been identified, which is a priority issue for most manufacturers. This forces them to accelerate the digitalization and localization of supplies. This is where 3D printing plays a key role, particularly in terms of speed, throughput, cost and sustainability.
Over the past two years, weaknesses in a complex and fragile supply chain have been identified, which is a priority issue for most manufacturers. This forces them to accelerate the digitalization and localization of supplies. This is where 3D printing plays a key role, particularly in terms of speed, throughput, cost and sustainability.
As the number of companies moving towards mass additive manufacturing increases, there will be an increased demand for scalable solutions for post-processing and full production automation. The basis for these solutions will be advanced adaptive machine learning and vision technologies to improve the stability and efficiency of production.
© Nexa3D
We will undoubtedly see an expansion of open ecosystems of innovation and collaboration, from which everyone will benefit. With greater and more flexible participation from around the world, this collaborative approach will help accelerate the adoption and development of technology.
Mohsen Seifi, Director, International AM Programs, Martin White, Program Manager, AM Europe, UK Alexander Liu, Program Manager, AM Asia, Singapore, and Terry Wohlers, Head of Advisory Services and Market Intelligence, ASTM International 9 Center of Excellence for Additive Manufacturing0209
In 2022, development is expected in two key areas:
In critical applications, site inspections can help ensure risk-adjusted structural integrity and certify large parts that are difficult to scan with CT. For example, ASTM is currently working with NASA on a three-year project to use site inspections to determine the effect of defects on structural integrity.
With regard to post-processing, it is obvious that in order to develop durable and reliable parts and products, it is necessary to optimize the surface treatment and internal structure (microstructures, porosity level). In some cases, more than 60% of the cost of the final product is in post-processing. Thus, we see that the industry is really striving to improve the quality of products. We believe that post-processing will have a significant impact on the success of additive manufacturing, as was already evident at Formnext 2021.
Thus, we see that the industry is really striving to improve the quality of products. We believe that post-processing will have a significant impact on the success of additive manufacturing, as was already evident at Formnext 2021.
iQB Technologies experts recommend article: 3D printing as a full-fledged manufacturing technology in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic
Daeho Hong, Production Manager nTopology
In 2022, many enterprises will develop core additive technologies, from prototyping and R&D to manufacturing. We expect more items in the aerospace, automotive, heavy industry, and medical device industries to be approved and put into production than in recent years.
More integrated and automated additive manufacturing will streamline product development and manufacturing by integrating enterprise systems, 3D printing software and hardware. This year we will see a transition from prototyping to manufacturing, with the main challenges being the stabilization of selected additive technologies, scaling up to reduce costs, and quality control.
Gil Lavi, Founder & CEO, 3D Alliances
In the short term, I see more synergy between the following four areas:
-
3D printing software,
-
3D printers,
-
post-processing,
-
materials for 3D printing.
With increasing awareness and demand from industrial users to introduce additive technologies into manufacturing processes, solution providers are realizing the importance of building a single end-to-end workflow. Therefore, in 2022, I look forward to greater collaboration between 3D printing hardware, software, and material suppliers to help users integrate 3D into manufacturing.
Another challenge, in my opinion, is to ensure that publicly traded 3D printing companies are valued on the stock exchange. Only a few of them will be able to achieve this only through high financial performance. Simply put, in the longer term, this industry will continue to evolve and push the boundaries, discovering new ways to transform analog and manual processes into digital ones.
Rush LaSelle, Senior Director, Additive Manufacturing, Jabil
We look forward to further development of initiatives aimed at reducing production costs through 3D printing. The results obtained will help to prove that additive processes have significant advantages over traditional ones in relation to the manufacture of medium-sized batches and industries that are sensitive to price fluctuations. The main costs will be aimed at increasing the productivity of industrial 3D printers relative to capital investments. In addition, you need to focus on reducing labor and material costs, as well as reducing the time from design to delivery.
Reducing the cost of acquiring and operating 3D printers remains a critical factor for mass-produced businesses. As users seek to realize the benefits of additive manufacturing to increase production volumes, it is essential to be able to increase the productivity of printers. The use of more lasers in powder melting/sintering plants or higher layering speeds while improving print resolution will increase cost efficiency and investment attractiveness.