3D printer filament made of
What filaments can be used for 3D printing?
David Roberson6 May 2021
Applications
3D printing is a versatile technology. Using it, you can create a wide variety of specialized applications in a wide variety of specialized materials. But before getting started, it’s important to understand what these materials are, what they can do, what they are made of – including plastics, resins, and powders – as well as what results you can expect when using them with your 3D printer.
In this guide, we cover:
What can you do with a 3D printer?
What is 3D printer filament made of?
Printer settings explained
Common 3D printer filaments (PETG, TPU, ABS, PLA)
Metal and wood 3D printing materials
Support materials
Filament, resin, and powder compared
What can you do with a 3D printer?
FFF 3D printing, or fused filament fabrication, is an additive manufacturing process in which thermoplastic material is pushed through a heated nozzle to create objects layer by layer. Key applications for FFF 3D printing include:
Manufacturing aids. With faster lead times than outsourcing and a wide
range of engineering materials, FFF 3D printing is used widely in manufacturing
industries. 3D printers deliver rapid tooling and replacement parts to maintain
maximum uptime and productivity on the production line. And they are used to
flexibly create end-use parts, such as bespoke quality gauges or small batch
first runs, to speed up time to market of a productEnd-use parts. 3D printing can also be used to produce low-volume, customized end-use parts. This offers greater flexibility, enabling businesses to run small batches of parts without the risks involved of manufacturing a larger batch. There’s also scope for "printing on the spot" and creating products for the customer while they wait
Prototyping. Low-cost materials and short lead times make FFF 3D printing ideal for the iterative design process.
 3D printed prototypes can be visual – parts that look close to a finished product – or functional – parts that are capable of being tested for technical performance
3D printed prototypes can be visual – parts that look close to a finished product – or functional – parts that are capable of being tested for technical performanceEducation. Affordable and easy-to-use FFF hardware enables a variety of education applications – from engaging younger students with STEAM basics to providing production labs for college and university students to work on engineering projects and develop skills for the modern workplace
A 3D printed end-use part – the nozzle on a movie effects snow machine
A 3D printed prototype – testing a tablet holder device
What is 3D printer filament made of?
The process of creating 3D printing filament is called "compounding". First, raw plastic resin is produced in the form of pellets. These can be mixed with additives to alter the properties.
The mixture is then dried, extruded to the desired width (usually 1.75 or 2.85 mm), and wound on a spool. Once wound, the material is ready to be used in 3D printing.
Settings for 3D printing materials explained
The properties of every material are different. So are the characteristics of every 3D printer on the market – size, enclosure, nozzle type, and many more features will affect how a material prints. The characteristics of your print job will also have an effect, such as your desired print speed or the geometry of your part.
Loading filament on an Ultimaker 3D printer
The next sections of this guide offers basic advice on how to print with some of the most widely used filaments.
Recommended print settings are given as a general guideline for FFF 3D printers and we advise to always check the manufacturer’s recommendations before printing. (If you’re printing with Ultimaker materials, more detailed guidance can be found on our support pages.)
This will help you compare materials and make some choices about which material is best for your chosen application. With a platform like Ultimaker, software comes with preconfigured printing profiles for our printers and materials, with the option to add hundreds more for third-party filaments via our Marketplace. All you need to do is choose your desired speed, quality, or application, and preconfigured profiles take care of the rest.
All you need to do is choose your desired speed, quality, or application, and preconfigured profiles take care of the rest.
Ultimaker offers the benefits of a seamless platform, but you can also use third-party materials
What is PETG?
PETG is a 3D printing material that combines the advantages of PLA and ABS filaments. It is tougher than PLA, with high impact strength, mechanical strength, and some flexibility. It also offers temperature, chemical, and wear resistance. When printed, it gives a glossy finish.
In terms of its uses, PETG is a great all-round material to have on hand. Its resistance to wear and harsh environments makes it suitable for creating tools, other end-use parts, and functional prototypes. This versatility makes it easy to scale and standardize across an organization – meaning fewer configuration changeovers and greater productivity.
How to print with PETG
A typical extrusion temperature range for a PETG filament is 225-245 °C. While a heated build plate is not essential for all PETG filaments and printers, it is highly recommended to ensure adhesion and print quality.
While a heated build plate is not essential for all PETG filaments and printers, it is highly recommended to ensure adhesion and print quality.
What is TPU?
TPU is a semi-flexible material that can be used in a wide variety of engineering applications where performance is more important than aesthetic qualities. TPU is an ideal 3D printing material when durability and flexibility are essential, as it features exceptional wear and tear resistance, and rubber-like flexibility.
You will often see TPU filaments with names that include two letters and a number – for example Ultimaker TPU 95A. This refers to the material’s hardness on a measuring scale known as the Shore scale. So in this case, the filament rates 95 on the Shore A hardness scale.
How to print with TPU
When 3D printing with TPU, most filament manufacturers recommend a nozzle temperature around 220-240 °C. Build plate temperatures can vary, so check the manufacturer’s recommendation. For best adhesion, it is often advised to apply a thin layer of glue to the build plate. A low relative humidity is also recommended to prevent moisture uptake.
A low relative humidity is also recommended to prevent moisture uptake.
If you want to avoid the trial and error that can come with trying to get the right print settings, Ultimaker filaments and those in our Marketplace come with preconfigured printing profiles for Ultimaker printers.
A 3D printed PETG part, showing the smooth and glossy surface finish
TPU's flexibility make it ideal for this pack spinner, which must withstand impact while not damaging products on the line
What is ABS?
ABS is a good choice for creating functional prototypes and end-use parts. It is often one of the first materials people try when they start 3D printing for more technical applications due to its good mechanical and thermal properties.
How to print with ABS
ABS should be printed on a heated build plate. ABS needs higher nozzle temperature than most other filaments, with manufacturers typically recommending between 220-260 °C.
Many ABS filament can be prone to warping when printed, although Ultimaker ABS is specially formulated to minimize this. Additionally, ABS prints best when it is enclosed on all sides, as it can be prone to delamination.
Additionally, ABS prints best when it is enclosed on all sides, as it can be prone to delamination.
What is PLA?
PLA is one of the most common FFF 3D printing materials. It prints reliably with high dimensional accuracy and a quality surface finish. This makes it an ideal material for a range of visual applications – from detailed prototypes to education models.
How to print with PLA
PLA prints at moderate temperatures, mostly around 190-210 °C. For the build plate, a temperature around 50-60 °C is ideal for heated build plates, but it is also possible to print PLA on a cold build surface.
Click here for a deeper discussion on ABS vs PLA.
A functional part 3D printed with ABS
A visual prototype in two colors, printed in PLA
What's the difference between PLA and PLA+?
Over time, several material products based on PLA have come to the market offering the easy printing experience of PLA filaments combined with additional properties. This is usually done through special additives to create a blend based on PLA.
This is usually done through special additives to create a blend based on PLA.
While some PLA-based filaments do indeed offer extra properties, such as Ultimaker Tough PLA, be sure to do your own research before deciding if a PLA+ filament is right for your needs.
Does the manufacturer promise superior visual quality? Check photographs of their prints to compare results. Does it claim to offer better mechanical properties? Check the material technical data sheets to be sure this claim has been tested.
The chemical composition of a filament should also be made clear in the manufacturer’s data sheets. Checking what a particular PLA+ is made of will also help you understand its true characteristics.
What is metal 3D printer filament?
Metal 3D printing filament is an FFF filament type made of a metal-polymer composite.
Metal 3D printer material can also be made of aluminum alloys, cobalt-chrome superalloys, inconel (nickel alloys), precious metals such as silver or gold, stainless steel, and titanium alloys.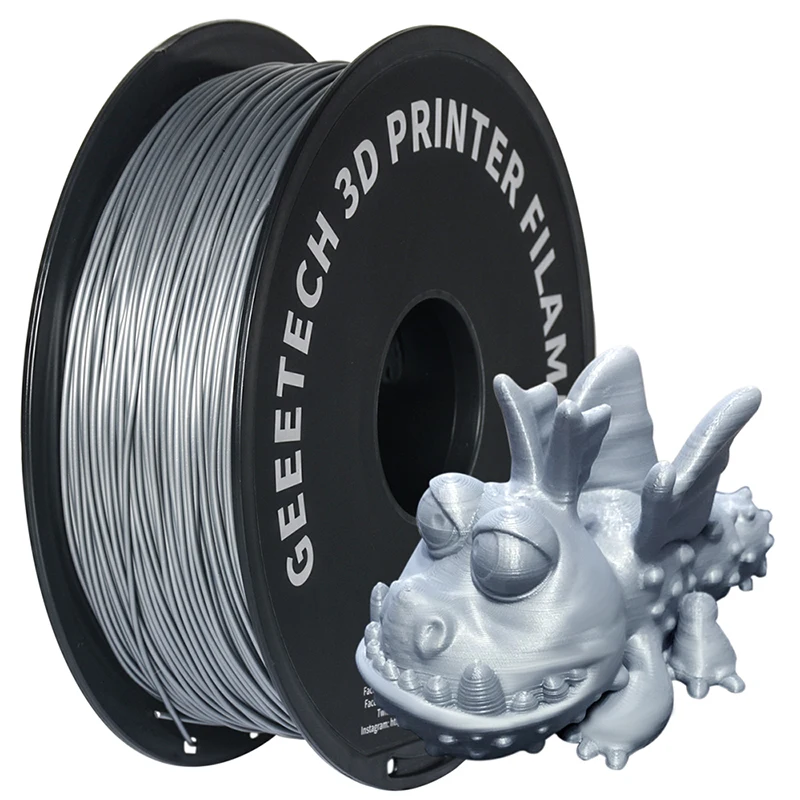 These are more commonly used with powder 3D printing techniques.
These are more commonly used with powder 3D printing techniques.
How to 3D print with metal
There are multiple ways of printing with metal. For FFF, you will need a metal-polymer composite material. Your 3D printer must also have an appropriate build plate with a temperature between 45-60°C, a specialized hardened extruder nozzle (such as steel or ruby), and a cooling fan.
For other 3D printing technologies such as SLM or DMLS, you will use metal powder. The printer’s build chamber will be filled with an inert gas, which reduces oxidation and enables the chamber to reach the desired temperature. Metal powder then is applied to the build plate. A laser scans the component’s cross-section, fusing the metal particles together to create each layer. When the first layer is complete, another layer of metal powder is applied, and the process is repeated. After printing, leftover powder must be disposed of safely.
A metal-polymer composite part, printed with BASF Ultrafuse 316L filament
Wood-based 3D prints used in an architectural model
What is wood 3D printer filament?
Wood 3D printer filament is filament made out of a polymer-wood composite. Typically, PLA is combined with wood fiber, or cork. A variety of wood 3D printing filaments are available, such as those made from bamboo and pine. 3D printing with wood filament results in a final print that looks and feels like wood.
Typically, PLA is combined with wood fiber, or cork. A variety of wood 3D printing filaments are available, such as those made from bamboo and pine. 3D printing with wood filament results in a final print that looks and feels like wood.
How to 3D print with wood
Wood 3D printer filament can be printed with similar settings to PLA. Note that a higher nozzle temperature can cause the printed wood to appear darker, as this will burn the wood in the filament. A larger nozzle than 0.4mm is also recommended, as this will help prevent clogging. While in theory wood filament should not be as abrasive as a material like carbon or glass fiber, it is still recommended to use an abrasion-resistant nozzle to be safe.
It is also important to note that there are many more types of 3D printer filament than those listed in this blog, such as ASA, Nylon, PP, TPE, PA, and copolyester. Many of these are covered in our other guides, including wear, temperature, and impact resistant materials, plus ESD-safe, flame retardant, and flexible filaments.
In the materials section of our website, you can browse a wide selection of Ultimaker materials and other filaments with specialized properties that are compatible with our printers.
What is support material?
Support materials literally ‘support’ a part during the printing process if its geometry would make it otherwise impossible to print. This support material needs to be removed before the print can be used.
Soluble support materials like PVA and HIPS are dissolvable, which means there is no risk of damaging the part’s surface as can happen when removing supports manually. PVA support material dissolves in water, while HIPS requires D-limonene solvent.
A material like Ultimaker Breakaway is manually removed. If you are in a hurry to start using your print, this is faster than waiting for material to dissolve. You can read more in our complete guide to support materials.
A gearbox printed with dissolvable PVA support material
After the PVA support material has been dissolved
Filament, resin, and powder compared
Materials come in different forms, depending on the 3D printer technology:
Filaments for FFF printers
Resin for SLA (stereolithography) and DLP (direct light processing)
Powder for fusion technologies like SLS (selective laser sintering)
What is a resin 3D printer?
The most common form of resin 3D printer uses SLA technology to create parts. SLA uses UV-curable resin as a raw material. The resin is poured into a glass-bottomed container, into which a build platform is submerged. A UV laser shines UV light on the resin to selectively harden it into a horizontal layer of the CAD data which forms the part. The platform then raises out of the container, allowing the uncured resin to level out. This process is repeated until a complete object is formed.
SLA uses UV-curable resin as a raw material. The resin is poured into a glass-bottomed container, into which a build platform is submerged. A UV laser shines UV light on the resin to selectively harden it into a horizontal layer of the CAD data which forms the part. The platform then raises out of the container, allowing the uncured resin to level out. This process is repeated until a complete object is formed.
What is a powder 3D printer?
The most common form of powder 3D printer uses SLS technology to create parts. SLS uses a powdered raw material, typically a polymer. The powder is stored in a container, where a recoating blade distributes a thin layer of material onto the build area. A high-powered laser fuses the small particles of material together, in order to form a single horizontal layer of the CAD data. The container then moves a fraction of a millimeter to start a new layer, and a recoating blade swipes across the build area to deposit a new layer of raw material.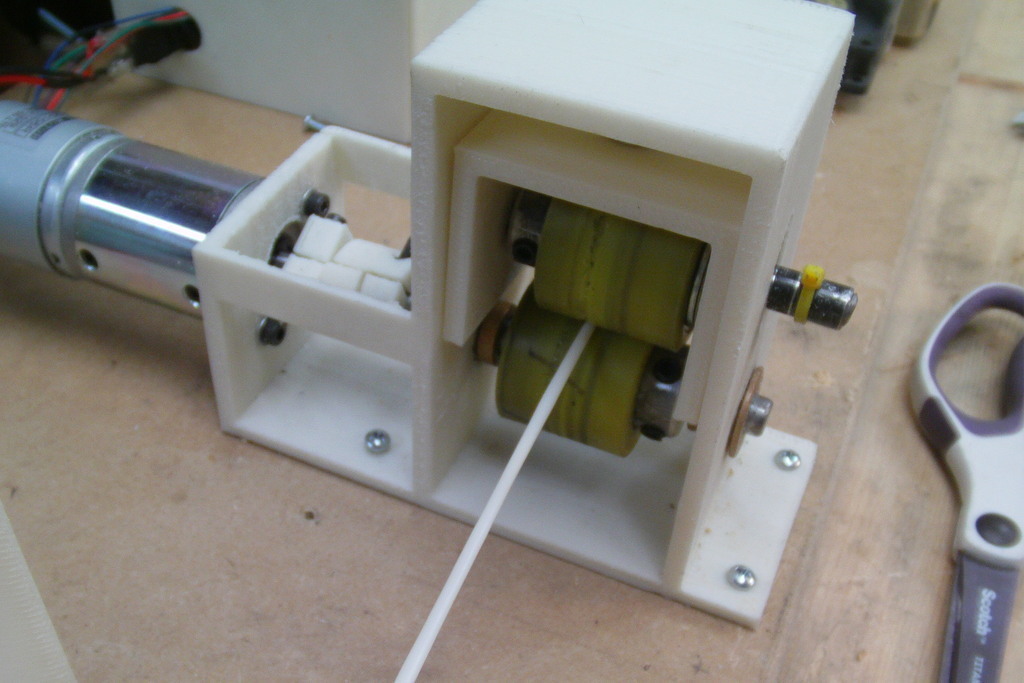 Unfused powder is recycled by sieving and mixing the sieved powder with unused powder. The process is repeated until a complete object is formed.
Unfused powder is recycled by sieving and mixing the sieved powder with unused powder. The process is repeated until a complete object is formed.
The Ultimaker S5 Material Station stores filament in optimal conditions and automatically loads the next spool
SLS 3D printing involves removal of leftover powder material when a print is finished
You can learn more about FFF, SLA, and SLS 3D printing technologies – and the differences between them – by reading our dedicated blog on the subject.
Want to know more?
We hope you found this guide to the basics of 3D printing materials useful.
Want to see how businesses are using various materials to unlock cost and time savings? Download a free white paper below and discover five key 3D printing applications.
Understand 3D printing's biggest cost-saving opportunities in this guide, including:
• The 5 most popular applications of 3D printing
• How to go to market quicker than your competition
• Proven examples that bring over 90% savings
• And lots more!
What is PLA plastic filament and how to use it for 3D printing ?
What is PLA plastic material ? Get all information and advice to help you print your 3D model with filament fabrication, using FDM 3D printing technology. Affordable and reliable, start 3D printing using PLA filament.
Affordable and reliable, start 3D printing using PLA filament.
Colors
Characteristics
Surface Look
Details
Strength
Flexibility
PLA Filament Material Guide
Overview
Design Guide
Technical Specifications
What is PLA material?
PLA plastic or polylactic acid is a vegetable-based plastic material, which commonly uses cornstarch or sugarcane as a raw material. The monomer is usually made from fermented plant starch. This material is a thermoplastic aliphatic polyester and it is the primary natural raw material used in 3D printing. PLA is a fully biodegradable thermoplastic polymer consisting of renewable raw materials. Among all 3D printing materials, PLA is part of the most popular materials used for additive manufacturing for filament fabrication.
The monomer is usually made from fermented plant starch. This material is a thermoplastic aliphatic polyester and it is the primary natural raw material used in 3D printing. PLA is a fully biodegradable thermoplastic polymer consisting of renewable raw materials. Among all 3D printing materials, PLA is part of the most popular materials used for additive manufacturing for filament fabrication.
PLA is a bioplastic, used in 3D printing using the FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) technology, and along with ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), this material is one of the standard materials for this technology. There is often a tendency to compare these plastic materials, as they are the two most common alternatives available for consumer printers. PLA plastic material is easy-to-use and offer some interesting mechanical properties.
PLA material is printed using BigRep 3D printers and mainly used to manufacture big parts up to 1x1x1m.
Even if this PLA material offers the opportunity to 3D print impressive big parts, please keep in mind that you will have to respect specific design guidelines to avoid any problem during the additive manufacturing process. Be sure to check the material design guidelines while creating your 3D file and before you send it for 3D printing.
Be sure to check the material design guidelines while creating your 3D file and before you send it for 3D printing.
If you want to know more about the general properties of PLA filament, you can check our “Technical Specifications” part.
What is PLA plastic used for ?
PLA plastic filament quickly became a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resources. PLA plastic material comes in the form of wire on a spool, which is fed into the extruder head where the plastic is melted and deposited in a continuous extrusion on the printing tray. This material is translucent in its natural form, but spools of coloured filament can be used to make objects in different colors.
When cooling, this material shrinks less than ABS, which gives it good geometric stability during the manufacturing process.
PLA can be useful for your product development, as this material can be used for rapid prototyping.
Large-scale 3D printing is the main advantages of the PLA we are offering at Sculpteo, which can be a great benefit for a wide range of applications. This material offers you the possibility to print professional and industrial parts of 1m x 1m x 1m thanks to a large 3D printer! BigRep PLA material, has good strength and stiffness, making this 3D printing material filament is ideal for demanding industrial production. 3Dp BigRep PLA can perfectly be used to 3D print large objects for architecture or construction fields but also for marketing displays, exhibitions or signage.
This 3D printing filament is an affordable and versatile plastic. It can easily be used for prototypes, pattern making, tooling parts, or end-use parts. However, there are still some disadvantages such as photodegradation which is caused by UV radiation if PLA is exposed to sunlight.
However, there are still some disadvantages such as photodegradation which is caused by UV radiation if PLA is exposed to sunlight.
We inform you that this material is not suited for applications requiring suitability with high humidity (more than 98%) or high temperatures (above 60°C). Make sure you check the physical mechanical properties of the PLA plastic 3D printing material before.
Pricing for PLA 3D printing filament
To get your PLA parts 3D printed, please contact directly our sales team to place your order. It is not possible to order your parts on the website.
However, the price of the design is calculated on a series of factors, including its size, its volume, and the amount of material needed to manufacture your parts.
Our sales team will keep you updated regarding the price and the shipping time of your parts.
How does FDM 3D printing technology work?
BigRep PLA parts are 3D printed using a traditional FDM 3D printing process.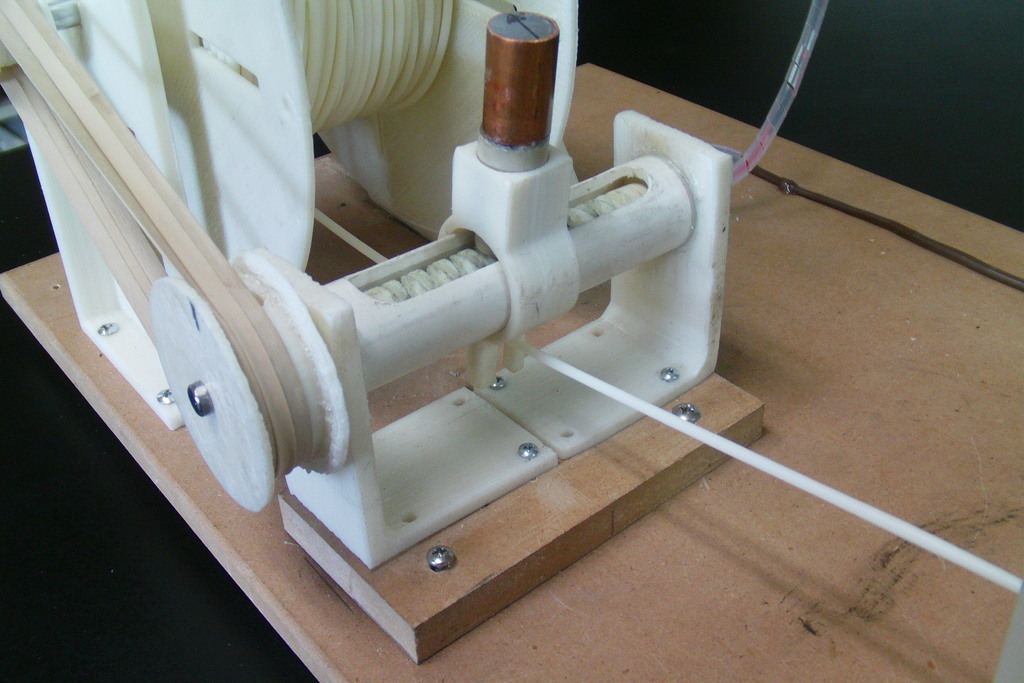 Even if BigRep printers are impressive and big machines, the FDM printing process stays the same. During the FDM 3D printing process, the filament is extruded through a nozzle which melts while being gradually deposited in a structured way on the build platform of the 3D printer until the object is finished.
Even if BigRep printers are impressive and big machines, the FDM printing process stays the same. During the FDM 3D printing process, the filament is extruded through a nozzle which melts while being gradually deposited in a structured way on the build platform of the 3D printer until the object is finished.
Colors and Finishings available for PLA plastic material
Your PLA plastic parts can take on a variety of colors with many color options available according to your project specifications. We are also offering Chemical Smoothing and painting options, please contact us to discuss your color and finishing options to your 3D printed PLA parts.
Maximum size
Maximum size | 1 x 1 x 1 m |
The maximum size of your models are limited by the physical size of our 3D printers – nothing can be printed larger than the printer bed. |
Mechanical Properties
Documentation
| Filament Sizes: | 2.3, 4.5, and 8.0 kg |
| Diameter: | 2.85 mm |
| Density: | 1.24 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Modulus (ISO 178): | 3800 MPa |
| Tensile Strength (ISO 527): | 60 MPa |
| Impact Strength Notched: | 7. 5 kJ/m² 5 kJ/m² |
| Heat Resistance HDT / B (ISO 75): | 40 °C |
| Hardness (Shore): | D 60 |
What does PLA material stand for?
PLA stands for Polylactic acid. It is a thermoplastic monomer derived from renewable, organic sources such as corn starch or sugar cane.
Is PLA plastic biodegradable?
PLA is biodegradable under certain composting conditions.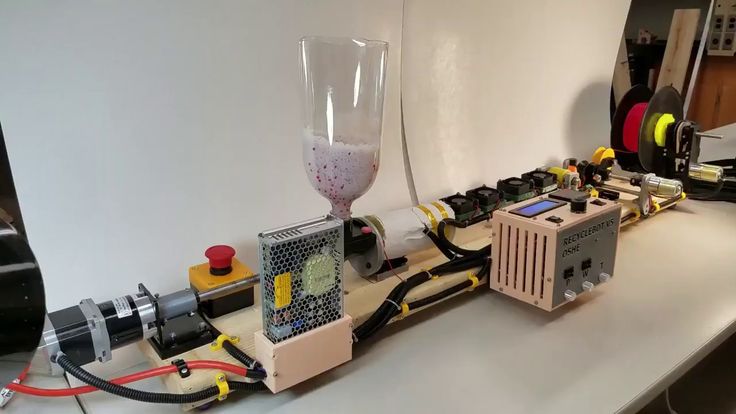 PLA is still a plastic material and requires a laundry list of conditions to effectively break down.
PLA is still a plastic material and requires a laundry list of conditions to effectively break down.
Is PLA actually plastic?
PLA is a plastic material. PLA is made from a biomass resource, it is a vegetable-based plastic material, which commonly uses cornstarch as a raw material.
Is ABS or PLA better for 3D printing?
PLA is a perfect material if you need to 3D print parts where aesthetics is important. ABS is a good material for applications where strength, ductility, machinability and thermal stability are required.
ABS is a good material for applications where strength, ductility, machinability and thermal stability are required.
Related blog posts:
Ready to 3D print with PLA plastic material?
With Sculpteo’s online 3D printing service you’re just a few clicks away from professional PLA 3D printing. Your 3D model is printed with the highest quality and delivered straight to your door.
Get started now to get your PLA prints!
Discover our other plastic materials...
filament from plastic bottles, how to make
filament productionBy making filaments for printing on a 3D printer on their own, the user can save a lot of money spent on consumables. Plastic filament for printing can be made from PET bottles. Consider which bottles are suitable for this, the procedure for manufacturing a filament, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of this method.
Is it possible to make plastic for a 3D printer from PET bottles?
When making plastic filament for 3D printing, it is recommended to use the following types of PET bottles:
- Blue.
 Such bottles have the hardest plastic, but when melted, it will be the most fluid of all.
Such bottles have the hardest plastic, but when melted, it will be the most fluid of all. - White and green. The plastic of these bottles is softer than that of the blue ones. In molten form, the material is thicker.
- Brown. These bottles have the softest plastic. When molten, it is highly viscous (similar to ABS filament). nine0010
How to make DIY thread and print with plastic bottles?
Preparatory work
Bottles must be unraveled into ribbons before production starts.
Soft bottles have a thinner plastic, so it is better to break them into strips of 10 mm.
Containers with medium hard or harder plastic material can be cut into thin strips, about 7 mm thick.
PET bottle 3D printer filament tools
To create a filament from PET bottles, you will need the following tools:
- utility knife or bottle cutter;
Important! When choosing a bottle cutter, you need to pay attention to the accuracy of cutting plastic.
 The width of different cut strips should not differ by more than 0.1 mm.
The width of different cut strips should not differ by more than 0.1 mm. - oven;
- plastic crusher;
- homemade vertical extruder - it has a metal pipe with a drill screw that rotates with a stepper motor, and a nozzle with two heaters from a 3D printer; nine0010
- rotary table;
- large basin;
- cold water.
Step-by-step instructions
The production of PET bottle filament for 3D printing is carried out in the following order:
- Cut plastic bottles must be melted in an oven at 180 °C. The melting time depends on the number of bottles.
Help. It takes approximately 40 minutes to melt 10 plastic bottles.
- After melting, the plastic must be completely cool. All excess moisture will evaporate from the material, and it will crystallize. In appearance, the polymer resembles glass.
- The cooled material must be ground in a crusher into a finer fraction.

- The crushed plastic is then fed into the vertical extruder. The rotating screw moves the ground polymer to the bottom of the device to the nozzle with heaters. The plastic starts to melt.
- The molten PET plastic leaves the nozzle and enters a basin of cold water, which is located on a rotating table. The rotation of the table will prevent sticking of the material. The thread must be cooled as quickly as possible so that it becomes flexible and transparent. In this case, it can be used for 3D printing.
- Let the homemade filament dry well before printing. Since in the presence of a large amount of moisture, a thread of molten plastic will exit the extruder in the form of foam. It is recommended to dry the skeins of thread in a closed container with silica gel at a temperature of 50–60 °C. To do this, you can use the oven or simply place the container on the radiator. nine0010
When using ready-made filament for 3D printing on a printer, several nuances should be taken into account:
- Print the product on a cold table, the temperature of which does not exceed 35 ° C.
 This limitation of the temperature regime is due to the fact that the plastic must quickly cool down to a temperature below 70 ° C. Otherwise, the material may almost completely lose its strength properties.
This limitation of the temperature regime is due to the fact that the plastic must quickly cool down to a temperature below 70 ° C. Otherwise, the material may almost completely lose its strength properties. - Extruder temperature should be around 265°C. But it may differ depending on the printing speed and the type of plastic from which the filament is made. nine0010
- If the feed mechanism of the 3D printer is made of brass, then it is better to put a thin-walled rubber hose on the roller. It will not allow the PET thread to slide.
The pros and cons of using bottles to create plastic
The main advantage of recycling PET bottles for plastic 3D printing filaments is that you can save on the purchase of industrial filaments and recycle unnecessary packaging, which, when taken to landfills, greatly pollutes the environment .
Disadvantages of using homemade filament:
- you can print products only at a low speed, as the thread breaks when it is increased;
- requires a crusher to grind the material and a separate extruder to transport the plastic;
- It is not possible to print large items because the thread length is limited.

Making your own 3D printing filament is a great way to save on consumables and recycle unwanted PET bottles. Homemade filaments are close in properties to purchased ones. Therefore, they can be used to print small products of excellent quality. nine0003
- March 14, 2021
- 12917
Get expert advice
What is 3D printer filament and how to choose it?
December 3, 2021
To print objects on a 3D printer, he needs the appropriate material. 3D printers typically use special plastics that have different properties depending on their composition. These plastics are called filaments. And because of their shape, in the form of a thin thread, everyone is used to calling them that way. And you yourself choose which filament for a 3D printer to buy in order to get the desired result. nine0003
It is important to understand that during the printing process, the filament is heated, melted and extruded through the 3D printer's extruder nozzle. There are many 3D printing filaments used in printing today, from standard plastic filaments to metallic imitations or wood or flexible filaments.
There are many 3D printing filaments used in printing today, from standard plastic filaments to metallic imitations or wood or flexible filaments.
It's important to choose the right filament for your 3D printer. Using filament with the wrong diameter or settings will inevitably result in printing failure or damage to the printer. This can be avoided if you understand which filament is best for your printer and your part. All 3D printers have a unique set of temperatures, speeds, and features that you must also consider in order to buy the right filament. nine0003
Each filament has its own set of characteristics both in terms of appearance and physical properties. Each offers its own set of features that you need to know to optimize your printing. You also need to consider what properties are needed for the object you are printing. Will the material be used indoors or outdoors? Should the part move and flex, or should it be absolutely rigid? What forces will be applied to the object? What post-processing methods will be applied to the finished 3D print? It depends on what thread you need to buy. nine0003
nine0003
Of the many threads available, some are more popular than others. These are such filaments as ABS, PLA and PET/PETG.
ABS is popular because it is strong and impact resistant. It's this strength and moderate flexibility that makes it a great choice for 3D printing. In addition, it is easy to extrude from the nozzles of the printer, so it is easy to work with and can be bought anywhere.
PLA (polylactic acid) is a special type of thermoplastic made from organic materials such as corn starch and sugar cane. The main benefits of PLA are that it is safer and easier to use and does not contain toxic fumes to worry about. Compared to ABS, PLA allows you to print more aesthetically pleasing 3D parts, thanks to its unique luster and smooth appearance. nine0003
PET, also known as polyethylene terephthalate, is a stable and harmless plastic, odorless and fully recyclable. In its raw state, the thread has no color and is crystal clear. After exposure to cold or heat, the material quickly becomes opaque.













