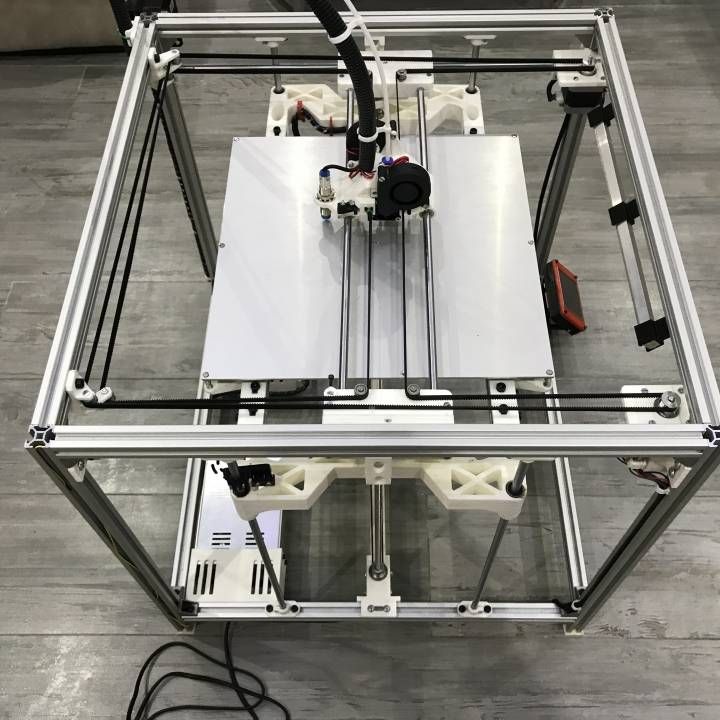
Heat bed 3d printer
Heat Beds in 3D Printing – Advantages and Equipment – Boots Industries
Why use a heat bed?Heat beds are used because they dramatically improve print quality by keeping the extruded plastic warm and thus preventing warping. Warping is a common condition caused by plastic on the edges of the part cooling down at an uneven rate when compared to the plastic inside of the part. The result is that corners warp up and deform your model.
Rafts are an effective ”no-heat bed” strategy to deal with warping when a heat bed is not available.In the past, techniques such as the raft (building parts on top of a ‘raft’ of material which is larger than the final part onto the build surface) were used to prevent warping by increasing the surface area of the part (and increasing it’s adhesion – thus fighting warping).
Derived from the raft, mouse ears are a clever and effective technique to make sure that the corners of your prints are well secured to the platform and won’t lift. Although they offer greater adhesion by increasing the surface area for your part to grip onto the bed, they are not 100% effective without a heat bed. Sometimes the warping forces are simply too great and can overcome the mouse ears.
Heat beds work to prevent this warping effect by keeping your part warm during the whole printing process which keeps the material at or above heat-deflection temperature (the temperature at which it is malleable). Keeping the parts in the heat-deflection range ensures that the part remains flat on the print bed. Heat beds, in combination with other tools to increase adhesion, will be covered in this article to bolster your ability to fight unwanted effects and improve your printing quality.
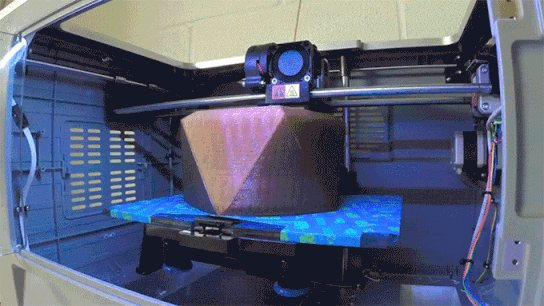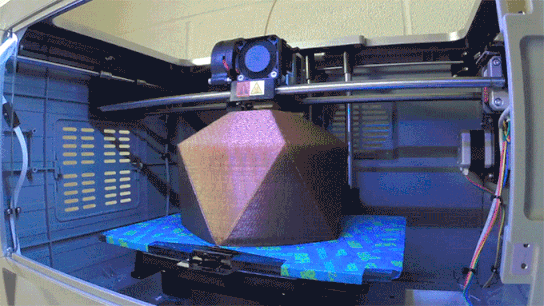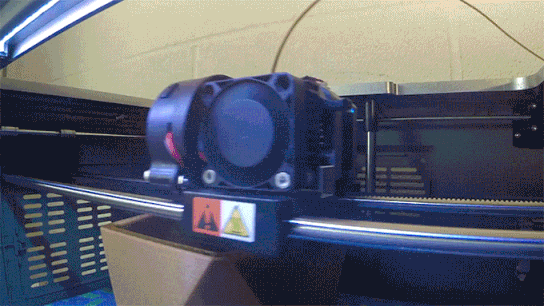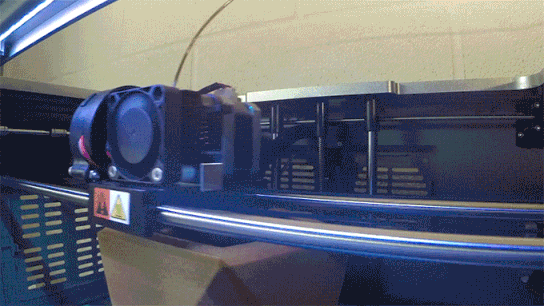
The following video shows what happens with no heat bed and no adhesive added to the glass. It depicts what can typically happen when printing on a non-sticky platform with no heat bed – Disaster!
No heat bed, print stuck to the extruder. Disaster!No adhesive used; a dramatic result and wasted PLA!
Disaster!No adhesive used; a dramatic result and wasted PLA!There are several types of heat beds & heating elements. We specifically discuss the PCB heat bed, the polyamide film heater (kapton film heater) and the aluminium clad heater. You can find a more exhaustive list of heater types here.
Types of heat bed
Regardless of the heat bed you are using, you should generally use these temperatures (heat deflection points) for PLA and ABS:
| PLA | 50-60°C |
| ABS | 100-110°C |
The MK2A heat bed (200mm x 200mm) is a good example of a PCB heat bed. These heat beds are used by many 3D printers and our own (Rostock V1.0) due to their great performance and affordability. This particular heat bed has 2 integrated LEDs and an integrated resistor which makes it rather ‘plug and play’ when compared to other solutions.
You can generally expect a simple & clean implementation with these heat beds thanks to the 5 holes available for leveling and installation purposes. They require little vertical clearance when compared to a stainless steel sheet mounted with aluminium clad resistors and offer an even heat distribution. The cons is that they can be slow to heat up especially when used with another surface such as a glass pane.
Kapton (Polyamide) film heaterKapton or polyamide is well know as a tape of choice for print surfaces, because of its heat resistance, smooth finish and high adhesion for PLA. Now think about two films of polyamide with a heating element sandwiched in between, now you have a polyamide film heater. Obviously, these are very thin, easy to install with an adhesive back, reliable and heat really fast. They have an integrated thermistor and are provided, unlike the PCB heat bed, in an unlimited variety of shapes. For these reasons, this is the type of heater foil we use on our latest 3D printer (BI V2.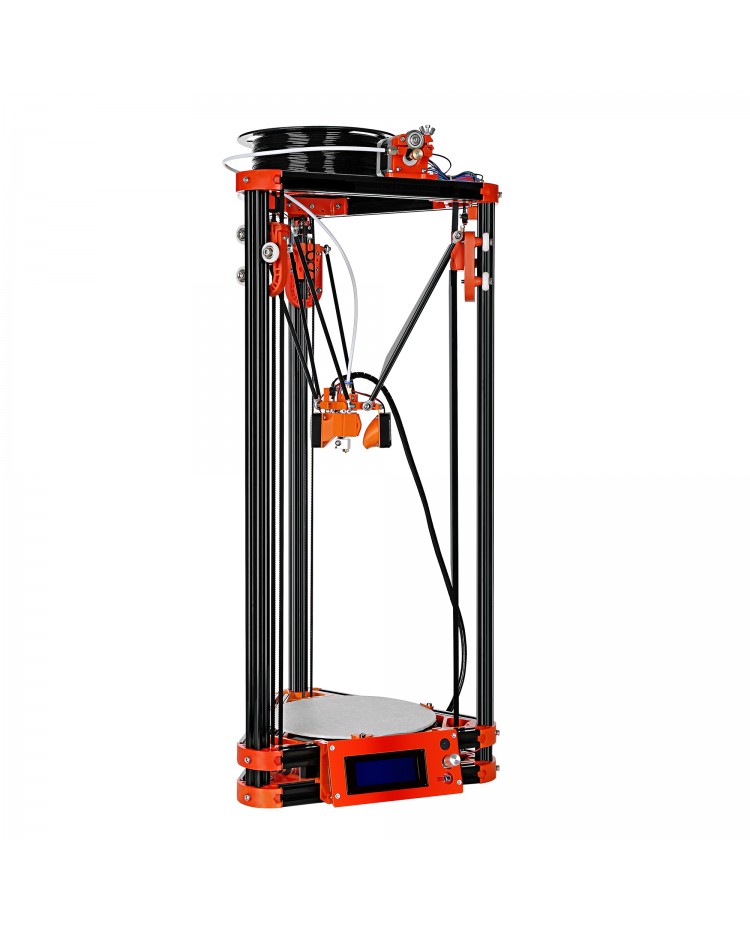 0).
0).
This type of heaters is both very efficient and inexpensive, but they require more installation steps than the last two heat source we’ve discussed. As a matter of fact, they need to be screwed onto a surface, normally a stainless steel or aluminium plate. Then, the electrical circuit needs to be completed with a thermistor and an insulator if you have any temperature sensible elements under the print bed. Finally, it’s also a good idea to use thermal paste between the clad heater and the surface to be heated.
Surface to use with heat bedsAll the heat sources mentioned in this article will typically need an added surface to preserve the quality & integrity of the heating element over time or to provide protection in the event of a hotend collision. Obviously, the aluminium clad heaters are always used in conjunction with a surface.
The recommended print surface to be used with a PCB or Polymide film heater is a borosilicate glass, or when unavailable, a tempered glass. For the PCB heat bed, we recommend layering Kapton tape or using a thin glass (2 mm) over-top.
For the PCB heat bed, we recommend layering Kapton tape or using a thin glass (2 mm) over-top.
In addition to a heat bed surface, most users will experience that some form of adhesive or method is required to make PLA or ABS stick properly. This is where Kapton tape, painter’s tape, glue or hairspray comes into play.
Painter’s tape is an ideal product for printing ABS with a heat bed because of it’s textured surface increasing adhesion. We’ve used it with varying degrees of success and others report great results as well.
As far as PLA is concerned, our experience is that it doesn’t stick well to heated painter’s tape and that painter’s tape itself doesn’t stick well to the glass when heated. However, we found that PLA sticks very well to Kapton tape which is typically layered to cover the entire print area. The Kapton tape needs to be periodically replaced and this process can be tedious. To remove this obstacle, you can buy Kapton tape in wider rolls which means you need to layer a lesser amount of strips onto the print area to fully cover it.
Glues are frequently used to make sure your print “sticks” to the print surface. The most common glue we have seen is the typical arts and craft glue stick (Elmers). This technique works well with ABS in conjunction with painter’s tape.
In the PLA department, we prefer to use hairspray on a glass surface. The glass surface is really flat and produces a really smooth finish for our parts. Another advantage of hairspray is that it can be applied in a few seconds and will typically create a thin film that strips away with the printed part or is easily scraped with a wood chisel or similar tool. Sometimes we use a wet rag to remove hairspray residue from the underside of parts when it’s not desired for aesthetic reasons.
What we recommendWe recommend the PCB heat bed or Polyamide film heater in conjunction with a glass surface. For PLA we always apply a thin coating of hairspray and so far this simple combination has been producing great results.
3D Printer Heated Bed - Everything About Heated Beds
ADVERTISEMENT
Table of Contents
With the advancement in 3D printing, a lot of new research and experiments have surfaced. Many of them are tailored towards finding the best way to increase the first layer adhesion.
And, we all know why it is so important. A 3D printer heated bed can handle that part pretty well. Although there are other alternatives to work with the first layer, nothing beats this one.
Most importantly, print beds are a very crucial part of the overall design of the machine. This is because, without a print bed, you won’t be able to create your models.
Hence, realizing how you can make the best use of it must be your first priority to know. Understanding the different types of heated beds and their usefulness would help you select the right device.
Understanding the different types of heated beds and their usefulness would help you select the right device.
So, before we progress to explore everything about the heated bed, let us get an idea about what 3D printing is. Most of us already know about it, but a quick recap will only ensure that all our readers are on the same page.
ADVERTISEMENT
What is 3D Printing?
We have been hearing about additive manufacturing or 3D printing for a long time now. There are few lucky ones who even had the chance to work with this technology. But it’s never late whenever you decide to do something.
3D printing has emerged as one of the most revolutionary technologies and is propagating to impact the entire ecosystem of manufacturing units.
But what the technology really entails or means? This is a process where the 3D printers create layers of 3D models, one over the other, to create a complete item.
There are various 3D Printing processes available. For instance, FDM, SLS, SLA, and many others. These differ in the way the layers are created and connected. However, the basics remain the same. The layers forms over each other to build the entire 3D model.
For instance, FDM, SLS, SLA, and many others. These differ in the way the layers are created and connected. However, the basics remain the same. The layers forms over each other to build the entire 3D model.
3D printing has made the creation of extremely detailed models and structures possible at much faster and affordable rates. But certain precautions need to be taken while using the printer to ensure the part being printed adheres closely to the desired specifications.
However, 3D printing comes with its own challenges. And, the biggest setback is when the layers rapidly heat and cool down.
One of the serious problems that occur because of such a process is wrapping. It changes the shape of the 3D model and deforms it. Hence, running the entire 3D printing project.
To cater to the problem, the 3D printer heated bed surfaced. These print beds are very successful in allowing the proper cooling of the layers.
At the same time, these help in controlling the temperature while the 3D Printing is in process. Hence, further resulting in proper bed adhesion.
Hence, further resulting in proper bed adhesion.
ADVERTISEMENT
What is a 3D Printer Heated Bed?
Coming back to the topic in the light, we must answer the question: What is a 3D printer heated bed? While we have already discussed in brief about the way heated beds are useful, let us find out more about them.
Heated Beds Using PCBs as Heating Element
A 3D printer heated bed design can differ. Among the most common types, the heated bed makes use of circuity boards or PCBs as the heating elements.
These are available with the budget 3D printers. However, these won’t last long if your 3D printing projects are complex and require frequent jobs with 3D printers. In short, they are meant for smaller projects that do not take much longer to complete.
The reason why these are not suitable for complex 3D printing is that the PCBs are made of copper s and aluminum strips.
And, these are susceptible to deformation when subjected to heat for longer periods. Over time, the heated beds will fail to do the task for which it was chosen in the first place.
Over time, the heated beds will fail to do the task for which it was chosen in the first place.
There is one more problem that won’t be acceptable to many. These take a longer time for heating up. You can actually get rid of that problem. But you may have to spare some more bucks to get the larger power supply source connecting the bed.
ADVERTISEMENT
Heated Beds Using AC Silicone Encapsulating Heated Element
One more type of heated bed is the one that uses AC silicone encapsulating heated elements. To design the arrangement, the heated element is stuffed between glass pieces and a thermal insulator.
This is to minimize the excess leakage of heat and to deliver the maximum amount of heat to the printing surface. Hence, realizing the efficient design for the creation of 3D printer heated bed.
Moreover, the electricity consumption is also less. And, they can work for longer without giving any trouble to the users.
You can 3D print without much hassle when using the heated bed with AC silicon encapsulating heated element.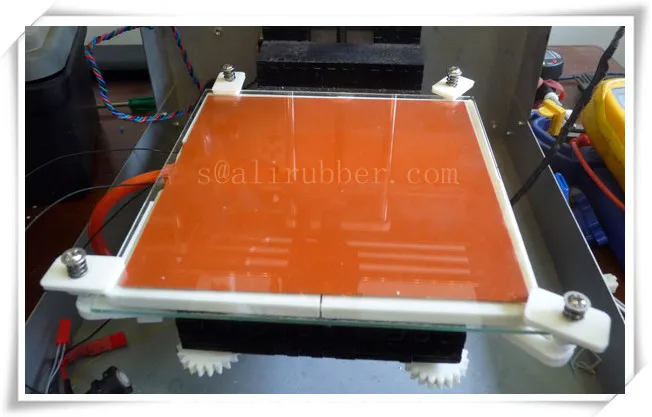 In addition, these are highly portable too. With all the right perks, it is worth spending a little more if your goal is to 3D print for long.
In addition, these are highly portable too. With all the right perks, it is worth spending a little more if your goal is to 3D print for long.
Working of 3D Printer Heated Bed
The 3D printer works by extruding the plastic filament over the printed bed. Right after coming out of the extruder, the filament starts cooling.
As we all know, with cooling shrinkage comes hand in hand. The problem arises when the layer does not cool consistently at all points. This leads to uneven shrinking and ultimately, warping of the entire 3D model.
To avoid plastic from cooling at different rates at varied points, heated beds were introduced. The job of the 3D printer heated bed is to make sure that the parts do not cool completely unless the printing is still in process. This allows for a more even shrinking process.
In short, the heated beds mainly take care of two things. First of all, by increasing the surface energy of the print bed, the heated bed strengthens the bonding of the top layer.
Plus, it ensures that the bottom layer stays hot enough for avoiding the warping issue in any stage of the 3D Printing process. Hence, the heated bed maximizes the efficiency and avoid excessive cooling of the layers.
When the filament is deposited on the print bed through the extruder, it carries with itself a certain degree of heat. For the best results, the heated bed temperature must be below the glass point.
This is to turn the liquid filament in solid form. The temperature sensor is responsible for maintaining the required heat of the print bed.
You may have to go through a few trial and error to understand the correct calibration of your machine based on the filament you use. This is because the melting point of filament differs widely.
ADVERTISEMENT
Few 3D Printer Heated Bed DIY Designs
We have already discussed the most basic one before. Let’s elaborate on the topic a little bit.
Apart from the PCB and AC Silicon encapsulating heating element, there are other DIY designs to replace your non-heated bed with a heated one.
Polyamide Film Heater
Polyamide which we also call Kapton is already providing huge benefit as a tape for print surfaces. These are best when used with PLA filament.
By providing efficient heat resistance, and high adhesion for printing with PLA, these are already very popular. These also help in increasing the surface finish of the 3D models.
However, you may not know that when coupled with a heating element which when sandwiched between two films of Polyamide you can come up with a Polyamide film heater.
Plus, they are simple to install as well by adding an adhesive to the back. These heat up really fast.
Moreover, these can be prepared in different shapes and sizes. And, are easily portable. Hence, a great choice for many 3D printing experts as well as beginners.
3D Printer Aluminium Clad Heater
If you are looking for the most effective as well as the inexpensive solution, this is what you must look for. However, do not forget, you may have to go through more steps for installing these heaters to your 3D Printer.
Not to forget, you must also require to screw these onto a surface. Usually, users suffice the arrangement with a stainless steel or 3D printer aluminum heated bed.
Later, you must complete the electric circuit arrangement using a thermistor and an insulator. It is the best way to go about it even if you do have any temperature sensible elements stuffed under the print bed.
Last but not the least, a thermal paste must stay between the clad heater and the build surface. This further enhances the healing process and brings more perks for the users.
ADVERTISEMENT
Do I Need A Heated Bed?
Because a lot of 3D printers do not have a heated bed, the question is: Is heated bed required? It is okay to be attentive to the details.
You may have heard that PLA does not need a heated bed to work with. Or, you may also have listened about printing ABS only with a printed bed. But what is the actual story?
But what is the actual story?
You do need a heated bed when 3D printing with ABS material. But why is that so? ABS has the characteristic to contract more than other filaments.
Hence, the chances of warping become higher when printing with ABS. However, with the inclusion of a heated bed, the material finds it easy to attach to the bed surface, while reducing the chances for contraction.
Now, what about PLA. Do we require a heated bed or not? In the case of PLA, we do not always need a Heated Bed. However, if you wish to 3D print is longer, or the bottom surface is larger, it is better to use a heated bed to eliminate the chances of probable problems.
Not just that, you must also understand the optimal temperature that you must maintain when working with different materials.
For instance, when working with ABS, you must heat your print bed to 110°C. On the other hand, PLA can be settled for a lesser temperature of around 60°C.
It is very easy to set the temperature of the heated bed with the help of the 3D Slicer. So, you can make the changes as and when required.
So, you can make the changes as and when required.
ADVERTISEMENT
Caution to Take When Working with Heated Beds?
Heated beds are maintained at a very high temperature. Though we cannot get rid of them because of the many benefits they add to the printing process, we must take the necessary precautions to work around them.
Users must carefully avoid injuries by staying alert and following preventive measures.
These heated beds, when it comes in contact with the skin can end up leaving scars for life. These are very hot and you must avoid any direct contact with the print surface.
If you have kids around, you must take the necessary precautions when working with the 3D printers. If possible, you can go to the closed chamber.
This would anyway help to enhance the 3D print results by letting you maintain a consistent temperature around the build surface.
You may get yourself in other problems when the heated bed is not installed properly. In case, the legs of the bed aren’t positioned evenly, or the bed isn’t placed on a uniform surface, it would lead to imperfection in the 3D models.
In case, the legs of the bed aren’t positioned evenly, or the bed isn’t placed on a uniform surface, it would lead to imperfection in the 3D models.
It is a good idea to purchase the 3D printer with its own heated bed that comes with the package. This is to ensure that the two combos work together in harmony.
Or else, you may find it difficult to fit the parts from different vendors together because of the difference in the temperature gradient.
The Conclusion
It is a very common mistake that we make when avoiding to look for more details about the crucial components of the 3D printer. But we must not do that.
3D printers are expensive and before buying one, we must understand what we should look for, depending on our needs.
And, even if a 3D printer heated bed seems to be something not needed at the moment, it may help you stretch your goals later.
So, understand the benefits of the same and look for 3D printers that offer a heated bed already.
Why do I need a heated table for a 3D printer?
3DPrintStory 3D printing process Why do you need a heated table for a 3D printer?
With the development of 3D printing, a lot of new research and experiments have appeared. Many of them are aimed at finding the best way to increase the adhesion of the first layer. nine0005
And we all know why this is so important. A standard heated 3D printer table will do the job. Although there are other alternatives when working with the first layer, nothing compares to this one.
Most importantly, 3D printer tables are a very important part of the overall design. In fact, without a table, you will not be able to create physical embodiments of your 3D models.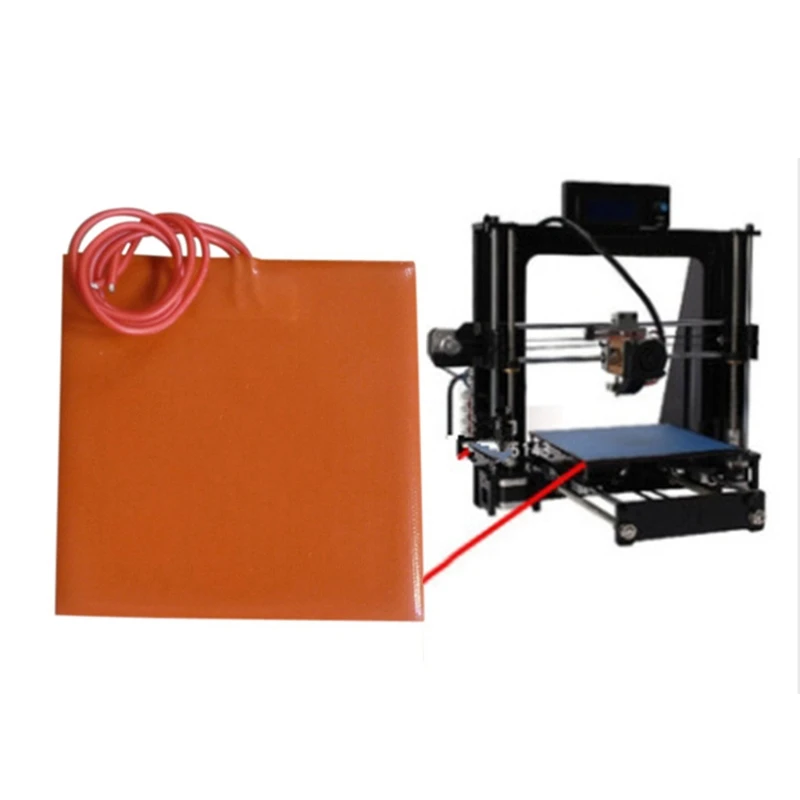 Therefore, understanding how you can make the best use of the table should be your top priority for quality 3D printing. Understanding and navigating the different types of heated tables and their features will definitely help you choose the right 3D printer and implement your own ideas. nine0005
Therefore, understanding how you can make the best use of the table should be your top priority for quality 3D printing. Understanding and navigating the different types of heated tables and their features will definitely help you choose the right 3D printer and implement your own ideas. nine0005
But before we get into all the 3D printer heated tables, let's get to the bottom of what 3D printing is. Most of us are already aware of this, but a brief overview will ensure that we are on the same wavelength in the context of the current article.
What is 3D printing?
We have been hearing about additive manufacturing or 3D printing for a long time. And the lucky ones who had a chance to work with this technology at least once are becoming more and more every day. nine0005
3D printing has become one of the most revolutionary technologies and is spreading very quickly, influencing the entire ecosystem of production, industry and hobby.
3D printing is a process in which 3D printers create layers one on top of the other to create a finished product of the desired shape and dimensions.
3D printing may differ in the principle of creating 3D models. For example, there are FDM, SLS, SLA and many others. They differ in the way the layers are created and connected. However, the fundamentals remain the same. Layers are stacked on top of each other to build the entire 3D model. nine0005
3D printing has made it possible to create extremely detailed models and designs in a short time and in many cases cheaper than classic manufacturing processes. But when using a 3D printer, certain precautions must be taken to ensure that the finished product exactly matches the desired characteristics.
However, 3D printing has its own problems. And the biggest of them is too fast heating and cooling of the layers of the 3D model. One of the major problems that arise from improper heating/cooling is shrinkage. It changes the shape of the 3D model and deforms it. Therefore, in this case, we get low-quality products. nine0005
To solve this problem, heated tables for 3D printers have appeared. These tables, among other things, are designed to maintain the required temperature of the first layers of the model and the entire model as a whole. They help control the temperature during the entire 3D printing process. Therefore, this additionally results in proper adhesion of the first layer throughout the entire 3D print time of your model.
These tables, among other things, are designed to maintain the required temperature of the first layers of the model and the entire model as a whole. They help control the temperature during the entire 3D printing process. Therefore, this additionally results in proper adhesion of the first layer throughout the entire 3D print time of your model.
What is a heated 3D printer bed?
Returning to the main topic of the article, we must answer the question: what is a heated table for a 3D printer? Although we have already briefly discussed the usefulness of heated tables, let's learn more about them. nine0005
Heated tables using printed circuit boards as heating element
Heated tables for 3D printer designs may vary. Among the most common types of heated tables, mounting or printed circuit boards are used as heating elements. They usually come with budget 3D printers. However, this solution is not very suitable if your 3D printing projects are complex and require frequent work with a 3D printer. In short, they are designed for small projects that do not take much time to complete. nine0005
In short, they are designed for small projects that do not take much time to complete. nine0005
The reason why they are not suitable for complex 3D printing is that PCBs are made of copper and aluminum plates, and they are prone to deformation when heated for a long time. Over time, heated plates will no longer perform the task for which they were originally designed.
There is another problem that may arise. They take longer to heat up. You can get rid of this problem, but for this you will need to replace the power supply with a more powerful one. nine0005
Heated tables using AC silicone encapsulating heating element
The second type of heated 3D printer table is one that uses silicone to encapsulate the heated elements. To create a structure, a heated element is inserted between pieces of glass and a heat insulator.
This is to minimize excess heat leakage and to deliver maximum heat to the table surface. In addition, electricity consumption also becomes smaller. And they can work longer without causing any problems to users. nine0005
And they can work longer without causing any problems to users. nine0005
This version of the heated table design is much more reliable and can last you much longer. In addition, the bill for consumed electricity will also be reduced due to minimization of losses for heating the table.
3D printer working process with heated table
The 3D printer works by extruding a plastic filament onto the table. Immediately after exiting the extruder, the material begins to cool. As we all know, shrinkage goes hand in hand with the cooling process. The problem arises when the layer is not cooled uniformly at all points. This leads to uneven shrinkage and, ultimately, to deformation of the entire 3D model. nine0005
To avoid cooling the plastic at different rates at different points, heated tables have been developed. The job of a heated 3D printer bed is to ensure that the parts do not cool completely until the 3D print is complete. This allows for a more uniform shrinkage process.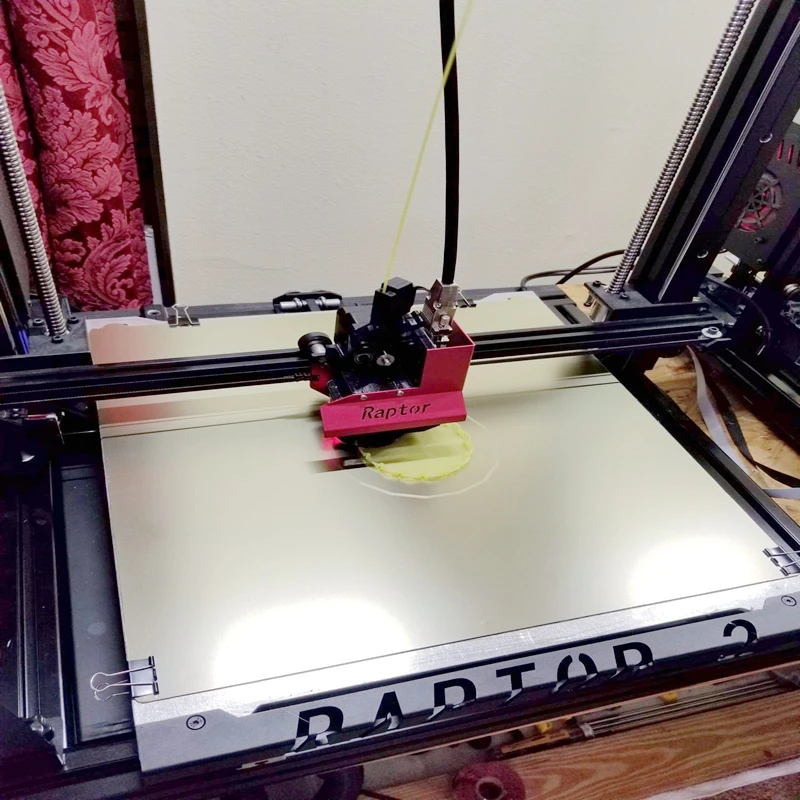
In short, heated tables basically take care of two things. First of all, by increasing the surface energy of the printing table, the heated layer enhances the adhesion of the first layer. Secondly, a sufficiently high temperature of the lower layer is ensured, which avoids the problem of deformation at any stage of the 3D printing process. Therefore, the heated bed maximizes efficiency and avoids excessive cooling of the layers. nine0005
When material hits the 3D printer bed through the extruder, it carries a certain amount of heat with it. For best results, the temperature of the heated bed should be below the glass transition point. This should turn the liquid thread into a solid form. The temperature sensor is responsible for maintaining the required temperature of the table.
You may need to experiment to find the optimum table temperature, as the melting point of different materials and manufacturers is different. nine0005
Several DIY Heated Table Designs for 3D Printer
The basics have already been discussed above, now let's look at some interesting DIY solutions.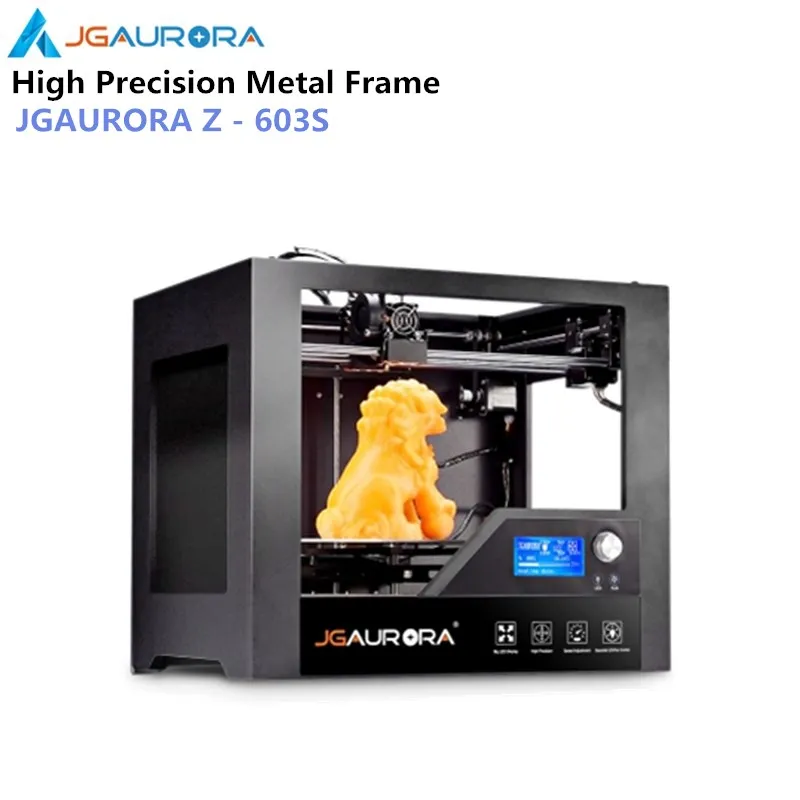
In addition to the PCB and AC sealed heating element, there are other DIY designs to replace your table with a heated table.
Polyamide Film Heater
Polyamide, which we also call Kapton, offers a huge advantage when used as a tape for printable surfaces. They are best suited for use with PLA plastic. Providing effective heat resistance and high adhesion for PLA printing, this film is very popular. The use of this film helps to improve the surface quality of 3D models. nine0005
However, you may not know that in combination with a heating element sandwiched between two polyamide films, you can get a polyamide film heater. In addition, they are easy to install by adding glue to the back. They heat up very quickly. In addition, they can be of different shapes and sizes. So this is a great option to upgrade your 3D printer table.
Aluminum Coated 3D Printer Heater
If you are looking for an efficient and cost effective solution, this is the one for you.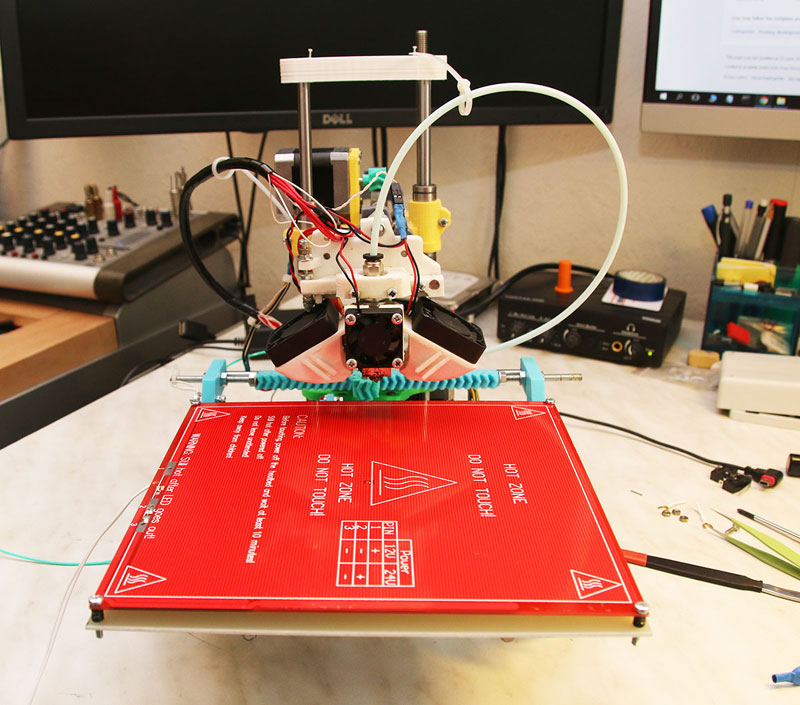 However, keep in mind that installing these heaters on your 3D printer may require some work. nine0005
However, keep in mind that installing these heaters on your 3D printer may require some work. nine0005
After installing the heaters, it is necessary to close the electrical circuit using a thermistor and an insulator. Last but not least, the thermal paste must remain between the lined heater and the build surface.
Do you need a heated table for your 3D printer?
Since many 3D printers do not have a heated bed, the question is, do you need a heated bed?
You may have heard that working with PLA plastic does not require a heated table. Or perhaps you've only heard of ABS printing on a heated table. But what is the truth? nine0005
When 3D printing with ABS you will need a heated table. Why is that? ABS tends to compress more than other materials. Therefore, the likelihood of deformation increases when 3D printed using ABS. With the table heating turned on, the material will better set on the first layer, minimizing potential deformations at the edges of the 3D model.
What about PLA? Do we need a heated table or not? In the case of PLA, heating is not always needed. However, if you want to print large models, it is better to use a heated bed to eliminate the possibility of possible problems. nine0005
As mentioned above, you also need to know the optimum temperature for your material. Otherwise, there will be no point. For example, when working with ABS, it is recommended to heat the table to 110 ° C. On the other hand, when using PLA, it is worth stopping at 60 ° C. By the way, the temperature of the 3D printer table is set at the stage of processing the model in the 3D slicer.
3D Printer Heated Table Precautions
Heated tables maintain very high temperatures, so you should take the necessary precautions. nine0005
Heated tables can leave scars for life if they come into contact with the skin. They are very hot, so direct contact with their surface should be avoided.
If you have children, you must take the necessary precautions when working with 3D printers.
If the heated table is not properly installed, you may experience other problems. If the legs of the table are uneven or the table is not placed on a level surface, this can lead to defective 3D models. nine0005
Conclusions
Heated table is an almost essential attribute of a 3D printer, which will provide high-quality 3D printing using various types of materials. If possible, it is better to buy a ready-made heated table, and not develop it yourself, since many subtle nuances in the assembly will already be taken into account. Remember to take precautions when working with heating elements and good luck with your 3D printing.
How to choose a 3D printer, or why you need a heating table and a closed chamber / Sudo Null IT News0001
Different models of 3D printers differ in the maximum heating temperature of the printing table. In this article I will talk about the different categories of printers for this very important parameter. After all, the range of materials that the printer can print also depends on the heating of the table. I will also touch on the question of why a closed chamber is needed.
After all, the range of materials that the printer can print also depends on the heating of the table. I will also touch on the question of why a closed chamber is needed.
Printers without underbed heating
They are able to print only one type of plastic - PLA. This material is suitable for prototypes, souvenirs, and when heated to 60 ° C, it becomes soft and the product loses its shape. With great effort on such printers, you can try to print with other materials, but the result will not please you. Usually these are Prusa-type printers with a movable table, but there are also "cubes". nine0005
Problems occur due to shrinkage (reduction in size) of the plastic product after cooling. If the plastic shrinks (and this is almost all plastics, except for PLA), then the edges of the product begin to tear off the table on which the print is being made, the geometry of the product is irreparably damaged or it completely peels off from the table, risking damage to the print head, which continues to move.
The plus (or minus?) of such printers is that manufacturers save not only on the table heater, but on everything else. Therefore, these are cheap printers. nine0129 At the same time, in the description of such printers, the absence of table heating may not be indicated in any way (be careful!), but the possibility of printing with other plastics, except for PLA, is sometimes indicated, which misleads the buyer. And you will encounter printing problems after purchasing such a printer.
The best known non-heated printer is the Makerbot Replicator 2
From Chinese models - TEVO Michelangelo
Next, the story will go about more interesting printers with a heated table from 100 ° C to 170 ° C, which are designed for printing with plastics with shrinkage - from classic ABS to Polycarbonate. The higher the maximum temperature of the table, the more plastics you can print, because. heating of the table prevents damage to the part due to shrinkage during printing. At the same time, the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the stronger the table should be heated. nine0005
At the same time, the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the stronger the table should be heated. nine0005
Printers with heated table up to 100°C
Suitable for printing with many plastics, except for technical ones. At the same time, printing large products with popular ABS plastic at such a low temperature will be problematic. In reality, ABS requires from 110°C to 130°C on the table, especially for cheap brands with high shrinkage, which are very widely represented on the market. Printing with more interesting technical plastics - nylon, polypropylene, polycarbonate, on such printers will not work at all. nine0005
Chinese printers include Anycubic, various Flashforge models.
Printers with heated table up to 120°C
Perfect for ABS printing. But, if you need to print large ABS products, then such a printer also needs a closed print chamber. It is needed to maintain a high air temperature around the printed product, which reduces shrinkage during printing along the entire height of the product. The higher the chamber temperature is kept, the better for printing! nine0005
The higher the chamber temperature is kept, the better for printing! nine0005
And this is where things get interesting. Those manufacturers who have conventional models with an "open chamber" cover them with a plastic transparent "aquarium" on top, and sellers offer them under the guise of printers with a closed chamber! Of course, such a solution is cheap, but the larger the volume of the chamber, the more difficult it is to maintain a high temperature in it, and in this case the volume increases significantly. This means that in such printers, the temperature in the chamber will be lower than necessary for high-quality printing.
Even more interesting is the situation when the printer is closed on the sides, but completely open on top and does not have any cover at all. At the same time, sellers pass them off as printers with a closed camera (be careful!).
The question is, why not cover any printer from above completely, without increasing the volume with an "aquarium"? Yes, because all simple models are designed so that a bundle of wires rises vertically from the extruder (print head), as well as a tube through which a thread with plastic is fed (look carefully at the photos of the printer from all sides when choosing). All this sticks out from the top of the printer and does not allow it to close normally. This is especially true for printers with remote Bowden plastic feed, where the motor pushing the plastic thread is placed on the printer body. nine0005
All this sticks out from the top of the printer and does not allow it to close normally. This is especially true for printers with remote Bowden plastic feed, where the motor pushing the plastic thread is placed on the printer body. nine0005
It would seem, so what? Well, turn the wires to the side of the extruder so that they do not stick up and do not interfere ... However, for this you need to apply design solutions with a horizontal arrangement of wires and tubes suitable for the extruder, and design the printer initially taking into account the closed chamber.
Interestingly, even some expensive closed imported printers have a large height and an increased clearance inside the chamber between the extruder and the top cover, because. in them, the designers could not (did not want to) turn the plastic supply tube horizontally. So, in them the volume of the chamber is larger than necessary. nine0005
Most of both imported and domestic printers fall into this category.
Printers with heated bed from 130°C to 150°C
These printers are already quite well developed by designers. Most of these printers do have a well-heated closed chamber with side wires and extruder tubes. They can print both large products made of ABS plastic, and small products made of technical plastics - nylon, polypropylene, polycarbonate. nine0005
Of the domestic printers in this category, we note Picaso3D and PrintBox3D.
Printers with heated table up to 170°C
Here we come to closed printers with a very high table temperature. These printers have been engineered to take into account the trend in 3D printing to increase operating temperatures, which means the ability to print with increasingly durable, heat-resistant plastics. There are few such printers, they are expensive, with rare exceptions.
Why heat the table so much? The fact is that the higher the melting temperature of the plastic, the more the table and the surrounding air in the chamber must be heated, otherwise the product will peel off the table during printing and printing will be interrupted. So, for polycarbonate, the extruder print temperature can reach 310 ° C. If small details can be printed at a table temperature of 130°C, then medium ones are already from 150°C, and large ones can be kept on the table only at 170°C.
So, for polycarbonate, the extruder print temperature can reach 310 ° C. If small details can be printed at a table temperature of 130°C, then medium ones are already from 150°C, and large ones can be kept on the table only at 170°C.
In addition, these printers have the potential to print other refractory plastics. For example, at an extruder temperature of 400°C, PEEK (polyether ether ketone) can be printed. This refractory and durable plastic is used in aviation and space technology. nine0005
In this high-temperature category, we note the Chinese Intamsys FUNMAT HT printer with an extruder temperature of up to 450°C, a bed temperature of up to 160°C.
Of the domestic ones, we cannot fail to mention the Faberant Cube
3D printer with extruder temperature up to 340°C, bed temperature up to 170°C.
Terminals
If you want to print with different plastics, and not just one PLA, then the 3D printer must have a heated bed.