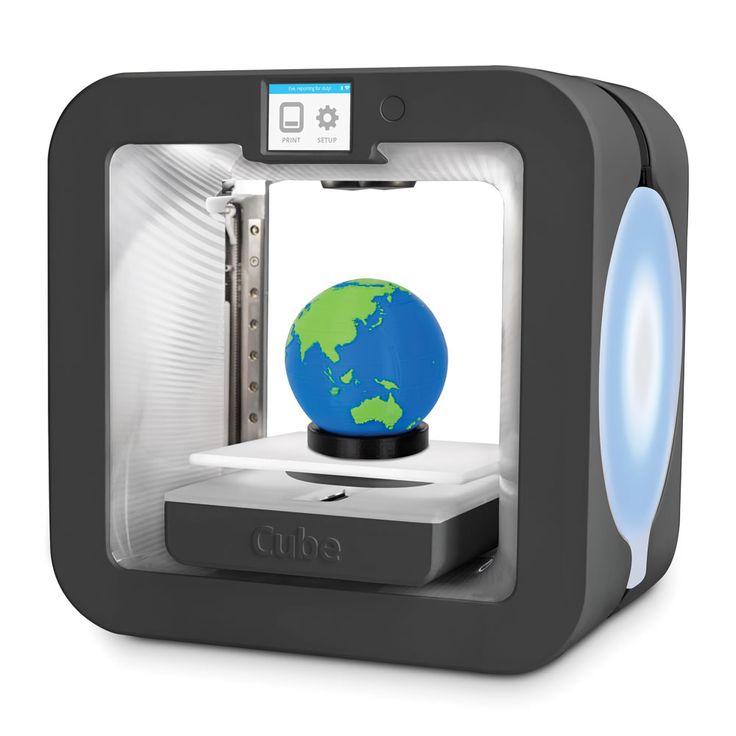
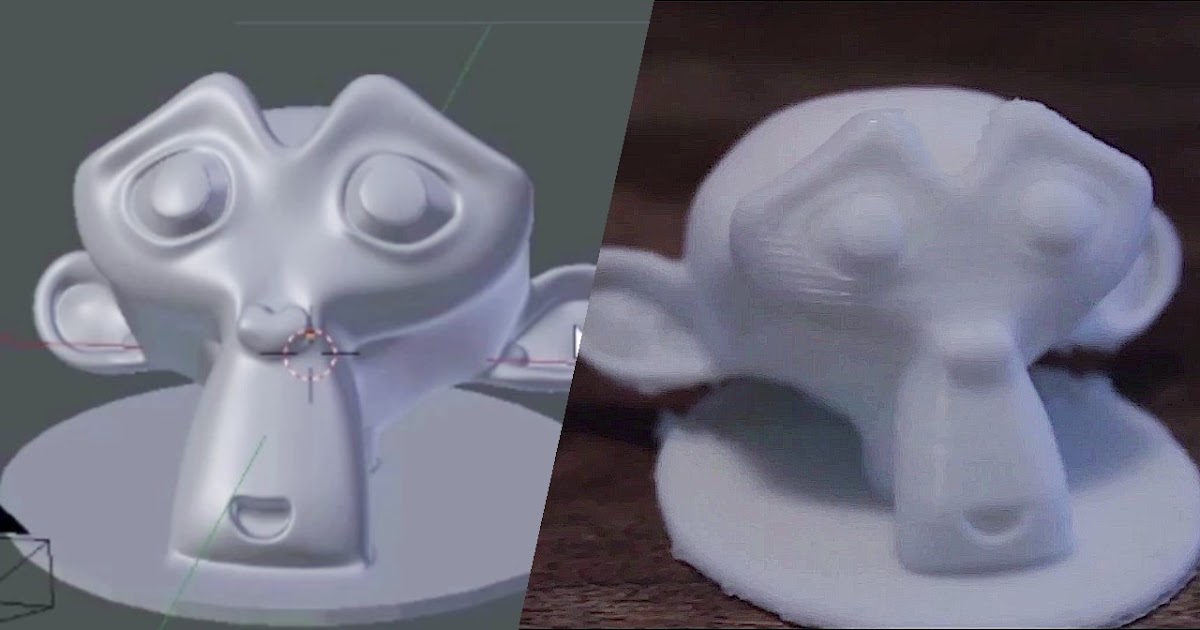
3D scanner and printer in one
Best 3D Printers with Integrated 3D Scanner
- Author
- Recent Posts
Martin
Martin has a M.Sc. in physics and has gained many years of experience in industry as a lab manager and quality assurance manager. He has now tested dozens of 3D printers and is happy to share the collected experience with each new article.
Latest posts by Martin (see all)
- BQ-Hurakan vs. Ender-3 V2 Neo | Comparison, Pros & Cons - November 10, 2022
- Mouse Ears (Brim Ears) vs. Warping in 3D Printing – Guide - November 10, 2022
- Ender-5 S1 vs. Ender-5 Pro | Comparison, Specs, Pros & Cons - November 9, 2022
Disclosure: Links marked with * are Affiliate Links. I earn from qualifying purchases if you decide to make a purchase through these links – at no additional cost for you!
The latest trend in the 3D printer scene is devices with a combination of 3D printer and 3D scanner. While it used to take several devices to successfully complete a 3D printing project, this will soon be a thing of the past.
There are now 3D printers with integrated 3D scanners for the hobby sector as well. They combine the advantages of both groups of devices and are so well matched that compatibility is ensured and the price is usually lower than buying two separate devices.
This article shows you which combination devices are suitable and why.
Table of Contents:
- 1 Advantages of 3D Printers with Integrated 3D Scanner
- 2 The Best 3D Printers with Integrated 3D Scanner
- 2.1 XYZprinting da Vinci Color AiO 3D Printer/Scanner
- 2.2 Ultimaker S3 3D Printer (alternatively S5) plus Shining 3D EinScan-SE 3D Scanner
- 2.3 All-in-one printer “Zeus” from AiO Robotics
- 2.4 XYZ Printing da Vinci Jr. 1.0 3-in-1
- 3 The Combo for People Who Like it Simple
- 4 Related Questions
- 4.1 Why is there only a small selection of 3D printer and scanner combo devices?
- 4.
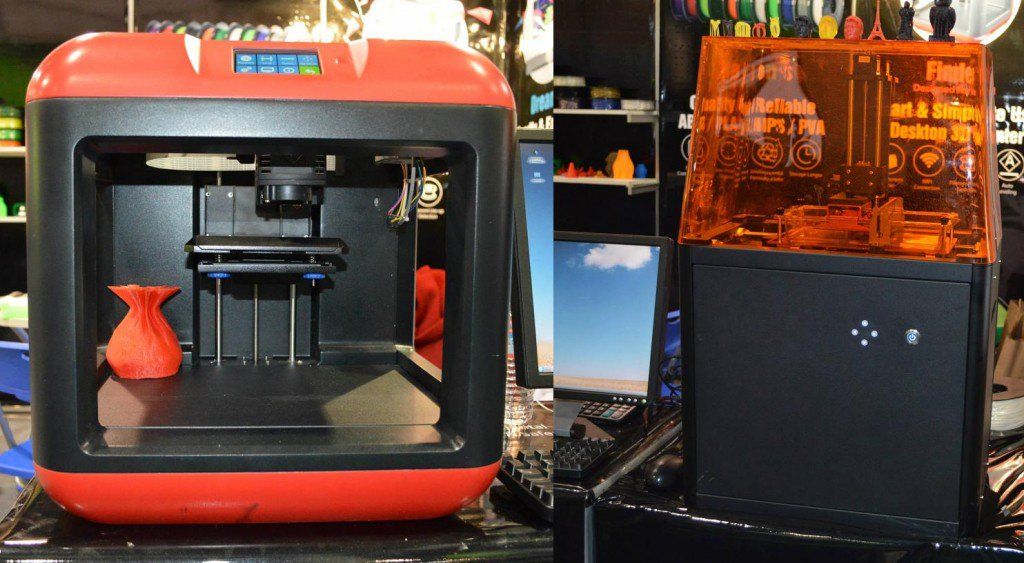 2 Do the scanners integrated in the printer work as carefully as the individual devices?
2 Do the scanners integrated in the printer work as carefully as the individual devices? - 4.3 Is the price of a 3D printer with integrated scanner higher than that of 2 individual devices?
- 4.4 Can I use the scanner integrated in my 3D printer for print objects from other printers?
- 4.5 Is the combination device suitable for scanning all sizes?
- 5 Conclusion
Advantages of 3D Printers with Integrated 3D Scanner
It is hard to imagine many 3D printing processes without 3D scanners. They are an essential milestone for improving and facilitating the modeling of a 3D printed object.
Because it is relatively tedious to constantly switch between multiple devices for a 3D printing project, there are numerous other reasons to have a single device of both 3D printer and 3D scanner:
- Faster results
- Improved resolution and accuracy
- Measurement errors can be avoided due to calibrated technology
- Space-saving (only one device instead of two)
- Optimally coordinated functionality of printer and scanner in one device
It goes without saying that two device modules in one device unit have an impact on the price.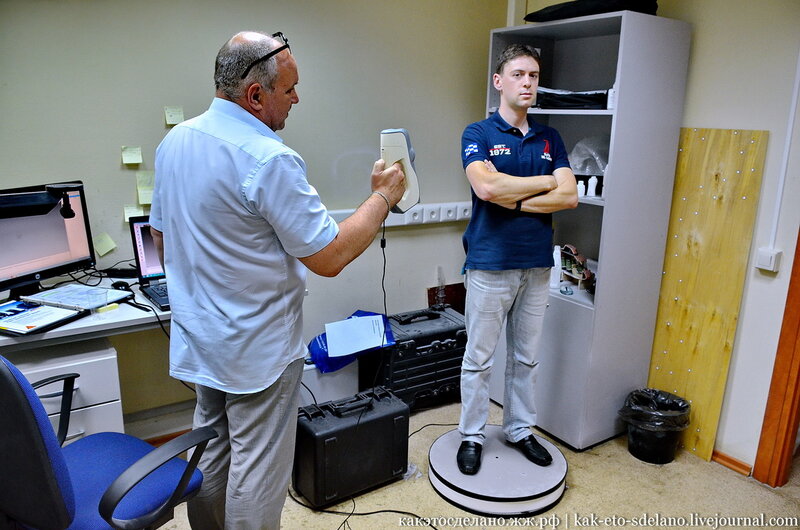 However, the purchase price for combination devices consisting of a 3D printer and 3D scanner is still at a lower level than the price for buying two devices.
However, the purchase price for combination devices consisting of a 3D printer and 3D scanner is still at a lower level than the price for buying two devices.
The Best 3D Printers with Integrated 3D Scanner
Among the combination devices of 3D printers with firmly integrated 3D scanners, a closer look reveals numerous differences. These are in the performance, in the equipment as well as in the price.
Therefore, think carefully about what you want to use such a 3D printing device for. Take your time and find the device that fits your needs. Furthermore, only a few manufacturers have decided to offer 3D printers and scanners in one device. Four of the best 3D combination devices are presented here for your orientation:
XYZprinting da Vinci Color AiO 3D Printer/Scanner
XYZprinting da Vinci Color AiO*Check Price at:
Amazon*
The XYZprinting da Vinci Color AiO 3D Printer/Scanner*, consisting of a 3D printer and 3D scanner in combination with numerous other elements, was already awarded the CES Innovation Award at CES 2018 and has taken the 3D printing scene by storm.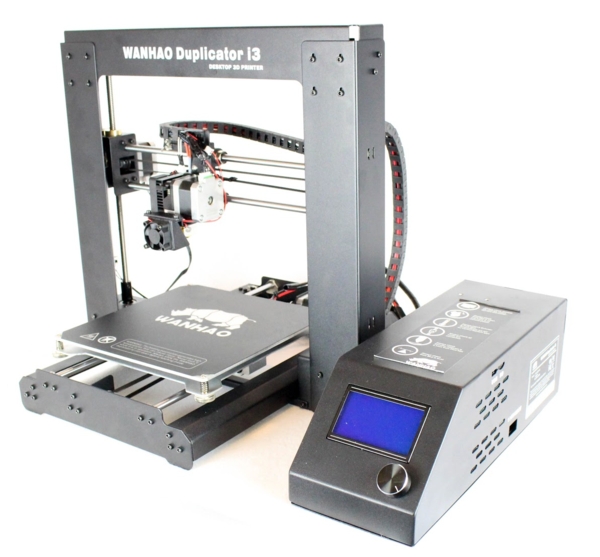 To date, it remains at the top of the list of combination devices in professional 3D printing operations.
To date, it remains at the top of the list of combination devices in professional 3D printing operations.
Another key advantage of this printer is the ability to switch between full-color 3D printing and inkjet printing. You can do numerous tasks with this one device.
This 3D printing unit is a large-scale device, which is why it was created more for professional or industrial needs than for home use. The printer dimensions are 600 x 581 x 640 mm. In terms of print space size, the unit differentiates between Monocolor (200 x 200 x 150 mm) and Fullcolor (185 x 185 x 150 mm). The print bed is unheated; print bed leveling is automatic. Printing material such as PLA, ABS and PETG is supported.
The scanning volume of this device ranges from 50 x 50 x 140 x 140 mm. Supported operating systems are Windows 7 and later, Mac OSX 10.8 and later. Because of the possibilities available to you with this 3D printing device, and also because of its notoriety resulting from the award, this printer is heading for a higher price range in the four-digit range.
Ultimaker S3 3D Printer (alternatively S5) plus Shining 3D EinScan-SE 3D Scanner
The Ultimaker S3* is considered the little brother of the Ultimaker S5*. The scanner is not integrated here but is included in the printer package. Automatic leveling based on a heightmap ensures a more precise print result.
The heatable printing platform enables better adhesion of the printed object to the plate from the very beginning. The build volume is 190 x 230 x 200 mm. A special feature of the S5 is the front door with the possibility to load a CC core. The protected build volume preserves the print object from harmful external influences, such as moisture and dust, and keeps the internal temperature stable. The Ultimaker also impresses with its built-in camera for print monitoring from various locations.
Multiple Ultimaker printers can also be connected to each other via Cura Connect, which is a significant advantage in production. The innovative filament flow sensor of the Ultimaker S3 or Ultimaker S5 as well as a modern intuitive and color touch display make working with this 3D printing device very comfortable for you. An integrated power supply allows it to be installed on a shelf and provides a level footprint. Optionally available are different nozzle sizes, 0.8 mm for fast printing or 0.25 mm for finest details and high-precision printing results.
An integrated power supply allows it to be installed on a shelf and provides a level footprint. Optionally available are different nozzle sizes, 0.8 mm for fast printing or 0.25 mm for finest details and high-precision printing results.
With the Ultimaker, you benefit from the variety of filaments that can be used. With PLA, Tough PLA, ABS, Nylon, CPE, TPU and PVA, you can create almost any imaginable print object with this printer. The extra-hard Ruby nozzle is designed specifically for abrasive materials.
The Ultimaker S3 3D printer also scores with its large scope of delivery, which includes numerous components in addition to the printing device and scanner:
- 2x Printcore AA 0.4 mm
- Printcore BB 0.4 mm
- Glass plate
- Power cable
- Ethernet cable
- XY Calibration overview (Calibration Sheet)
- Calibration Card
- Bobbin holder with material guide and NFC sensor
- USB Stick
- Hexagon socket screwdriver 2mm
- Ultimaker Tough PLA, 350g
- Ultimaker PVA, 350g
- Axle oil
- Spindle grease
With this extensive component mix, you really don’t have to expect any additional acquisition costs initially.
The Shining 3D EinScan-SE desktop scanner offers you an automatic scan mode of up to 200 x 200 x 200 mm as well as a free scan mode of up to 700 x 700 x 700 mm. Therefore, this scanner is also suitable for larger objects. The 360° scan is done at high speed in just two minutes. The 1.3-megapixel camera captures both colors and textures of the model during the scanning process. Scan software, calibration board and various cables are also included.
All-in-one printer “Zeus” from AiO Robotics
“Zeus” from AiO Robotics*Check Price at:
Amazon*
The all-rounder all-in-one printer “Zeus”* is equipped with a 3D printing and scanning function. In addition, the 3D printer has a copy and fax function. You are working with an innovative multifunctional device that leaves hardly anything to be desired.
However, this device was designed by experts more for industry and business, less for private use. Thus, the 3D printer with an integrated scanner falls under the high-priced devices available on the current market. This is a project published by kickstarter.com. The size of this printer is said to be similar to that of a microwave oven. Thus, this versatile 3D printing device can be set up anywhere.
This is a project published by kickstarter.com. The size of this printer is said to be similar to that of a microwave oven. Thus, this versatile 3D printing device can be set up anywhere.
The multifunction device works with an ARM-based 1.7 GHz processor. An SD card can be connected, which enables the additional feeding of digital models into the print. Another feature worth mentioning is the interface to cloud services. The 7-inch touch display is said to be easy to use. The scan resolution is 0.125 mm, and the print resolution is 0.1 mm. With a coarse resolution of 0.2 mm or 0.3 mm, quick printing also works smoothly. You print your objects wirelessly via the Wifi wireless interface. In 2014, the device went into development with great media interest and is still a success today.
XYZ Printing da Vinci Jr. 1.0 3-in-1
XYZ Printing da Vinci Jr. 1.0 3-in-1*Check Price at:
Amazon*
Just like the XYZprinting da Vinci Color AiO 3D printer with an integrated scanner, the XYZ Printing da Vinci Jr. 1.0 3-in-1* also features the popular 3D printer and 3D scanner combo. By having both functions, printing and scanning, in one device from the same manufacturer, the interaction works optimally.
1.0 3-in-1* also features the popular 3D printer and 3D scanner combo. By having both functions, printing and scanning, in one device from the same manufacturer, the interaction works optimally.
The compact and fully assembled 3D printer with a scanner makes it easy especially for beginners but is also popular for complex printing projects. In addition to laser engraving, 3D scanning and 3D printing, this printer offers you even more conveniences. The auto-calibration ensures a balanced print result. Wireless printing makes working with this 3D printing device uncomplicated.
The scan size is 3 x 3 cm – 12 x 12 cm. You get your 3D print model from the filaments PLA, PETG as well as Tough PLA in the print dimensions up to 15 x 15 x 15 cm. All common operating systems, such as Windows 7 upwards, Mac OS X 10.10 and higher or Linux v14.04 and v16.04 are supported. Laser printing gives you a fine and precise print result. If you want to add an engraving to your printing unit, the engraving area of up to 15 x 15 cm offers you enough space for it.
The Combo for People Who Like it Simple
For consumers who want to make their 3D printing projects as easy as possible, a device combo consisting of a 3D printer and 3D scanner is ideal. If you don’t want to create your own templates or lack the knowledge to do so, and ready-made templates aren’t your thing either, then an all-in-one device could be the solution for you.
The 3D scanner integrated in the printer digitizes an object and creates the necessary template. You then use this for the print to marvel at the print result later. This combination solution has only one small weakness. With integrated 3D scanners, the size of the template is limited to the size of the build space. If you want to scan larger objects, you would still have to use a separate scanner.
Related Questions
Why is there only a small selection of 3D printer and scanner combo devices?
When the first combination devices, consisting of a 3D printer and scanner, conquered the market, development was already a step ahead. Developers recognized that the future of 3D printers would focus on the highest print quality.
Developers recognized that the future of 3D printers would focus on the highest print quality.
In addition, some users prefer separate scanners to the 3D printer/scanner combo because they use the scanner at different locations. Furthermore, there is a problem with combination devices in the event of damage. If the 3D printer no longer functions, the integrated functioning scanner is also almost unusable, since a completely new device must be purchased.
Do the scanners integrated in the printer work as carefully as the individual devices?
Yes. The print result can even be more precise, as manufacturers fine-tune and adapt the 3D printing device’s built-in scanners and their functions to this one 3D printing instrument.
Is the price of a 3D printer with integrated scanner higher than that of 2 individual devices?
If you purchase 2 individual devices, you will probably have to dig a little deeper into your pocket. However, the price of the combination devices depends heavily on the quality of the equipment. If you buy a high-quality 3D printer with a lower-quality integrated scanner, you could pay less. However, the printing device and the integrated scanner are usually of the same high quality and therefore cost more.
If you buy a high-quality 3D printer with a lower-quality integrated scanner, you could pay less. However, the printing device and the integrated scanner are usually of the same high quality and therefore cost more.
Can I use the scanner integrated in my 3D printer for print objects from other printers?
This works if the 3D printer scanner has special interfaces or a fax function.
Is the combination device suitable for scanning all sizes?
No. For 3D scanners that are hardwired to the 3D printing unit, the scan size is limited to the size of the printer’s build envelope.
Conclusion
The simplification as well as the advantages for the user, who uses a 3D printer with an integrated 3D scanner, are easily recognizable. The optimal template from the 3D scanner in the printing device favors an optimal printing result. The inconvenience of switching between devices and the space savings (one device instead of two) are persuading more and more consumers to switch to such combination devices. But the potential of 3D printers is far from exhausted.
But the potential of 3D printers is far from exhausted.
Meanwhile, more and more all-rounders are gaining importance in the market. 3D printers with integrated 3D scanners that deliver perfect print results.
Disclosure: This website is the property of Martin Lütkemeyer and is operated by Martin Lütkemeyer. Martin Lütkemeyer is a member of the Amazon Services LLC and other Affiliate Programs. These are affiliate advertising programs designed to enable websites to earn advertising revenue through advertising and linking to Amazon.com and others. Links marked with * are affiliate links.
How to Choose the Best 3D Scanner to Use With Your 3D Printer
3D scanning has an important place at the beginning and end of 3D fabrication workflows. Engineers, product designers, and researchers use 3D scanners as a faster and more efficient way to start constructing digital models, whether by incorporating existing designs via reverse engineering, digitizing hand-sculpted clay designs, or referencing the exact shape of the human body.
After fabrication, 3D scanning can support quality control and help to verify the accuracy of a 3D printed part, or, after the part has been used, a scanner can reveal how it’s performed—a scan of a deformed part can show you where to reinforce the design in the next revision.
With such a wide range of product options from handheld 3D scanners to desktop 3D scanners, it can be difficult to choose the best 3D scanning system that’s right for your application and budget. In this post, we explore the most important factors to consider when purchasing a 3D scanner and showcase some of the key applications that are empowered by combining 3D scanning and 3D printing.
White Paper
3D scanning and 3D printing workflows can be applied to replication and restoration, reverse engineering, metrology, and more. Download our white paper to explore these applications and learn how to get started.
Download the White Paper
There are multiple scanning technologies currently on the market, all offering their own advantages and weaknesses.
Laser triangulation uses light projected onto the object to take up to millions of measurements (dots) per second. The light reflected from the dots back into the scanner’s sensor to help it capture the geometry of the object. These types of scanners are often the most accurate, and are great for highly detailed parts that have opaque surfaces.
Laser triangulation scanners do have limitations. For example, this technology is not used in most portable scanners because the laser dots need to project from a stable source, and the source has to be kept a close distance from the scanned object. Laser triangulation scanners don’t always work on transparent or shiny surfaces either. Typically, they require reflective markers to be applied onto the object, which need to be removed after use and can be an obstacle depending on the object being scanned.
Finally, the laser dots can be harmful to human eyes, so it is important to use extra safety precautions when scanning body parts with a laser triangulation system, or to check with your scanner manufacturer to make sure the device is eye-safe.
Structured light scanners (also known as white light scanners or blue light scanners) generally use a projector with two cameras at angles on either side. A pattern of light is projected and laid over the component being scanned, the cameras capture the ways in which the object deforms the light pattern, and then multiple images are integrated into a single 3D snapshot.
Structured light scanners are available in both stationary and portable format—the technology is the most commonly used process for handheld 3D scanners. Structured light scanners are far more common in medical applications, since it is safe to use on both humans and animals and excels when an object is not perfectly still. Traditional white light scanners have been slower to scan than laser triangulation scanners.
Structured light scanning is the most commonly used technology in handheld 3D scanners.
Depth-sensing cameras project a field of dots in infrared (IR) to sample a 3D scene. Depth-sensing cameras are simple to use and are the least expensive scanning option, but their accuracy and resolution are low, and fine details are sometimes lost. Large objects may be captured with depth-sensing cameras, but accuracy declines with increased distance from the subject and at steeper angles to the camera.
Depth-sensing cameras are simple to use and are the least expensive scanning option, but their accuracy and resolution are low, and fine details are sometimes lost. Large objects may be captured with depth-sensing cameras, but accuracy declines with increased distance from the subject and at steeper angles to the camera.
Photogrammetry means the act of deriving precise measurements from photographs. It involves taking a set of overlapping photos of an object, building, person, or environment, and converting them into a 3D model using a number of computer algorithms. This is the most commonly used method when creating a 3D scan with a smartphone, since modern phone cameras are capable of capturing and combining a large numbers of photos. Photogrammetry should be considered the least expensive and least accurate method for creating 3D prints, and is not suitable for serious business applications.
LiDAR (light detection and ranging) sensors can be found on some higher-end smartphones and tablets, such as the latest versions of the iPhone Pro and the iPad Pro. This has made the iPhone and iPad viable scanners for those with only occasional scanning needs, offering performance a step above devices that only have access to photogrammetry. Applications that generate 3D mesh files via your smartphone’s or tablet's camera should be seen as the floor for entry-level scanning; users should expect additional work in their CAD software to remove gaps in meshes and improve the 3D model for applications like sending it to a 3D printer. Smartphones use fewer light points when scanning objects, resulting in less detail than a true, stand-alone scanner. iPhones are good substitutes for scanners if you have significant CAD design ability or need to transfer basic models into a digital space.
This has made the iPhone and iPad viable scanners for those with only occasional scanning needs, offering performance a step above devices that only have access to photogrammetry. Applications that generate 3D mesh files via your smartphone’s or tablet's camera should be seen as the floor for entry-level scanning; users should expect additional work in their CAD software to remove gaps in meshes and improve the 3D model for applications like sending it to a 3D printer. Smartphones use fewer light points when scanning objects, resulting in less detail than a true, stand-alone scanner. iPhones are good substitutes for scanners if you have significant CAD design ability or need to transfer basic models into a digital space.
WEBINAR
Watch this webinar with Peel 3D to explore how to integrate 3D scanners into your 3D printing workflow to elevate your product development process.
Watch the Webinar Now
Scan accuracy varies considerably between scanner technologies, and higher accuracy generally comes at a higher cost. The required tolerances of your final part can be a helpful guide for determining your accuracy requirements for a 3D scanner.
The required tolerances of your final part can be a helpful guide for determining your accuracy requirements for a 3D scanner.
| High Price, Highest Accuracy ($15,000 and more) | More Affordable, High Accuracy ($12,000 and under) | Low price, Low Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Zeiss T-Scan Hawk Scantech Simscan EviXscan Optima+ M Creaform HandyScan 307 Silver Series | peel 3d peel 1, peel 2 & peel 2-S FARO Freestyle 2 Polyga Compact S1 | iPhone Pro and iPad Pro Structure Sensor Matter and Form 3D Scanner V2 Revopoint POP |
With accuracy in the range of 0.1 mm or better, laser and structured light scanners are a good fit for professional applications and alongside high-resolution 3D printers. Formlabs stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers (such as the Form 3+) produce parts at a similar accuracy, and with a similar printable area, to the scan volume of many desktop 3D scanners.
Besides the accuracy between measured points and their actual location, scanners also vary in terms of resolution, which is the distance between captured points at a given scan distance. This means that details on the scanned object that are smaller than the scanner’s resolution won’t be captured. For example, a highly accurate 3D scanner with a lower resolution might detect the general shape of jewelry on a statue, but not clearly show individual details on a ring or necklace. Depending on your project requirements, this may or may not be a dealbreaker.
An easy way to remember these metrics is: accuracy is the measurement error between the part and digital value. Resolution refers to the density of measurements.
Accuracy can mean slightly different things depending on the manufacturer and 3D scanning technology. For example, the accuracy of handheld scanners depends on the distance to the subject and the quality of scan reconstruction, while desktop scanners have consistent accuracy within the constrained scan volume. If you are considering buying a 3D scanner for precise measurement, make sure to compare like to like.
If you are considering buying a 3D scanner for precise measurement, make sure to compare like to like.
In general, structured light scanning provides the best resolution and accuracy when compared to laser scanning. For some artistic use-cases for 3D scanning you may need a lot of detail, while overall accuracy is less important—especially if you don’t require your part to fit precisely with other parts in an assembly. In these cases, photogrammetry is an excellent low-cost option to explore.
Both depth-sensing cameras and photogrammetry are a good solution for scanning large objects in order to create 3D printed scale models and also offer enough accuracy for capturing the shape of the human body.
Several entry-level laser scanners are available using technology similar to higher-end systems. These scanners are a great way to start replicating small objects at 1:1 scale. As one would expect, the accuracy of entry-level laser 3D scanners is lower than a high-end scanner, but they can easily provide enough detail to replicate small decorative objects and figures where accuracy is not critical.
If you only have occasional 3D scanning needs, digitization services can scan your object, as well as perform CAD translation and accuracy inspection.
The area that a 3D scanner can capture varies significantly between scanners. Find a scanner that fits your size and resolution requirements without too much overhead, as cost typically increases with scan volume.
Handheld scanners can be manually moved around the object and have fewer size constraints than desktop models. Most inexpensive handheld scanners can capture objects from the size of a basketball to an entire room. High-end handheld scanners have an even wider range, and fill the niche for all objects that require precise measurements, but cannot fit in a desktop scanner. Handheld scanners are also able to capture objects nearly instantaneously, which makes them well-suited for taking human measurements (where the subject is not perfectly still) for ergonomics and medical applications.
If the area of the model can’t be seen by the scanner, it will cause a gap in the model. You can automatically repair small missing sections with most scan software programs to create a 3D printable model. However, repaired holes are rarely accurate to the original object. For parts that demand close to perfect accuracy, auto-repair of gaps or holes will not be sufficient. Read our MeshMixer tutorial for advanced tips to edit and repair 3D files for 3D printing.
You can automatically repair small missing sections with most scan software programs to create a 3D printable model. However, repaired holes are rarely accurate to the original object. For parts that demand close to perfect accuracy, auto-repair of gaps or holes will not be sufficient. Read our MeshMixer tutorial for advanced tips to edit and repair 3D files for 3D printing.
Many scanners use turntables to increase what the scanner can see. The sophistication of a scanner’s turntable affects how easily and completely the object is captured: some scanners have the ability to move the object around multiple axes, imaging the object from more angles. This feature is important when reverse engineering plastic parts with deep recesses and ribs, which are impossible to capture from a single angle.
Scanners may rotate the object to capture occluded areas. Red regions are occluded and will be missing in the scan. Areas with deep relief are difficult for a single axis turntable to fully capture due to occlusion.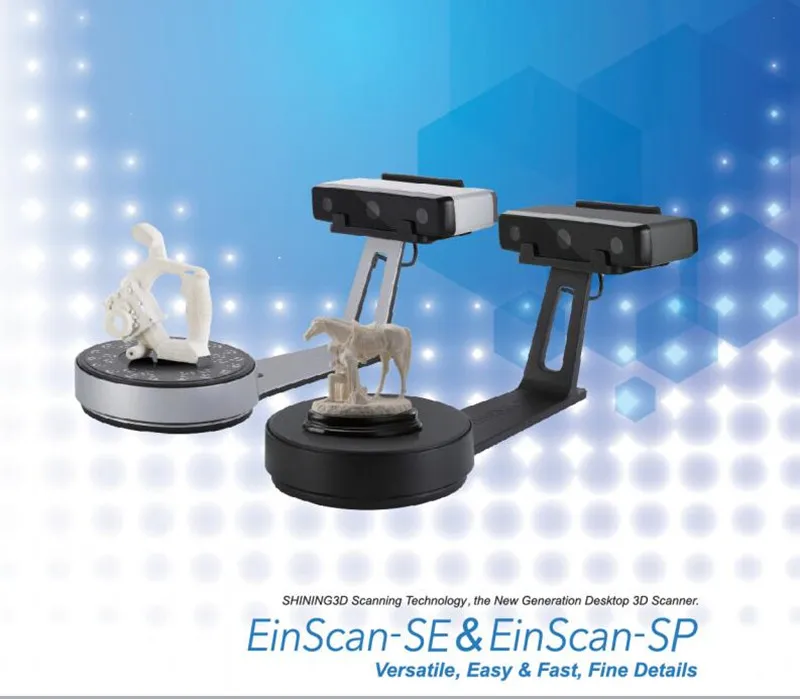
Cost concerns are straightforward; how much you are willing to spend on a scanner will reflect your business’s budget and how often the scanner is going to be used. Higher cost scanners will be able to capture small objects and create highly-detailed meshes that don’t require significant touch-ups in CAD software. Handheld scanners are also often on the higher end of the price range, due to their portable nature. The low-cost scanning market offers a wide range of options, but you have to know what to look for.
Use this flowchart to determine what scanner you need based on accuracy, scan volume, and budget.
Download the high-resolution version of this infographic here.
A 3D scanner expands the capabilities of a 3D printer, allowing you to replicate the shape of almost any object. Together, the two technologies create a powerful, digital workflow that can simplify and sophisticate processes in a range of industries.
The output from a 3D scanner is a mesh of triangles representing the surface of an object at a real-world scale. In some cases, the scan can be used directly to replicate objects without any CAD work. A hybrid workflow can also be powerful, where solid CAD models are combined with scanned 3D models. For example, customized ergonomics capture a physical imprint of a part of the human body, and integrate them with a mechanical design.
In some cases, the scan can be used directly to replicate objects without any CAD work. A hybrid workflow can also be powerful, where solid CAD models are combined with scanned 3D models. For example, customized ergonomics capture a physical imprint of a part of the human body, and integrate them with a mechanical design.
3D scanners are also valuable tools for measuring the accuracy of manufactured objects. Many factors affect 3D print accuracy, and metrology-grade 3D scanners provide a clear picture of how a material performs for demanding applications.
A variety of powerful workflows are enabled by combining a 3D printer and a 3D scanner:
- Reverse engineering to create replacement parts, products with custom ergonomics, and more.
- Replication and restoration of parts, especially in art and jewelry.
- Consumer audio for creating custom earpieces.
- Dental and medical applications, and how 3D scanning is enabling patient-specific workflows.

- Metrology to validate and measure the accuracy of manufactured objects.
Webinar
Watch this webinar for a detailed look at how to start using 3D scanning to improve part design and production when paired with reverse engineering CAD and 3D printing.
Watch the Webinar Now
3D scanners and 3D printers are essential parts of digital workflows across industries. Download our white paper or watch our webinar to get a detailed look into how to start using 3D scanning to improve part design and production and learn how to pair 3D printing and 3D scanning to empower a variety of workflows in engineering, product design, and more.
Learn more about the 3D printer side of the equation: get to know stereolithography (SLA) and selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing technologies and see Formlabs advanced 3D printing materials for yourself with a free sample 3D printed part.
Explore Formlabs 3D PrintersRequest a Free Sample Part
TOP 12 Inexpensive 3D Scanners
TOP 12 Inexpensive 3D Scanners
Introduced in the late 1970s, laser triangulation technology paved the way for the first devices capable of digitizing objects in 3D.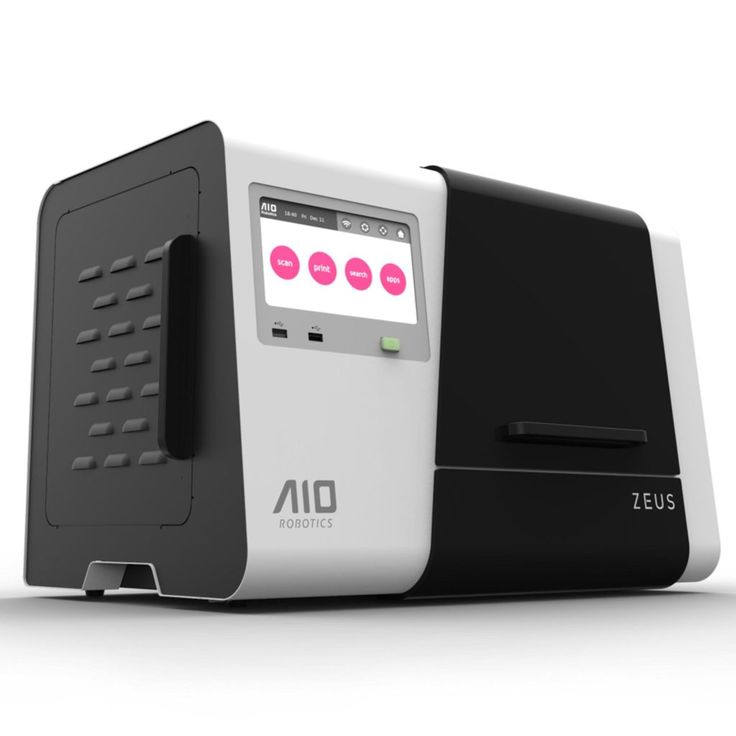 This tool, long reserved for industrialists, has gradually become so popular that we are now finding affordable 3D scanners that are easy to use. From Einscan-SE by Shining 3D to Ciclop by BQ, find our TOP 12 cheap 3D scanners (under 7000€), sorted by increasing price!
This tool, long reserved for industrialists, has gradually become so popular that we are now finding affordable 3D scanners that are easy to use. From Einscan-SE by Shining 3D to Ciclop by BQ, find our TOP 12 cheap 3D scanners (under 7000€), sorted by increasing price!
TOP 1 - XYZprinting 2.0 Scanner A
Chinese 3D printer manufacturer XYZprinting added its first 3D scanner to its range in 2015. A new version, 3D Scanner 2.0, has recently been released. It is relatively small and light with its 238 grams, offering the user great portability and ease of use. It includes 4 different scan modes which allow you to scan objects, the whole body, head or face. The maximum scan size is 100 x 100 x 200 cm. Lateral resolution, it ranges from 1 to 2.5 mm. Price available from 199€.
TOP 2 - Ciclop BQ
Ciclop was developed by the BQ teams and is the only open source 3D scanner in this ranking. It comes with Horus software and all information regarding its design, software and electronic components is freely available on the Internet.
It comes with Horus software and all information regarding its design, software and electronic components is freely available on the Internet.
Ciclop is based on laser triangulation technology and can scan objects in less than eight minutes. This version is available at the price of 249€. It contains a step by step guide to install the 3D Scanner by yourself in less than an hour.
TOP 3 - Structure Sensor
This amazing scanner has the feature of connecting directly to your Apple tablet or smartphone. After downloading the appropriate application, you will be able to scan 3D models with an autonomy of 4 hours thanks to the built-in battery.
Its dimensions are 119.2 x 28 x 29 mm and weighs 95g makes it one of the smallest 3D scanner in the world. Its accuracy can reach 0.5mm. Its cost is 379 dollars, which is about 345 euros.
TOP 4 - inexpensive 3D scanner Cubify Sense
Sense was developed by American 3DSystem and today remains one of the most popular inexpensive scanners on the market. It can scan large volumes from 200 x 200 x 200 mm up to 2 cubic meters. This portable scanner measures 178 x 129x 330 mm and offers an accuracy of 0.90 mm.
It can scan large volumes from 200 x 200 x 200 mm up to 2 cubic meters. This portable scanner measures 178 x 129x 330 mm and offers an accuracy of 0.90 mm.
It uses structured lighting technology and comes with 3D Sense software, which includes a simplified interface and interesting post-processing tools. It also offers an image resolution of 1920 by 1080 pixels for scanning textures and colors. The scanner is available from 479 €.
TOP 5 - Matter & Form V2
This 3D scanner was developed by the Canadian company Matter and Form. With two lasers, the Matter & Form V2 can scan objects up to 25 cm in size and 18 cm in diameter. With an accuracy of 0.1 mm, it is compatible with all by 3D printers and can be used by manufacturers for applications ranging from art to design to education. The 3D scanner is currently available for $749. the 3D scanner itself; As the name suggests, this is a hybrid machine that allows you to scan, print and burn for 899 euros. Therefore, a scanner module is built into the machine, which works through laser triangulation. If you look at its specifications, the scanner offers an accuracy of 0.25 mm and a resolution of 2,140 dots per cm2. A machine that will allow you to cover the entire creation process, from design to manufacturing.
Therefore, a scanner module is built into the machine, which works through laser triangulation. If you look at its specifications, the scanner offers an accuracy of 0.25 mm and a resolution of 2,140 dots per cm2. A machine that will allow you to cover the entire creation process, from design to manufacturing.
TOP 7 - Einscan SE
The first 3D scanner from the Chinese company Shining3D hit the market thanks to a Kickstarter campaign. From now on, the range has expanded, and the manufacturer offers 3D scanners adapted to any need. EinScan-SE is an evolution of the S, with a new design and improved performance, even more suitable for beginners, education and desktop 3D printing .
Like its predecessor, the EinScan SE uses structured white and invisible light technology, making it much safer for children. This scanner offers two types of scanning: automatic scanning and fixed scanning. First, you place the object to be digitized directly on the turntable; after two minutes, the scan scans the object at a 360° angle with an accuracy of 0. 1mm. For larger models (700 x 700 x 700 mm) you need to use the second method, where you place the part at the end of the stand, i.e. in place of the board. This scanner is available from 1438 €.
1mm. For larger models (700 x 700 x 700 mm) you need to use the second method, where you place the part at the end of the stand, i.e. in place of the board. This scanner is available from 1438 €.
TOP 8 - RangeVision Smart
This structured light 3D scanner was developed by Russian manufacturer RnageVision. This is a professional desktop scanner tripod that is ideal for scanning objects from 4 cm to 1 meter. In terms of specifications, it provides 0.1mm accuracy and 0.12mm resolution. Its near scan range is 150 x 112mm and its furthest is 500 x 375mm. Finally, it has two cameras and autofocus, making it easy to calibrate. It is now available in grey, yellow and red from €2,500. Several accessories can be added to the RangeVision Smart as a turntable.
TOP 9 – NextEngine Ultra HD
NextEngine, an American manufacturer, stands behind the NextEngine Ultra HD professional 3D scanner. It is able to scan various textures as well as objects in color. Its near scanning surface is 130 x 97mm and its distance is 343 x 257mm. NextEngine Ultra HD is based on laser triangulation and offers a maximum resolution of 0.1mm. It can scan 50,000 points per second with a maximum accuracy of 0.13mm. Finally, it can work with or without a tray, thus opening up a field of possibilities. Scanner available from € 2995.
Its near scanning surface is 130 x 97mm and its distance is 343 x 257mm. NextEngine Ultra HD is based on laser triangulation and offers a maximum resolution of 0.1mm. It can scan 50,000 points per second with a maximum accuracy of 0.13mm. Finally, it can work with or without a tray, thus opening up a field of possibilities. Scanner available from € 2995.
TOP 10 - HP Pro SLS-3
This professional structured light scanner is an evolution of the DAVID Pro SLS-3D manufactured by DAVID Laserscanner, which was bought in 2016 by the American giant HP. With a scanning price of 3930 euros and a 360° scan, this scanner has an accuracy of 30 microns or 0.5 mm, which corresponds to 0.05% of the size of the object being scanned. It includes an adjustable metal stand and tripod. It consists of a video projector and a professional HDMI camera.
TOP 11 - EinScan Pro+
Shining3D's EinScan Pro+ was officially unveiled at CES 2017. It is a professional handheld structured light scanner that can be used without support limitation, increasing the possible scan size . It offers multiple scanning modes: Quick Manual Scan, HD Manual Scan, Auto Scan and Free Scan. It offers 0.24mm resolution and is available starting at $5.890 euro.
It is a professional handheld structured light scanner that can be used without support limitation, increasing the possible scan size . It offers multiple scanning modes: Quick Manual Scan, HD Manual Scan, Auto Scan and Free Scan. It offers 0.24mm resolution and is available starting at $5.890 euro.
TOP 12 – Eva Lite from Artec 3D
The EVA Lite 3D scanner is the most affordable version of the professional Artec 3D scanner. This professional scanner is suitable for scanning complex geometries such as the geometry of the human body, so it is widely used in the medical sector. It uses structured light technology and although it is not capable of scanning colors and textures like most of the brand's scanners, it has an accuracy of 0.5mm. Scanner available from €6700.
3D scan at home. Cheaper and easier than ever!
In the world of 3D technology, scanning is the yin to the yang of 3D printing. While the printer turns computer models into real things, the scanner turns real things into computer models. Along with sketch-based modeling, 3D scanning - in which a real part is scanned into a model in a computer - is another technology for preparing prototypes for subsequent printing.
While the printer turns computer models into real things, the scanner turns real things into computer models. Along with sketch-based modeling, 3D scanning - in which a real part is scanned into a model in a computer - is another technology for preparing prototypes for subsequent printing.
Advanced 3D scanners are available, but they can be quite expensive and sometimes even more expensive than professional 3D printers.
Fortunately, today there are home 3D scanners that can achieve outstanding results. Today, there are three scanning methods: laser line scanning, structured-illuminated scanning, and image-scanning modeling.
Line laser scanning.
Probably the most popular scanning method for personal scanners. It obtains data about the model by illuminating it with a laser beam. These scanners work best with a neutral background, such as an all-white back set at an angle of 90 degrees. Such a background is inexpensive to make, and scanners based on this technology are cheap. The addition of a 360-degree rotating platform on which the scanned model can stand can greatly improve the quality of the scan.
The addition of a 360-degree rotating platform on which the scanned model can stand can greatly improve the quality of the scan.
When everything is ready, you simply turn off the light, illuminate the model with a laser from all sides, the software does the rest.
Although it is possible to use, for example, MATLAB to convert raw scanned images obtained in this way into a full-fledged 3D model, since 2006 the German company David Vision Systems began to develop special low-cost software for this purpose. This software simulates a 3D model in real time, and you immediately see the result of your work. It composes images taken from different angles and forms a 3D model in a format that is convenient for you. The latest versions of the software also support structured-illuminated scanning (see below). You can even use the free trial version to try it out.
Patterned Illuminated Scanning
This method combines a light projector, digital camera and image analysis software for the 3D scanning process and is generally faster than the line laser method. An additional plus is that there is no need to prepare the background from behind. The projector imposes a certain light pattern on the scanned model, often a grid of light and dark stripes, so that the program can determine the shape and coordinates of the object, depending on how the light pattern is distorted on it. The light pattern can be both visible and made in the form of infrared radiation, which you will not even notice.
An additional plus is that there is no need to prepare the background from behind. The projector imposes a certain light pattern on the scanned model, often a grid of light and dark stripes, so that the program can determine the shape and coordinates of the object, depending on how the light pattern is distorted on it. The light pattern can be both visible and made in the form of infrared radiation, which you will not even notice.
Infrared scanning has its advantages, for example, because this radiation does not conflict with external light radiation. For example, the Microsoft Kinect device for the XBOX gaming platform uses exactly the method of structural lighting through infrared radiation.
Prior to the use of infrared radiation, conventional visible color was commonly used. Using this technology, for example, Radiohead's video for the song "House of Cards" was filmed in 2008. The software that supports structured-illuminated scanning is David's software, as mentioned above, as well as ThreePhase, a utility designed specifically for working with structured-illuminated scanning. Most programs are usually written for Mac OS X, but ThreePhase can run on all platforms - Mac OS, Windows, Linux.
Most programs are usually written for Mac OS X, but ThreePhase can run on all platforms - Mac OS, Windows, Linux.
However, since the introduction of the Kinect by Microsoft in 2010, scanning at home has changed a lot. After several years of development, as well as millions of dollars invested in its research, the Kinect device was obtained, consisting of five elements: right and left microphones, an RGB video camera, an infrared radiation projector, and a monochromatic sensor suitable for a laser. A pair of sensor / laser and allows you to scan and analyze the movement of a person.
In general, the release of the Kinect device prompted many to develop this technology, including in the field of 3D scanning. Against this background, as well as the inexpensive price of the device, interest in structured-illuminated visible light scanning has completely disappeared. Kinect is an incredibly powerful device at a very cheap price and is a great alternative to visible light. At the time of writing, the Kinect sensor costs about $100.
Among all the programs for 3D scanning, one of the leading programs is the ReconstructMe program from the Austrian company Profactor. This is a quality commercial product that can easily be used for personal purposes. ReconstructMe scans the model immediately at its actual scale, so no further scaling is required. Unfortunately, the program is only available for Windows.
Skanect from the French company Manctl is another popular program that works with both Windows and Mac OS.
Modeling based on image scanning
If you have many photos of the same part from all angles, then special software will convert them into a 3D model. This method is sometimes called photogrammetric, and it has often been used in forensics to analyze crime scenes, car accidents, and so on. based on conventional 2D photos. In this method, the most important thing is to choose the right photos, shooting angles, and also choose the right software.
Programs like Eos Systems' PhotoModeler, David's D Sculptor, and Autodesk's 123Catch make it very easy to select anchor points for photo alignment and then create a 3D model.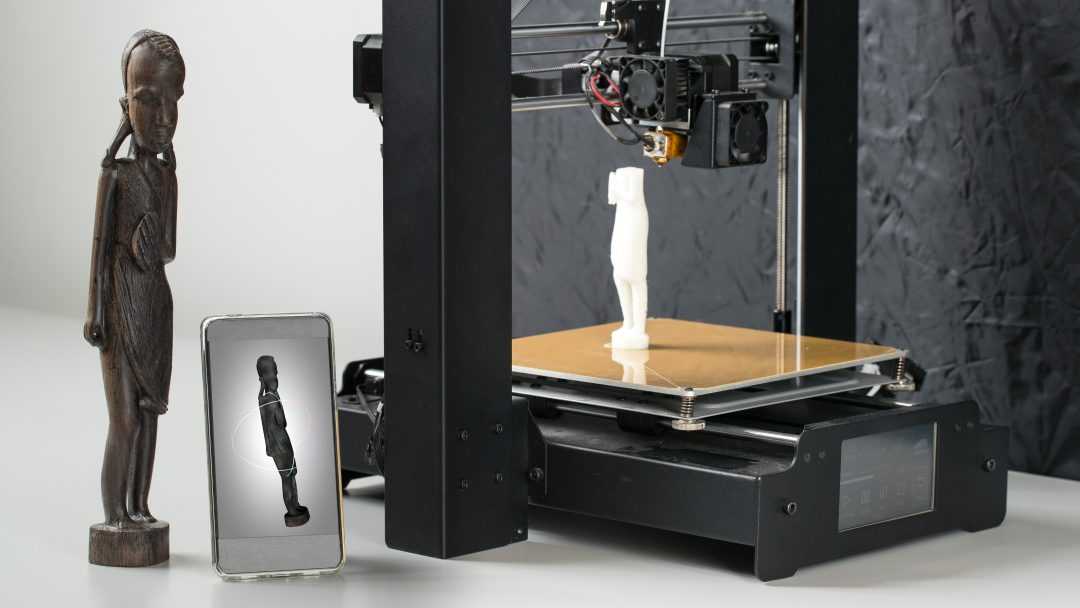
This simulation works best when you have full access to the subject and the ability to take an unlimited number of photos. The more photos, the better the lighting and the more correctly the photo shooting angles are chosen, the better and clearer the models will be.
With good observance of all the factors described above, the programs themselves find a way to combine photos to obtain a model, and human intervention is not required at all.
What should I use?
The choice of one of the three methods described above is based on what equipment you have, what size models you are going to scan, and access to the object - the ability to turn and inspect the model from all sides. If you need some kind of rough rule of thumb to start with, then use laser line scanning for small models (less than a human head), for medium-sized objects, structured-illuminated method, and for something large (for example, for scenery) the optimal choice there will be a simulation based on image scanning.